Introduction to AI-Driven Ansible Automation

1. Lab Introduction
In this lab, you will build an intelligent, self-healing automation workflow using:
-
🧠 Red Hat AI for understanding service issues
-
✨ Ansible Lightspeed to generate remediation playbooks
-
🔁 Ansible Automation Platform (AAP) workflows for orchestration
-
📡 Event-Driven Ansible (EDA) to listen to real-time service events
The goal is to showcase how automation + AI can be used to detect, analyze, and remediate application failures without writing any playbooks manually. For a quick overview consider this ~2 minute YouTube video. Quick plug! Please consider subscribing to the Ansible Team!
2. Background
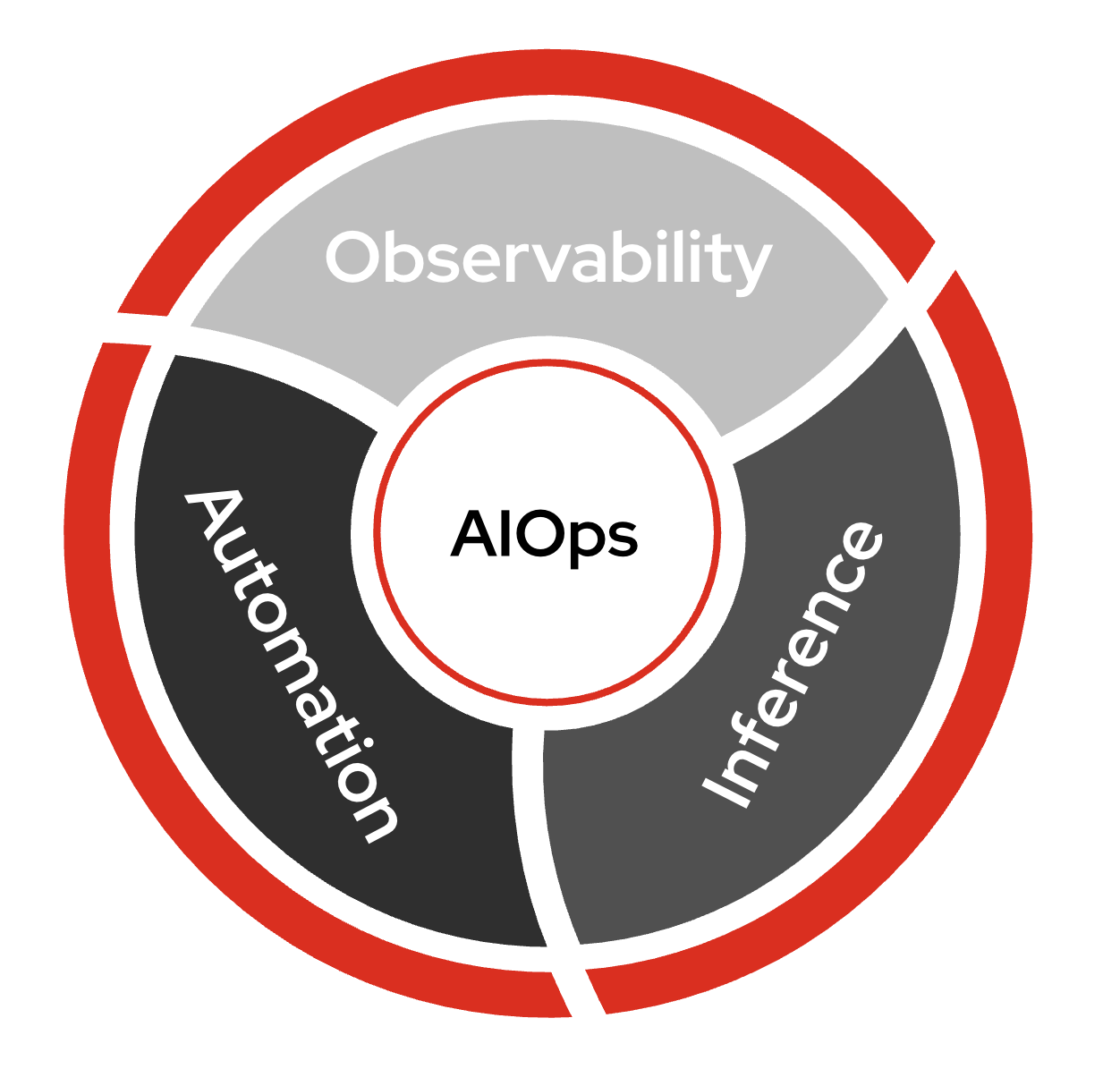
AIOps stands for artificial intelligence for IT operations. It refers both to a modern approach to managing IT operations and to the software systems that implement it. AIOps uses data science, big data, and machine learning to augment—or even automate—many of the processes traditionally handled manually by IT teams. Its goal is to improve issue detection, root cause analysis, and system resolution by making IT operations more intelligent and efficient. To read more about AIops there is a great article on redhat.com.
