ChatOps Generative AI Demo with LLM, RAG and Data Science Pipelines
Introduction
Welcome to the demo on LLM with RAG. One of the most powerful applications enabled by LLMs (Large Language Models) is sophisticated question-answering (Q&A) chatbots. These are applications that can answer questions about specific source information. These applications use a technique known as Retrieval Augmented Generation, or RAG.
Let’s briefly understand what is a model and LLM in the AIML landscape here:
In AIML, a model refers to the structure or framework that chatbot operates within. It consists of a set of rules, patterns and responses that the chatbot uses to understand and respond to user inputs.
LLM, or Large Language Model, is a type of artificial intelligence that understands and generates human-like text.
-
Here’s an example of a chatbot providing answer to our question but not satisfactory.:
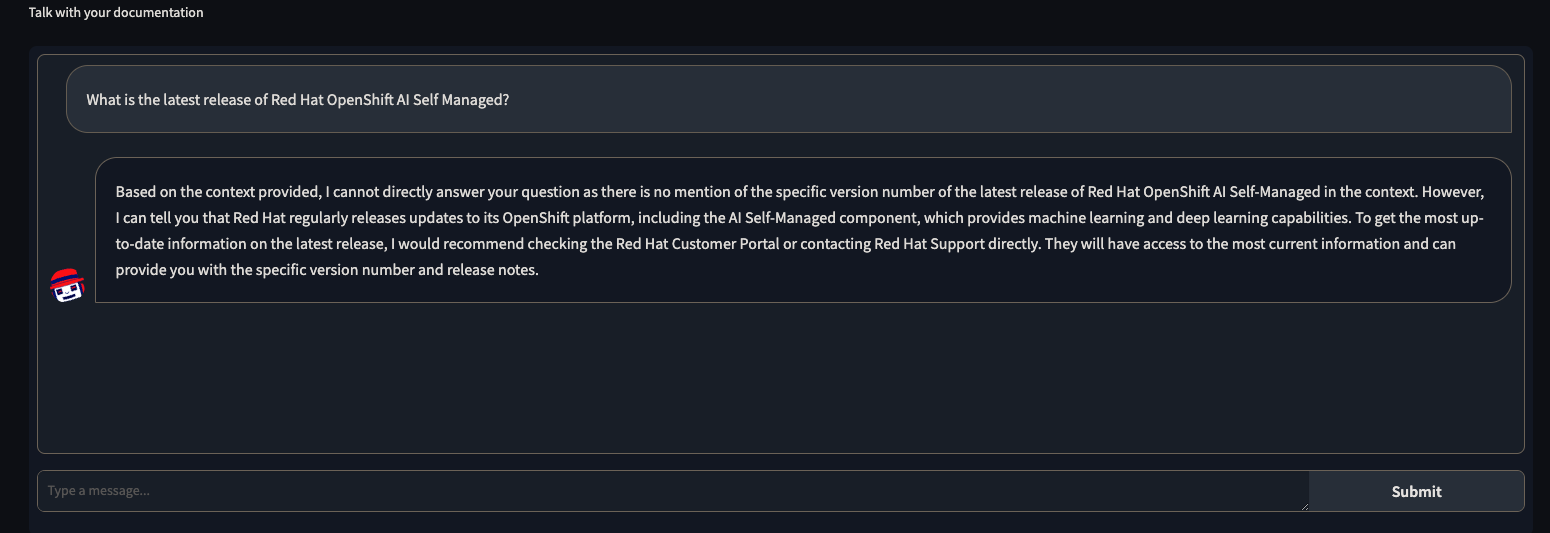
So we get our custom documents and make it part of RAG so that we get good output from the chatbot without retraining the complete LLM model. Note its a very costly deal to re-train a huge LLM model requiring lots of GPU resources and time. RAG offers a good alternative and provides domain specific knowledge to our chatbot to help provide effective answer’s w.r.t our specific domain form a general purpose LLM.
