Demo Guide
Login to Openshift console: {openshift_console_url}
username: admin
password: {password}
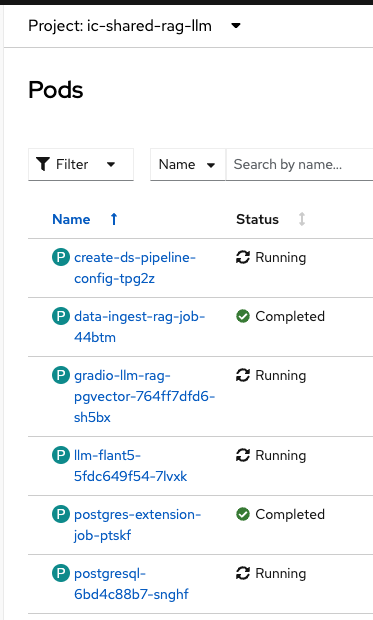
Ensure that all the pods are running fine on ic-shared-rag-llm project. This is the project configured with RAG along with vectorDB as well as a pipeline server in OpenShift AI Dashboard. The gradio chatbot in there connects to the shared llm deployed in the ic-shared-llm project.
Some job pods initially may have errors but a related job should be in completed state.
There are other two related projects ic-shared-rag-db and ic-shared-rag-minio.
Open OpenShift AI Dashboard as well as ArgoCD console.
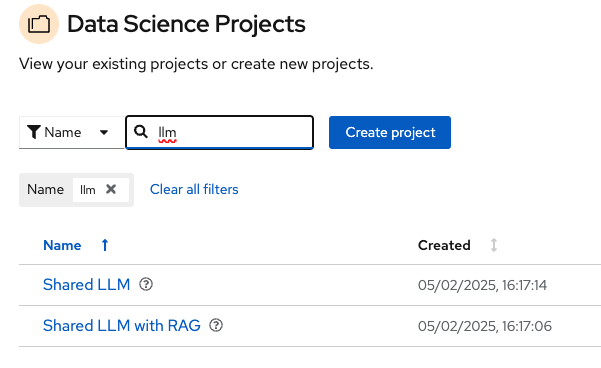
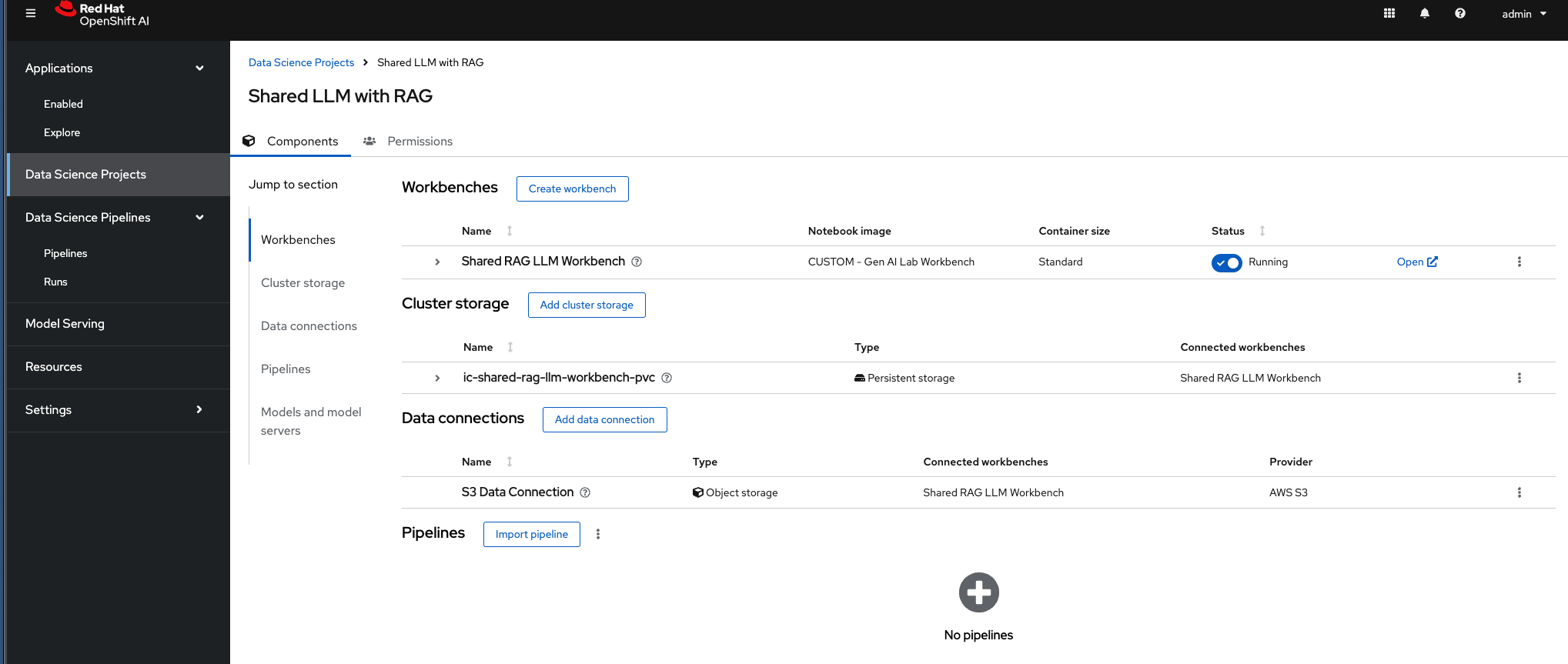
Login to OpenShift AI Dashboard and go to ic-shared-rag-llm data science project to view all the components including workbench pre configured.Search for llm and select “Shared LLM with RAG” Data Science Project.
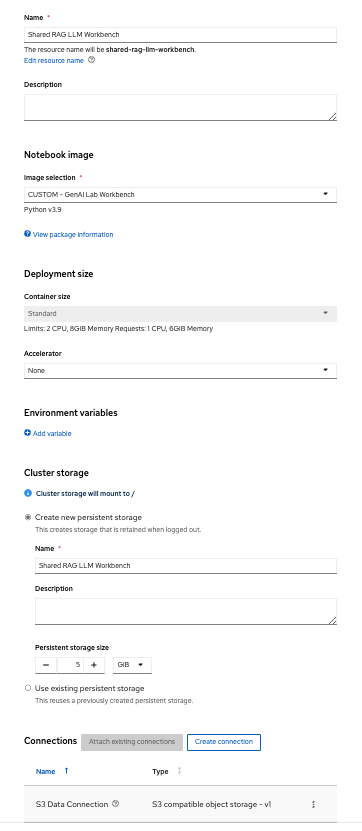
Create a workbench named “Shared RAG LLM Workbench” as shown below.