In AIOps there are three major parts:
-
Obervability
-
Inference
-
Automation
-
Observability is the ability to understand the internal state of a system by collecting, analyzing, and visualizing data from logs, metrics, and traces. This can be another AI tool such as IBM Instana Observability. For this lab we are simply relaying logs using Filebeat, a Lightweight shipper for logs. Ansible Automation Platform can integrate with obervability tools using Event-Driven Ansible (EDA).
-
Inference - Inference in AI refers to the process of using a trained model to make predictions or decisions based on new, unseen data. For this AIOps workflow we are using Red Hat AI for understanding service issues like an application outage, and Ansible Lightspeed to create an Ansible Playbook.
-
Automation is the ability to automatically detect, respond to, and resolve IT issues without human intervention. We are using Ansible Automation Platform to tie observability and inference together to direclty to create workflows for self healing infrastrucure.
It is important to note that AIOps can be adopted incrementally and it is not all or nothing. You do not need to have fully self healing infrastrucure on day one to start realizing value. At Red Hat we like to say: "Start small, think big!"
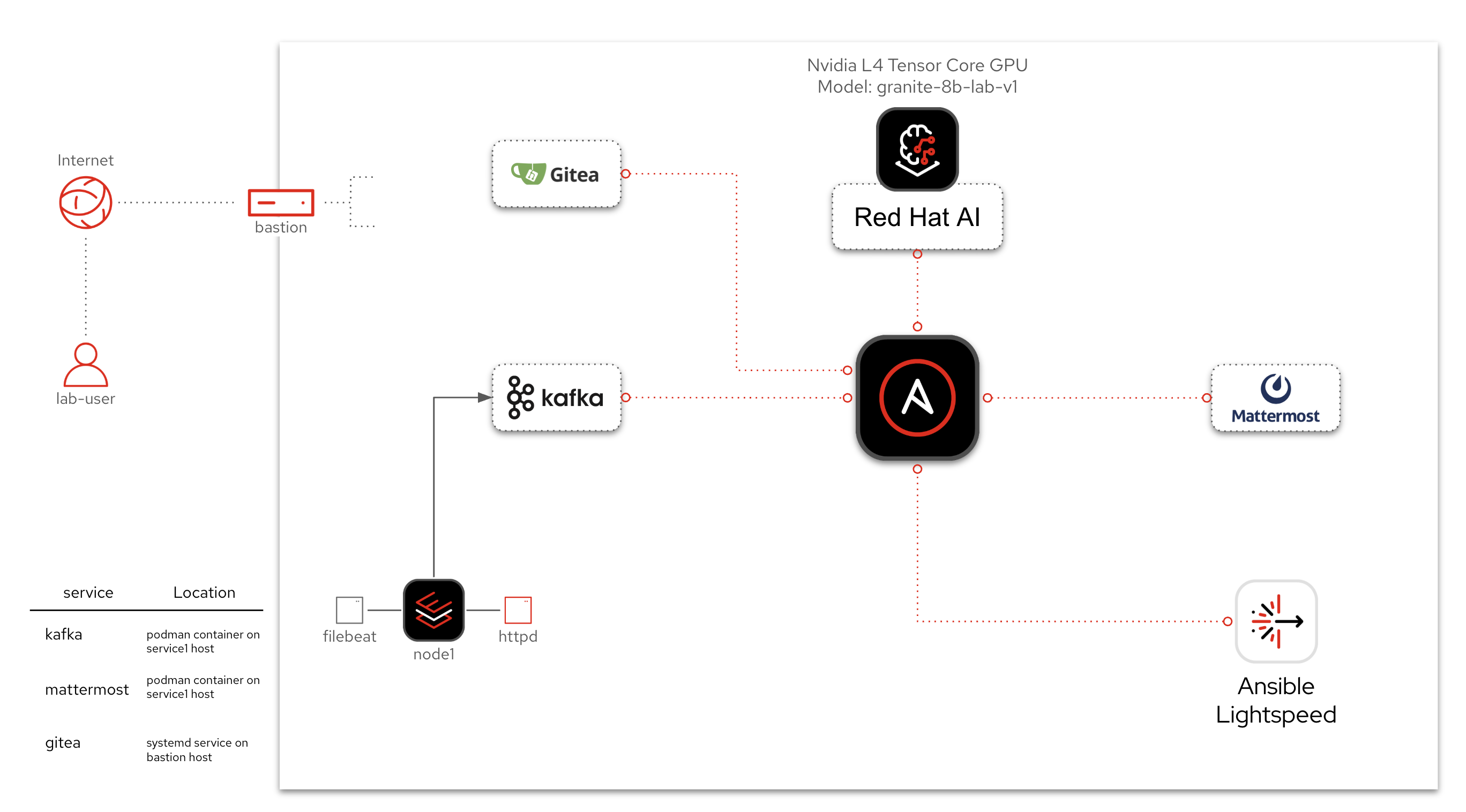
3. Lab Environment
-
A RHEL(Red Hat Enterprise Linux) node with Apache (
httpd) installed -
Filebeat monitoring Apache logs
-
Kafka acting as the event transport
-
Event-Driven Ansible is listening to Kafka and launching workflows based on defined rules
-
Red Hat AI to infer incident context from logs
-
Ansible Lightspeed to generate a remediation playbook
-
Gitea for source control management of Ansible Playbooks
-
Ansible Automation Platform to run job templates and workflows
-
Mattermost for message notifications