-
Good response from chatbot after using Red Hat OpenShift AI documents with RAG:
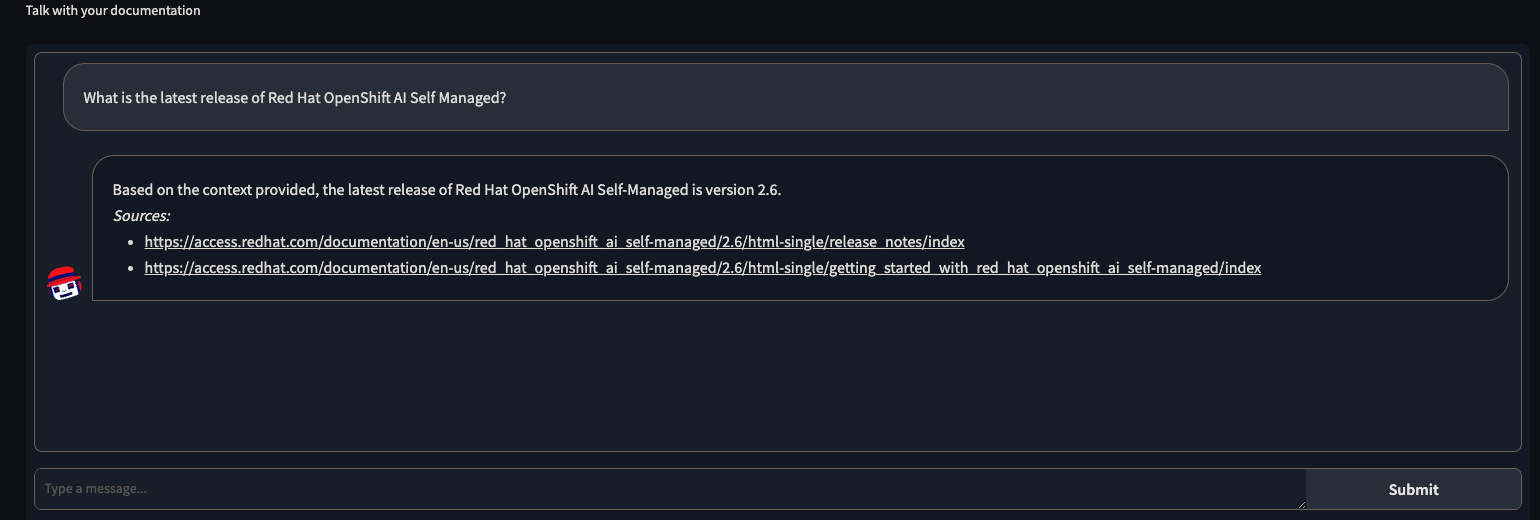
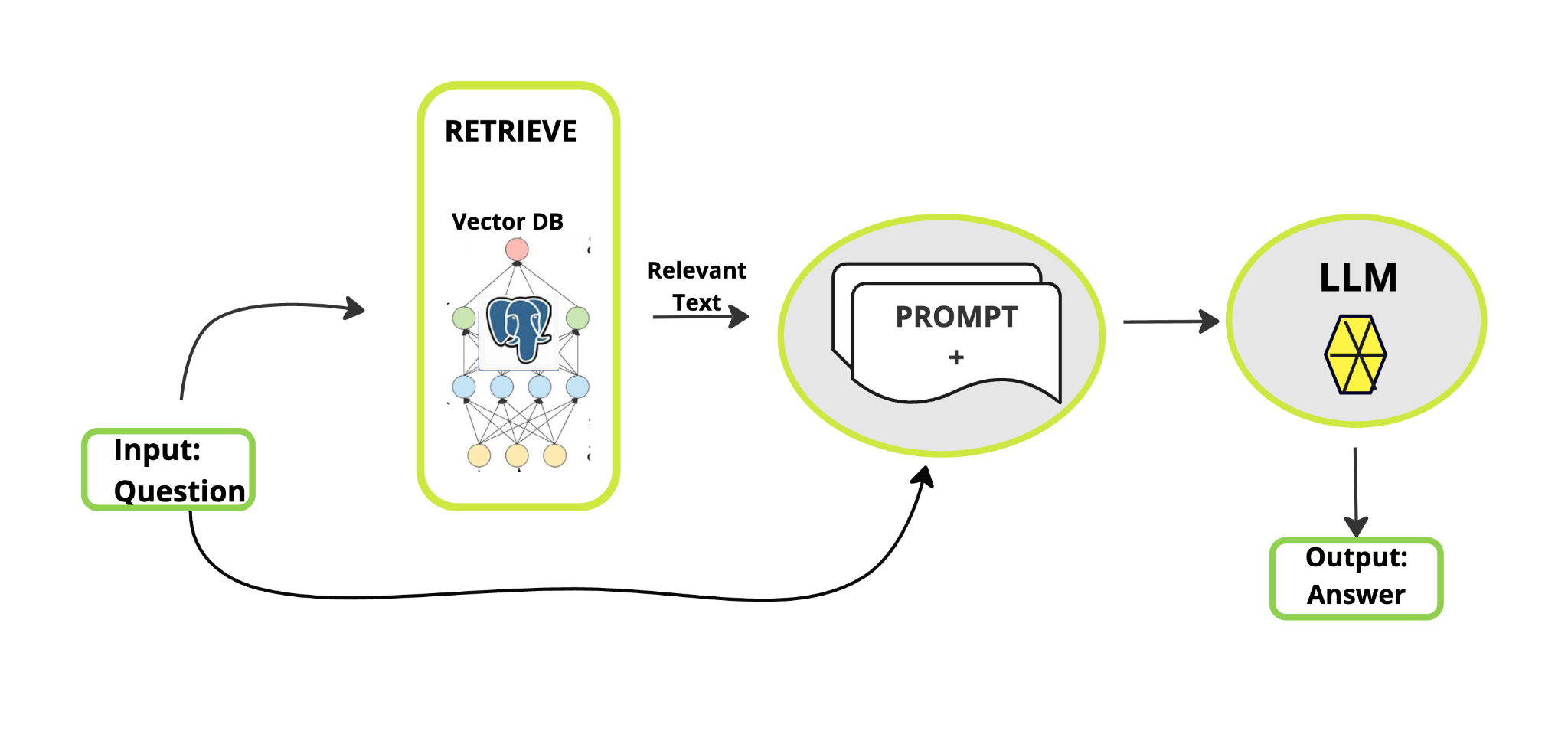
Let’s understand a bit about how RAG works.
What is RAG?
RAG is a technique for augmenting LLM knowledge with additional data.
LLMs can reason about wide-ranging topics, but their knowledge is limited to the public data up to a specific point in time that they were trained on. If you want to build AI applications that can reason about private data or data introduced after a model’s cutoff date, you need to augment the knowledge of the model with the specific information it needs. The process of bringing the appropriate information and inserting it into the model prompt is known as Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG).
LangChain has a number of components designed to help build Q&A applications, and RAG applications more generally.
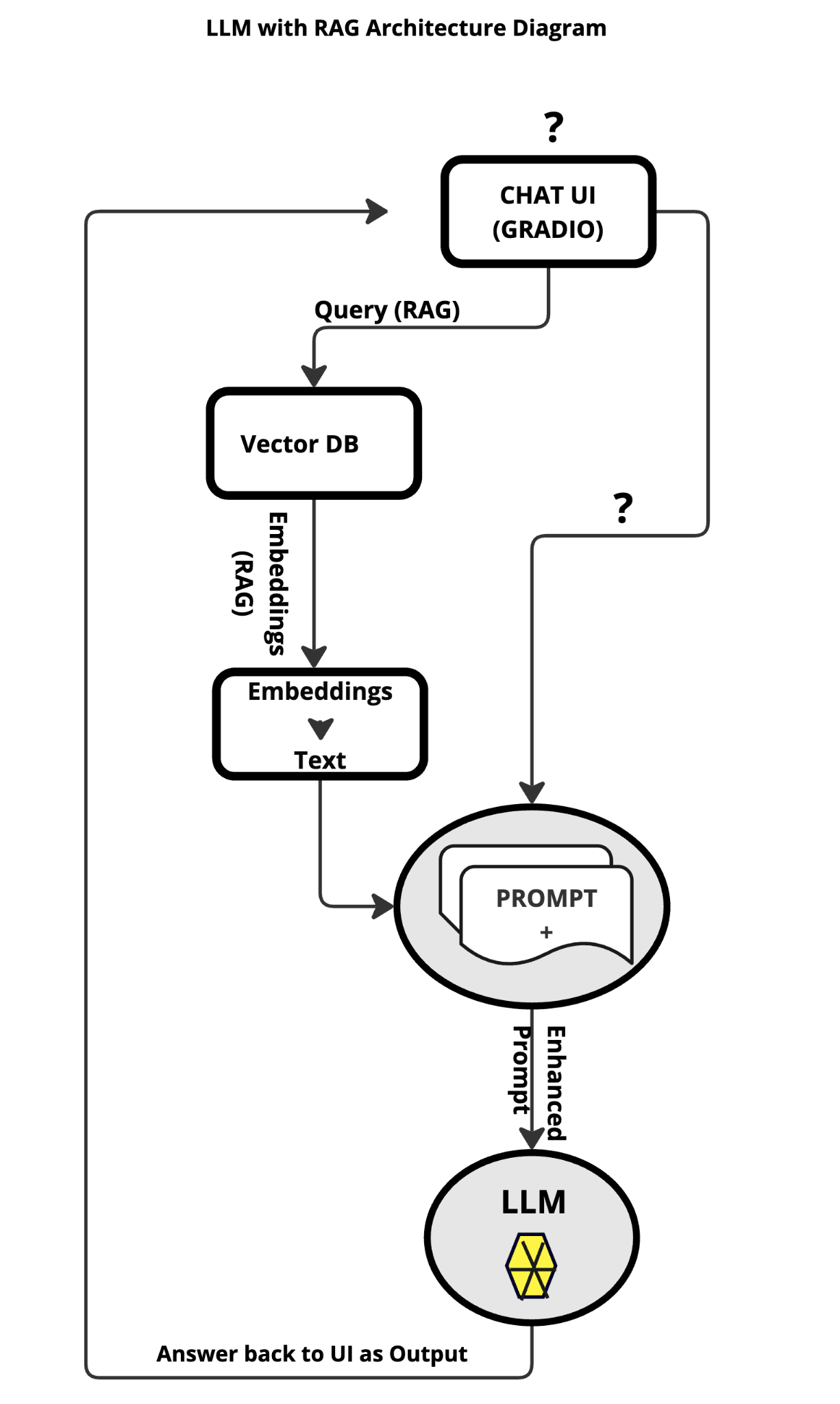
RAG Architecture
A typical RAG application has two main components:
Indexing: a pipeline for ingesting data from a source and indexing it. This usually happens offline.
Retrieval and generation: the actual RAG chain, which takes the user query at run time and retrieves the relevant data from the index, then passes that to the model.
The most common full sequence from raw data to answer looks like:
Indexing
-
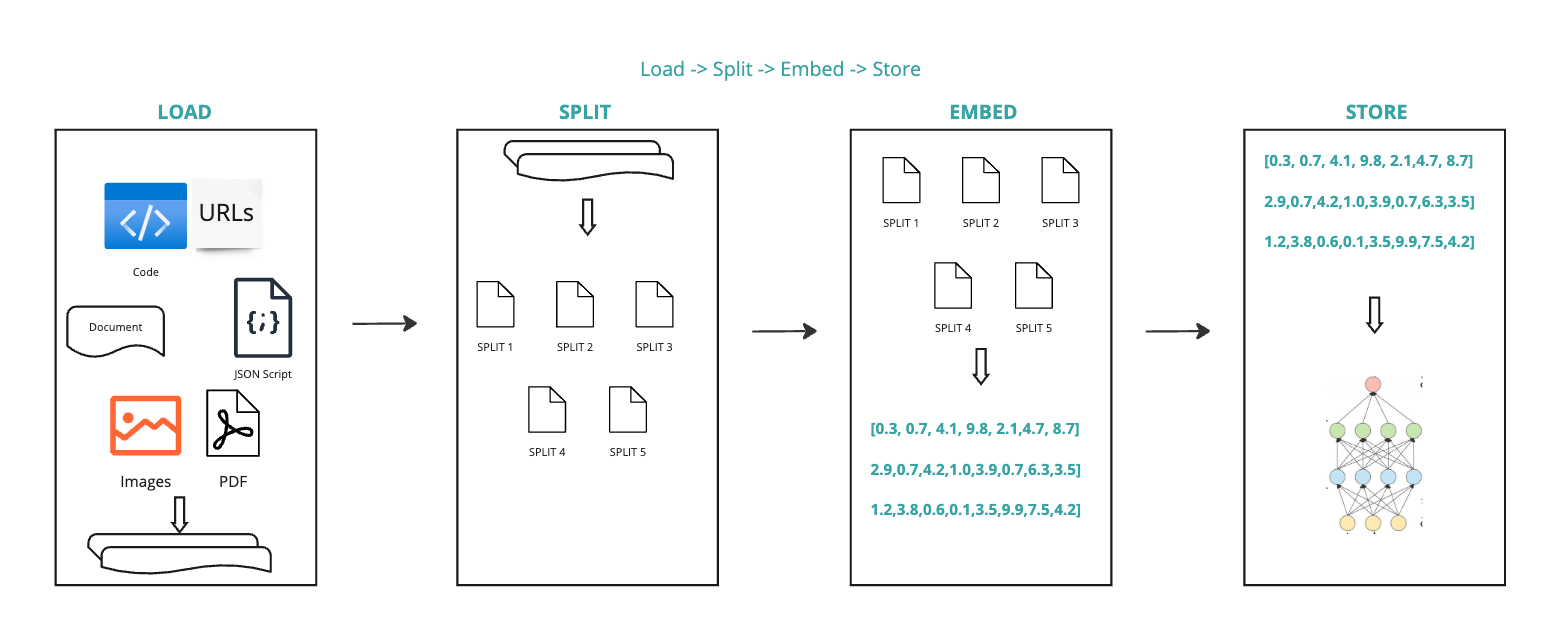
Load: First we need to load our data. This is done with DocumentLoaders.
-
Split: Text splitters break large Documents into smaller chunks. This is useful both for indexing data and for passing it into a model, since large chunks are harder to search over and won’t fit in a model’s finite context window.
-
Store: We need somewhere to store and index our splits, so that they can later be searched over. This is often done using a VectorStore and Embeddings model. Load → Split → Embed → Store
Retrieval and generation
-
Retrieve: Given a user input, relevant splits are retrieved from storage using a Retriever.
-
Generate: A ChatModel / LLM produces an answer using a prompt that includes the question and the retrieved data