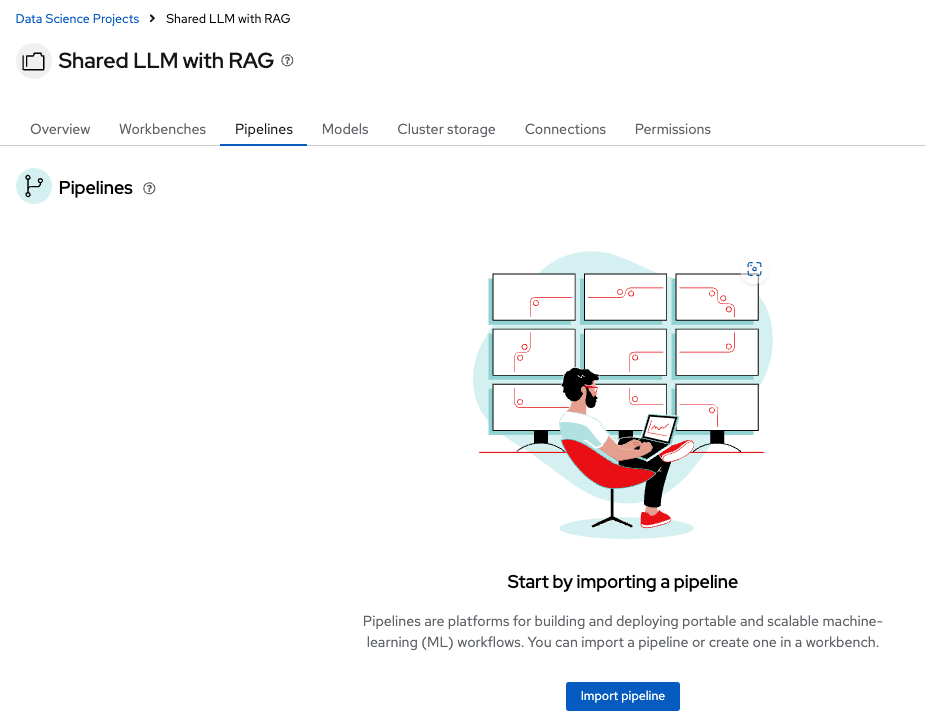
There are two ways to work with Data Science Pipelines.
-
Importing pipeline manifest directly into OpenShift AI dashboard. (Admin Persona)
-
Creating the pipeline in Elyra pipeline editor, say, developer/data scientist and run from there creating the same effect as point 1. (Data Scientist Persona)
Admin persona - First scenario (using pipeline manifest):
Note that the pipeline service is pre-configured here. Import this pipeline run yaml file, Select Import pipeline based on the snapshot above in Pipelines section. (You need to download this file locally before you can upload to the OpenShift AI pipeline Dashboard. https://github.com/ritzshah/llm-rag-deployment/blob/update-for-2.15/examples/pipelines/working-new-llm-ingestion-test.yaml
Import pipeline
Upload the file you downloaded from the above git url - working-new-llm-ingestion-test.yaml
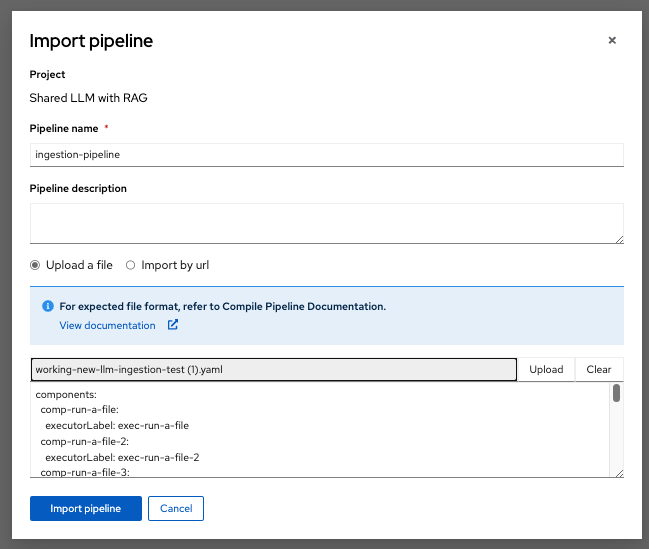
This will create a DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph)
Now Import Pipeline.This will create a pipeline which you can use to create a pipeline run. Once you create a pipeline run, it triggers a tekton pipeline run in OpenShift.
Select Create run from the above and fill the Name, Description (optional) and select Pipeline from the drop down menu. Also note that you can run it immediately or schedule it for a recurring run. This scheduling is important for RAG data ingestion w.r.t periodic change in the data being ingested into RAG Vector DB.
Update the name of the run and review other parameters.
Push the Create Run button and this will trigger a data science pipeline run.