💡 EDA (Event-Driven Ansible) is part of Ansible Automation Platform. It is referred to separately sometimes depending on the workflow. EDA uses rulebooks to monitor events, then executes specified job templates or workflows based on the event. Think of it simply as inputs and outputs. EDA is an automatic way for inputs into Ansible Automation Platform, where Automation controller / Automation execution is the output (running a job template or workflow).
4. Workshop Agenda
For this workshop are there four (4) Parts:
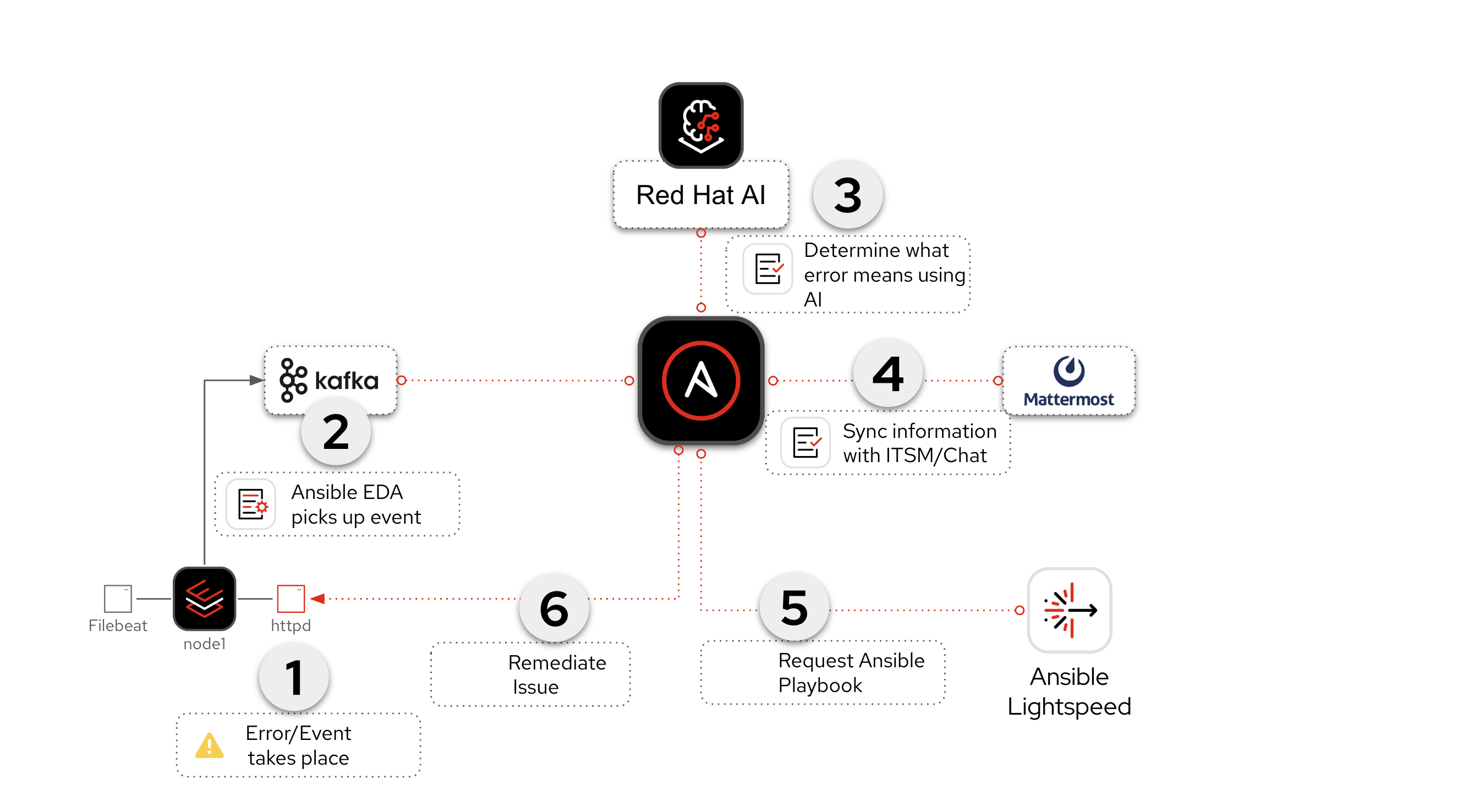
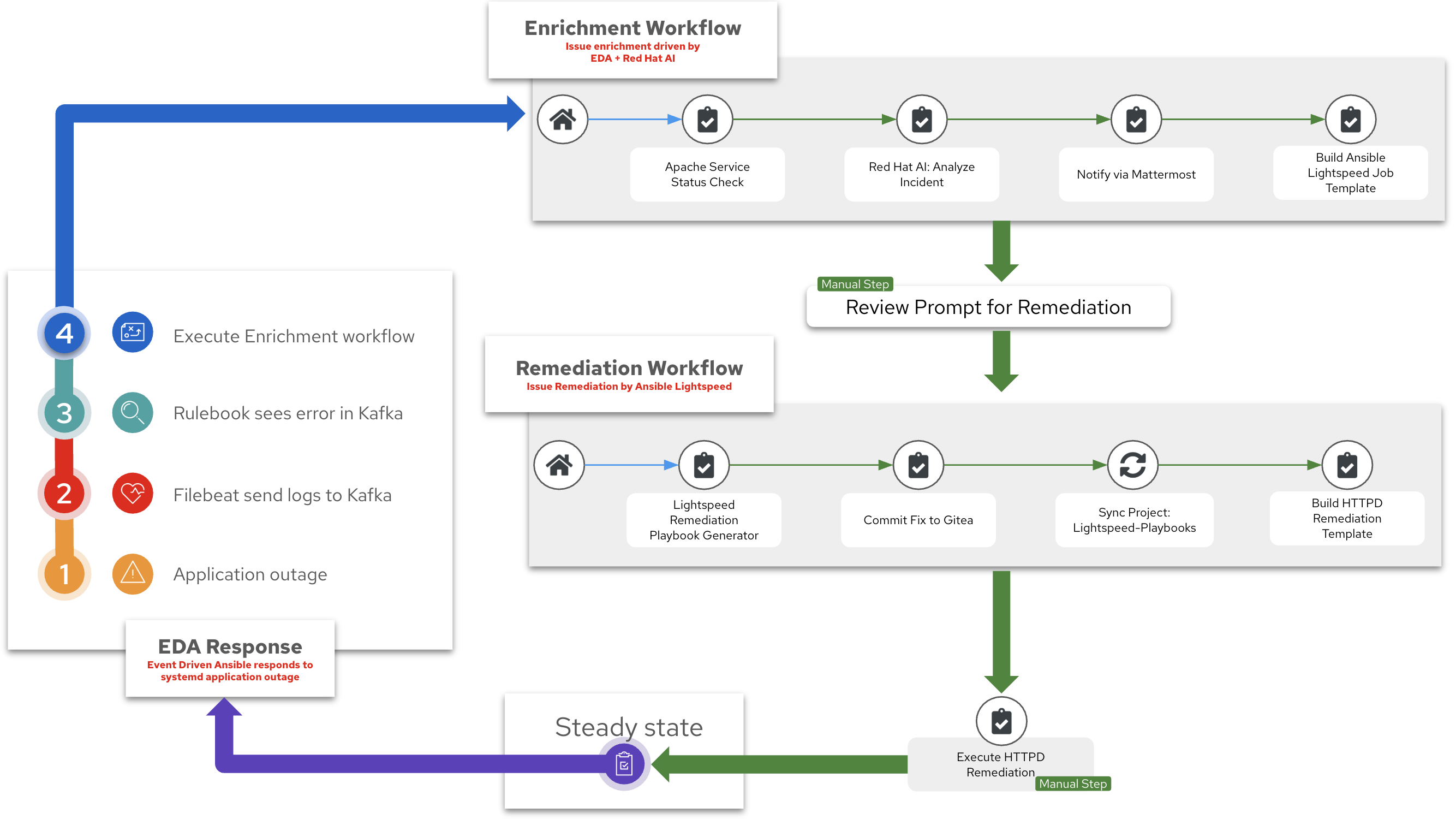
-
Event-Driven Ansible (EDA) Response - Event Driven Ansible will respond to a systemd application outage
-
Log Enrichment and Prompt Generation Workflow - Ansible Automation Platform (AAP) - will retrieve systemd logs, coordinate with Red Hat AI to analyze the incident, notify Mattermost then automatically create a Job Template for us to use in the subsequent workflow.