Now let’s focus on how OpenShift AI works here right from the development environment for data scientists to model deployment and lifecycle management. Apart from the jupyterhub notebook which you saw earlier, I would like to demonstrate one more important functionality here. Developers right from their IDE for e.g. jupyterhub notebook create a pipeline which they want to test and it automatically creates an OpenShift Pipeline Run within OpenShift and runs it. Developers do not have any understanding of OpenShift and OpenShift pipelines. We are doing Quality check from response and response time perspective as well as security check by verifying the sha of the model we are using just to ensure that it’s the right model we need to use. We are storing the results in a s3 bucket.
Last but not least you can also serve models from Red Hat OpenShift AI dashboard as well as manage its lifecycle.
This is all I wanted to demonstrate for now. Thanks for watching this demo on LLM with RAG.
Business Benefits of using LLM with RAG:
Using Large Language Models (LLMs) for businesses, especially in combination with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), offers several benefits:
Enhanced Customer Support: LLMs can be deployed in chatbots or virtual assistants to provide instant responses to customer inquiries, improving response time and customer satisfaction.
Content Creation: LLMs can generate high-quality content for marketing materials, blog posts, product descriptions, and more, saving time and resources for businesses.
Personalized Recommendations: By analyzing customer data, LLMs can generate personalized recommendations for products or services, enhancing the customer experience and driving sales.
Automated Data Analysis: LLMs can analyze large volumes of data to extract insights, trends, and patterns, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions more efficiently.
Improved Search Relevance: RAG combines the power of LLMs with retrieval models to provide more relevant search results to users, enhancing the user experience on websites and applications.