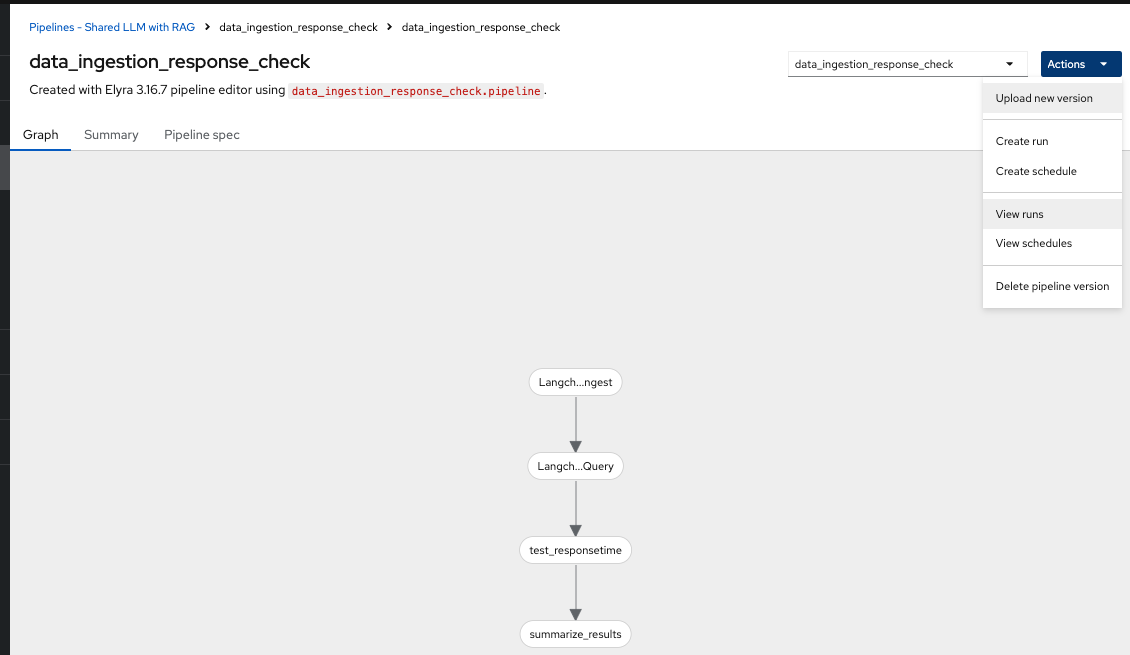
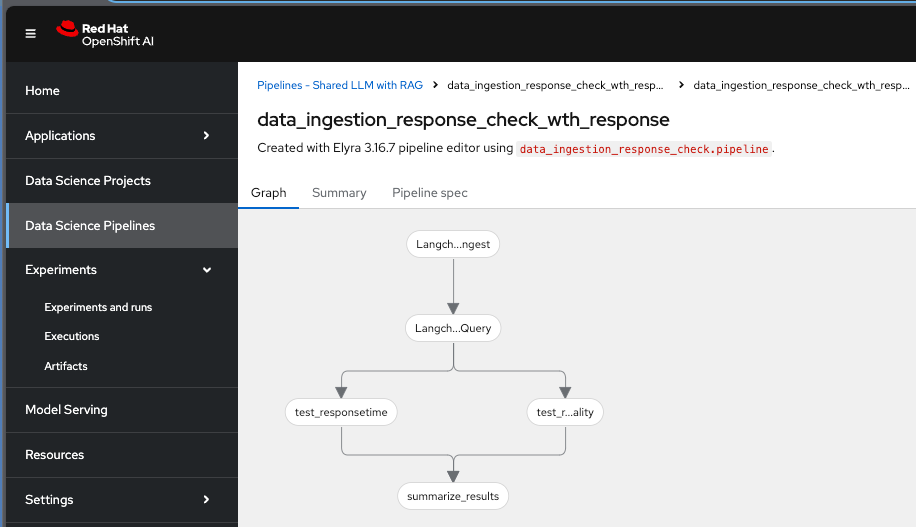
There are 4 tasks in the pipeline,
Task 1 is to ingest the data into PG Vector DB.