-
Remediation Workflow - This workflow will focus on automatically creating an Ansible Playbook to resolve the issue by using Ansible Lightspeed. This workflow will take the prompt created by the previous workflow, request a playbook from Ansible Lightspeed, sync this playbook to Git and then automatically create a Job Template for us to remediate the issue.
-
Execute HTTPD Remedation - This is the final Job Template that will actually fix the application outage on the RHEL webserver.
💡 Could this all be one workflow? Yes. This is purposely broken up at natural breakpoints where a human user can review what the AIOps workflow is doing and course correct if required. This also allows organization to incrementally adopt AIOps workflows. Organization can benefit greatly from any of these individual parts!
Here is a diagram of the entire workflow:
❓ Why Mattermost? Mattermost is an open-source, self-hostable online chat service with file sharing, search, and third party application integrations. It is designed as an internal chat for organisations and companies, and mostly markets itself as an open-source alternative to Slack and Microsoft Teams. It is used in this workshop as an example and can be replaced with any Chat or ITSM (e.g. ServiceNow) of your choice. It is really easy to setup an individual Mattermost container per student in the workshop!
❓ Why Gitea? Gitea is a self-hosted, open-source software development service that provides Git hosting, code review, team collaboration, package registry, and CI/CD, similar to platforms like GitHub, Bitbucket, and GitLab. It could be replaced by Github, Gitlab or any Git service of your choosing. It is a a very lightweight solution that works great for workshops.
❓ Why Kafka? Apache Kafka is a distributed streaming platform used for building real-time data pipelines and streaming applications, enabling applications to publish, consume, and process high volumes of data streams. It is all open-source and self hosted and works great for workshops. This could be replaced by any event bus of your choosing. Event-Driven Ansible has numerous plugins including integratrions with AWS SQS, AWS CloudTrail, Azure Service Bus, Prometheus, dynatrace, IBM Instana, BigPanda, Zabbix, CyberArk and more.
I need more details!

Let’s take a closer look at each step in the workflow, broken down clearly for you.
We will break this up into sections though! As you go through each module we will break down each individual workflow and go step-by-step! Red Hat and Ansible Automation Platform will make AIOps simple for organizations to adopt and scale 🎉
5. Access & Credentials
You’re already logged into the environment as lab-user. No manual setup is needed.
All lab content is preconfigured and ready to run.
5.1. Systems Overview
This lab environment includes a variety of tools working together to demonstrate AI-driven remediation. You’ll interact with the following systems:
-
Ansible Automation Platform (AAP) - Executes workflows and job templates. Already opened in your lab interface.
-
Gitea - Git service used to host the Lightspeed-generated playbook.
-
Mattermost - Used for automated notifications during log enrichment.
-
RHEL node - The webserver (
httpd) that will experience and recover from failure. -
Red Hat AI & Lightspeed - AI services that analyze logs and generate remediation content.
5.2. Access Table
| System | URL | Credentials |
|---|---|---|
Ansible Automation Platform |
AAP is preloaded in the lab interface. Click link if you want to open it in full tab: AAP Web UI |
Username: |
Gitea |
Username: |
|
Mattermost |
Username: ansibleadmin@ansible.com
Password: |