Efficient Knowledge Management: LLMs can be used to create and maintain knowledge bases, FAQs, and internal documentation, facilitating knowledge sharing and collaboration within organizations.
Adaptive Learning Systems: By continuously training LLMs with new data, businesses can create adaptive learning systems that improve over time and adapt to changing customer needs and preferences.
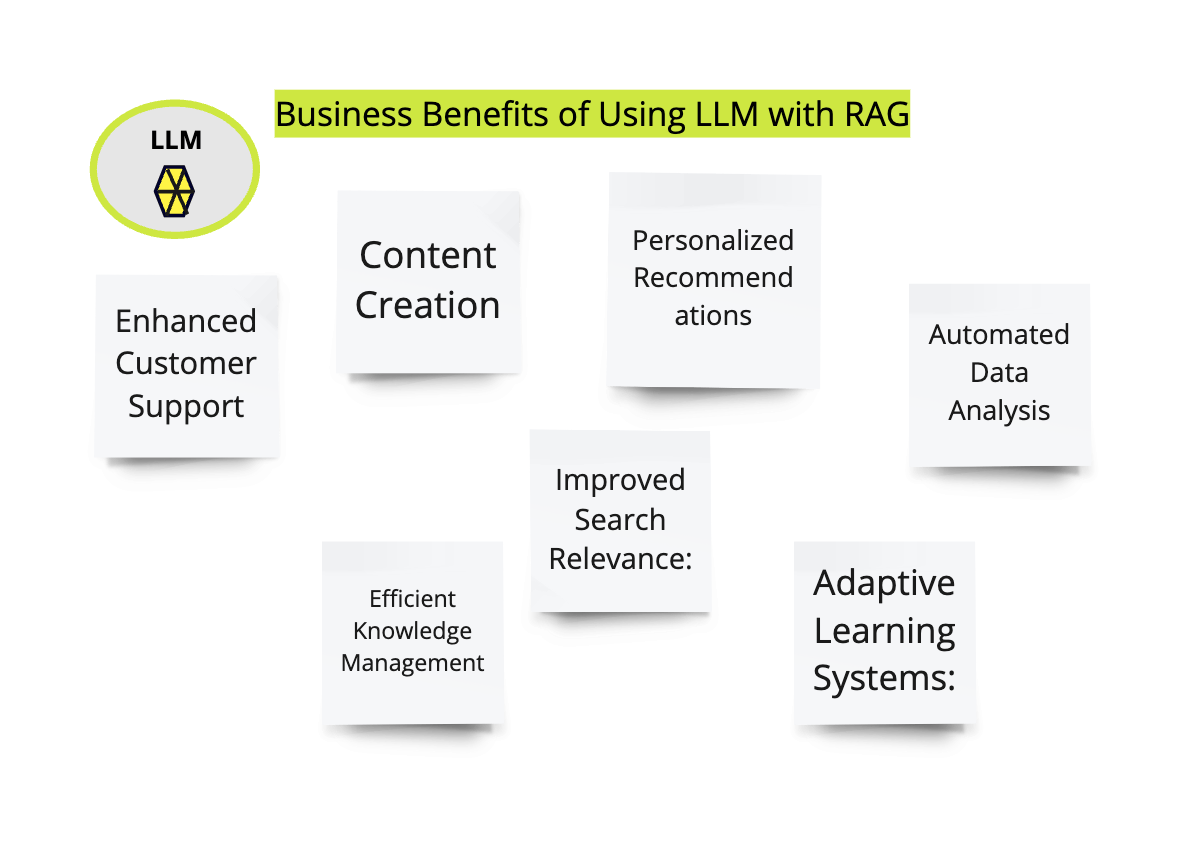
In summary, leveraging LLMs, especially in combination with RAG, can significantly benefit businesses by improving customer support, content creation, data analysis, and decision-making processes.