Task 2 is to verify that data is ingested into the PG Vector DB and can query the DB without any issues post data ingestion.
Task 3 is to test the response time of the llm and to ensure that everything from LLM is working fine post ingestion of the new data in VectorDB.
Task 4 summarizes the results into a minio bucket folder.
In Task 1 currently we are just adding very minimal documentation of Red Hat OpenShift AI 2-latest Release Notes.
Why 2., just to showcase that the LLM with RAG in our case provides specific information we have added into vectordb and not hallucinating too much (this is a problem to discuss some other time).
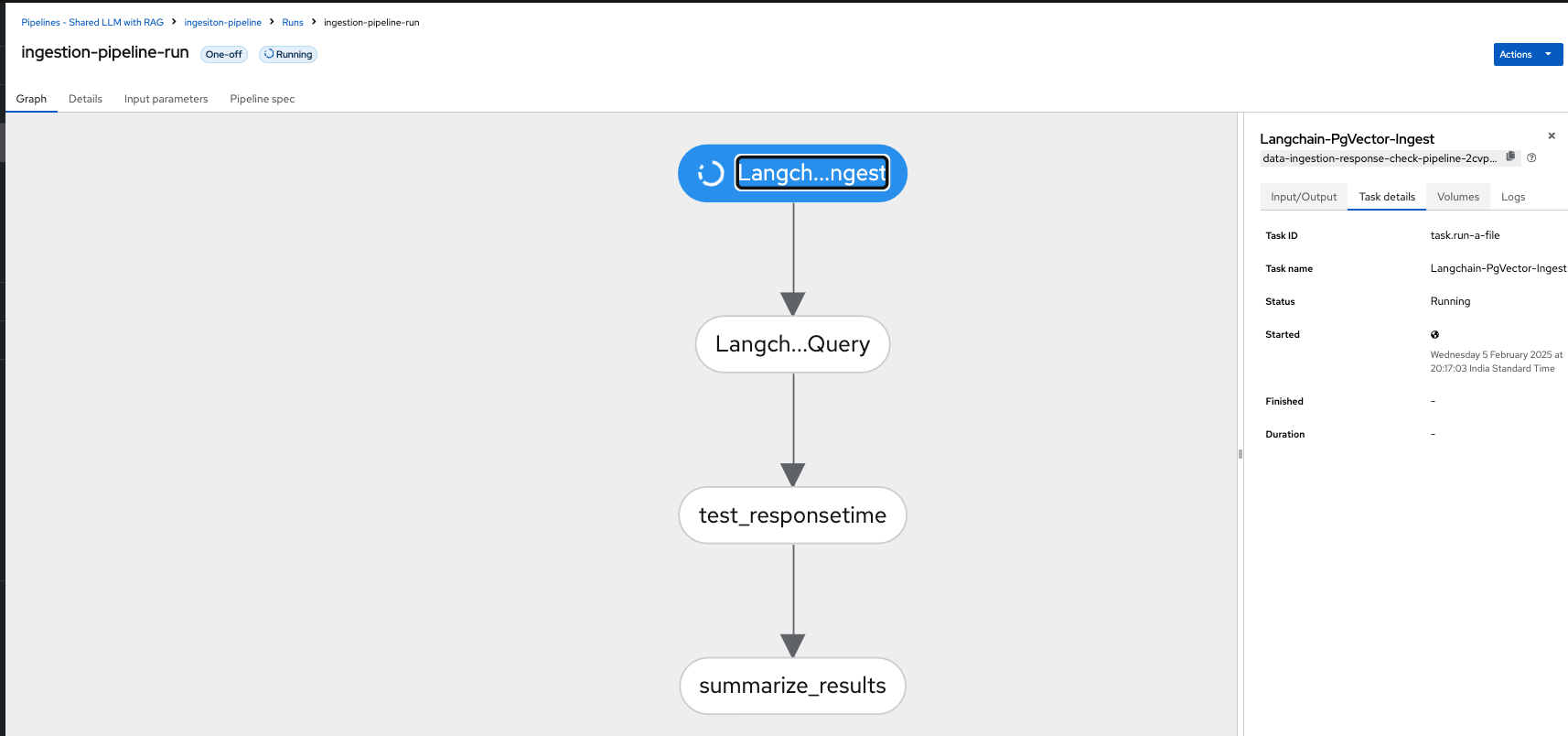
This is what you see in OpenShift AI Dashboard
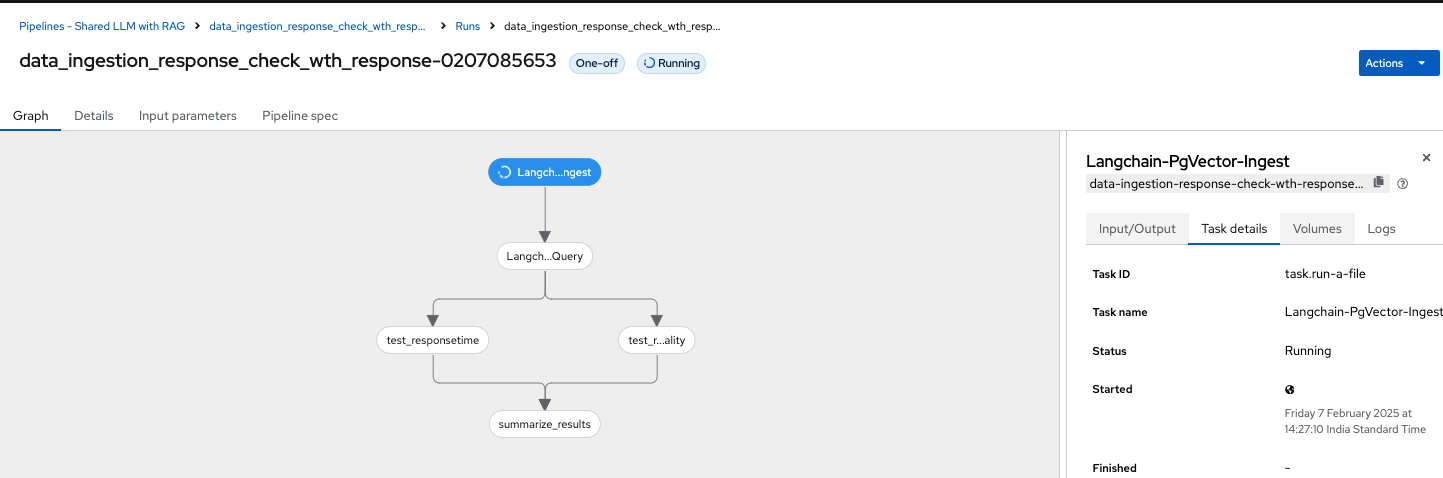
Get the pod name from the above and check the run in OpenShift. Its the same project where you run the above data science pipeline.

This is what you see in the OpenShift console/dashboard.Selecting the task will give you Logs for the task run. The pipeline takes around 10 to 12 minutes to run, so make sure that you have one already in the finished state before the demo so that you can straight away move to the finished pipeline and save time there.
