LB1344: Bring Your Knowledge to OpenShift Lightspeed
OpenShift Lightspeed is a virtual assistant for the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform. It helps users with general knowledge, troubleshooting, skill development, root cause analysis, and more. Powered by large language models (LLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), OpenShift Lightspeed makes OpenShift more accessible to users and helps increase user productivity.
OpenShift Lightspeed Architecture
OpenShift Lightspeed today is a relatively small and lightweight system that you deploy into each OpenShift Container Platform cluster. The operator deploys three components:
-
A web console plugin (the chat interface)
-
A back-end server (the chat interface calls the server)
-
A PostgreSQL database (for temporary conversation caching)
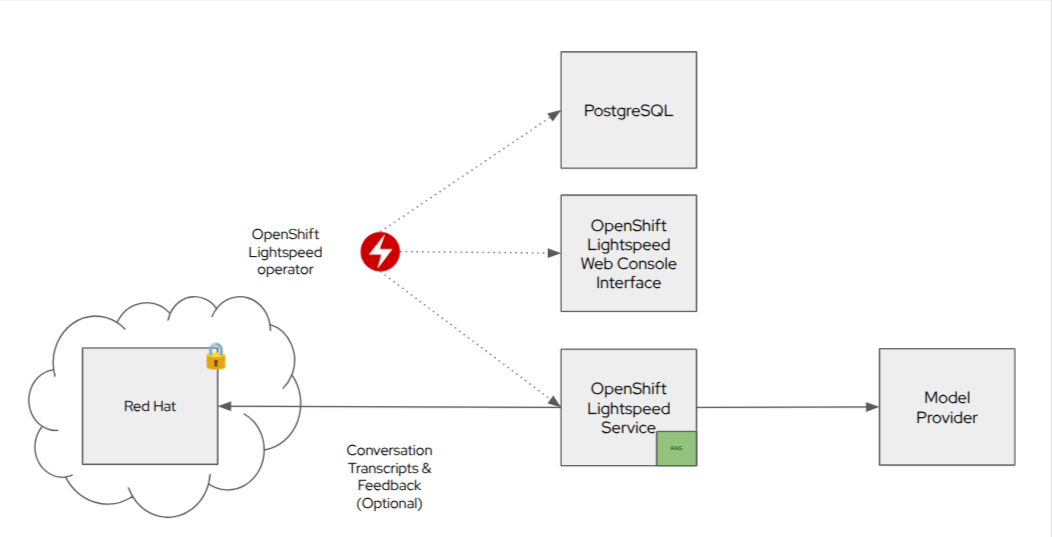
You can also see that OpenShift Lightspeed talks to a model provider. In the case of this lab environment, that provider is Azure OpenAI using the GPT-4o model. There are three supported public model providers:
-
WatsonX
-
Azure OpenAI
-
OpenAI
Additionally, if you want to self-manage your LLM, we also support the Red Hat on-premise model provider solutions:
-
OpenShift AI
-
RHEL AI
The little green box says RAG which stands for retrieval-augmented generation.
RAG Basics
RAG is a way of providing additional context to an LLM to help improve the quality of responses. When relying on only the LLM, two common problems can arise:
-
Hallucination - the model invents an answer that is not grounded in fact, even when the model was trained with the answer
-
Missing data - the model was never trained on the required information in the first place, so answers could be anything
When providing contextual information to the LLM at the time of asking a question, the response quality can be dramatically improved, even if the model was never trained on the specific contextual information.
OpenShift Lightspeed will grab the relevant OpenShift Container Platform documentation to match the cluster version when it deploys, and it uses that documentation as the additional context for answering user questions.
The specific details of vector databases and embedding and encoding are outside the scope of this lab.
Now, with your understanding of the fundamentals, let’s try and use OpenShift Lightspeed.