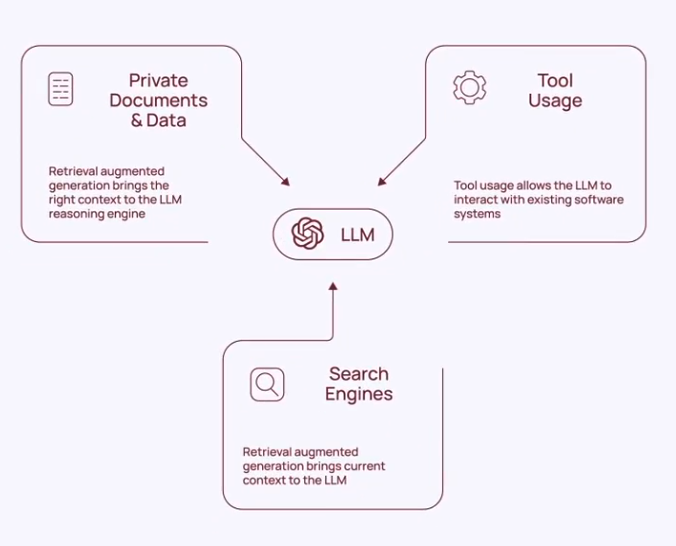
LLM + RAG (Summary in a diagram) :
Resources
V0.2 - Without LLM+RAG Intro and more focused on OpenShift AI (sort of transcript)
Welcome to this demo on Large Language Model with Retrieval Augmented Generation based solution on Red Hat OpenShift AI.
Imagine querying our LLM model about “ What is the latest release of Red Hat OpenShift AI?”, only to receive inaccurate responses. It’s frustrating, isn’t it? But not to worry because with the implementation of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), our chatbot’s performance undergoes a remarkable transformation. RAG seamlessly integrates domain-specific knowledge into our LLM, eliminating the need for costly retraining efforts. Now, our chatbot effortlessly taps into a vast repository of custom documents, delivering precise and tailored responses tailored to your specific domain.
However, RAG is just one piece of the puzzle. Enter OpenShift AI, the cornerstone of our comprehensive solution. Red Hat OpenShift AI empowers organizations with a myriad of benefits like:
-
Accelerated AI/ML workflows: Simplify the development, deployment, and management of AI/ML models, allowing your teams to focus on driving innovation and business value.
-
Improved collaboration: Centralize your AI/ML projects on the Red Hat OpenShift AI platform, fostering seamless collaboration between data scientists and IT operations administrators, and streamlining workflows for maximum efficiency.
-
Enhanced scalability: With Red Hat OpenShift AI, effortlessly scale your AI initiatives up or down in response to changing business demands, ensuring optimal performance at all times.
-
Increased security: Rest assured knowing that your sensitive data and models are safeguarded by Red Hat OpenShift AI’s robust security features, including role-based access control and encryption, ensuring compliance and peace of mind.
-
Greater flexibility: Deploy Red Hat OpenShift AI in any environment - on-premise, in the cloud, or in a hybrid setup - giving you the flexibility to adapt to your organization’s evolving needs seamlessly.
But we don’t stop there. Our pipeline in OpenShift AI ensures that we not only check the quality of the LLM output but also automate the process of updating the RAG database (VectorDB) with the new information so that LLM is able to provide us information which includes my company or research specific information as well. A data scientist from their IDE can create a pipeline using a simple user interface on the same IDE without knowing the underlying technicalities of OpenShift Pipelines. Submit this pipeline from the same IDE and it creates and executes the pipelines in openshift. This is the power of how deep engineering level integrations can provide ease of use to the developers and ensure complex tasks are simplified as well as developer’s productivity is enhanced.This can be further extended to the world of MLOps. In this demo, you can upload this pipeline manifest file (same what you saw earlier in Elyra) directly in your OpenShift AI UI Pipeline Serving section and create a new pipeline run to automatically run the same in OpenShift as Tekton pipeline and complete the tasks which you have included in your pipeline run. We can schedule the pipeline triggers so that new information from our private data can always be available into the RAG Vector DB and becomes part of your query and output.
In summary, by harnessing the combined power of LLM with RAG and Red Hat OpenShift AI, we empower organizations to unlock a world of possibilities. Drive efficiency, foster innovation, and elevate customer satisfaction to unprecedented heights with our transformative AI solution. Welcome to the future of AI excellence with OpenShift AI.