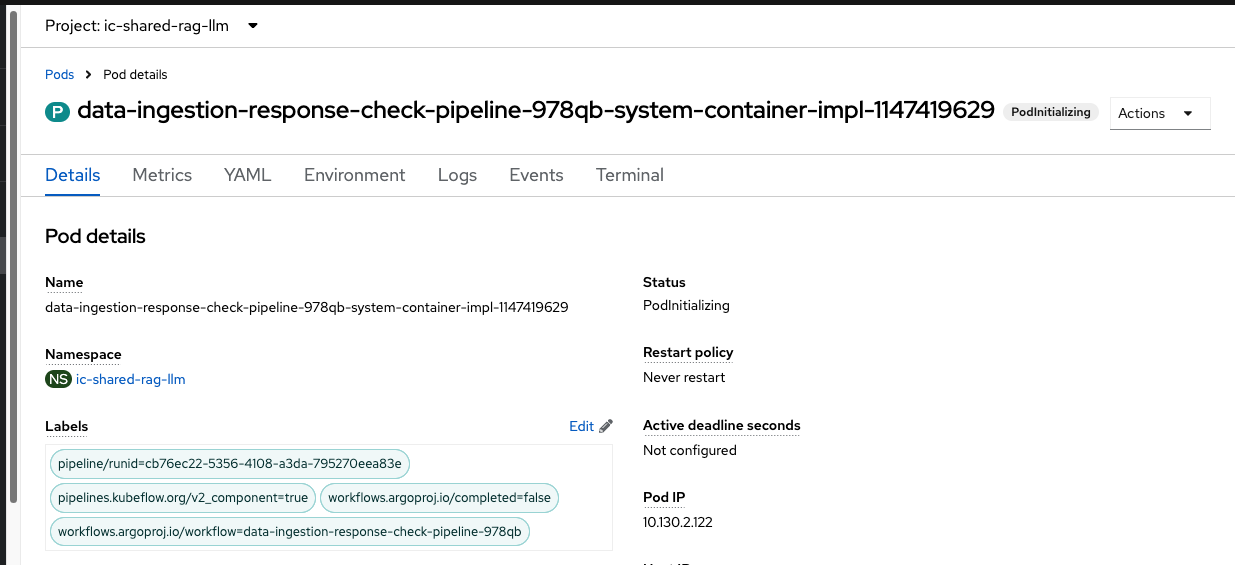
You can check the logs either in OpenShift AI task Logs (for Data Scientist Persona) or in OpenShift (for admin persona).

Show the finished pipeline in both OpenShift AI Dashboard. Each task is a pod running in the
If you move to some other section in OpenShift AI dashboard and want to go back to view the running pipeline you can “View Runs”:
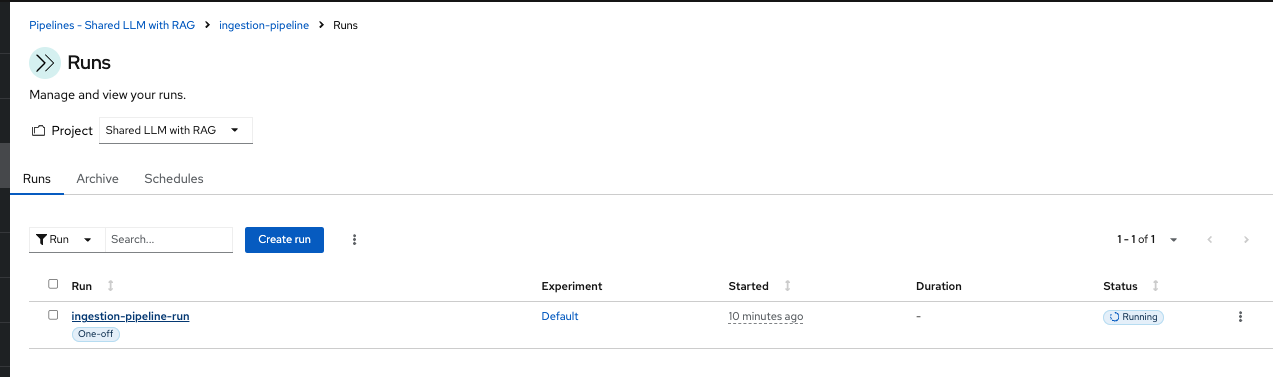
Once the Run is completed, you will have this output visible in the Runs:
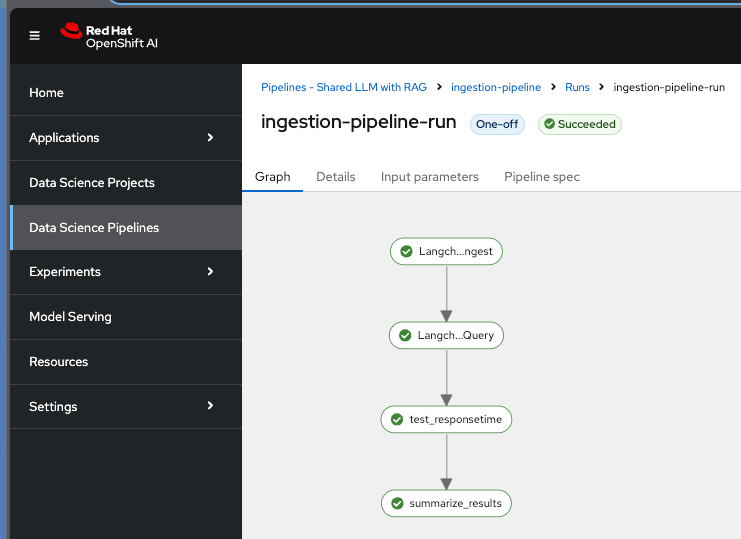
Note that a successful completion of the pipeline ensures that new data is ingested in the RAG database and tested. Note that in real world situations, the tests can be very different and very specific to check the quality of the data ingested and retrieved. It takes around 10 minutes to complete the pipeline run.
Data Scientist /Developer persona - Second scenario
(Optional demo only if there is a developer in the audience)
Data Scientist using Elyra pipeline editor to create and run the above pipeline.
Everything you need is already set in this environment like pipeline server, runtime environment, etc. Elyra run will convert your pipeline on canvas to creating a pipeline run for tekton in OpenShift.
Go back to the Data Science project ic-shared-rag-llm your OpenShift AI Dashboard and create a workbench similar to the one already running. Once the new workbench is created, open it and clone the git repo before you do the demonstration to save time.
Create a new workbench → llm test
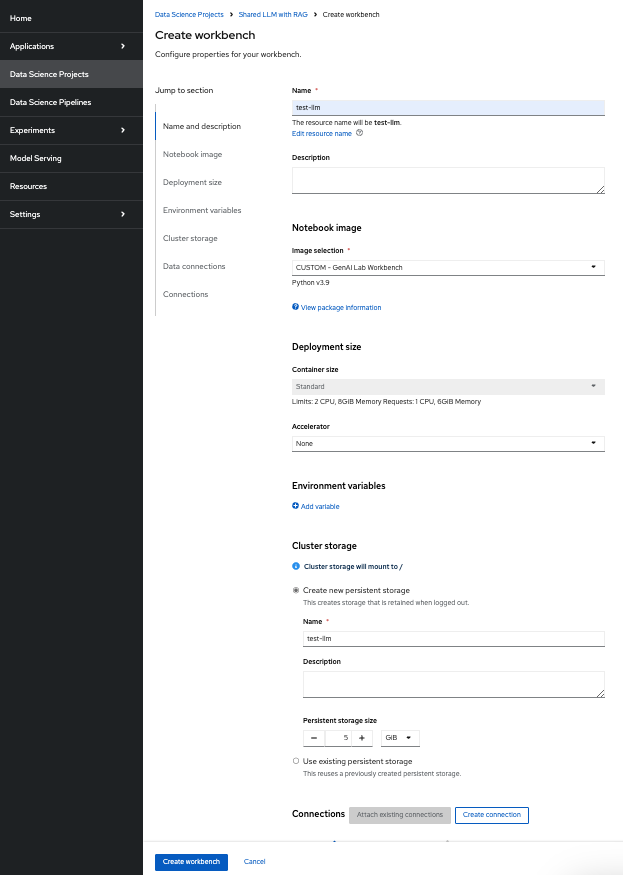
Once the workbench is created, you should select “Open” for llm test workbench only.
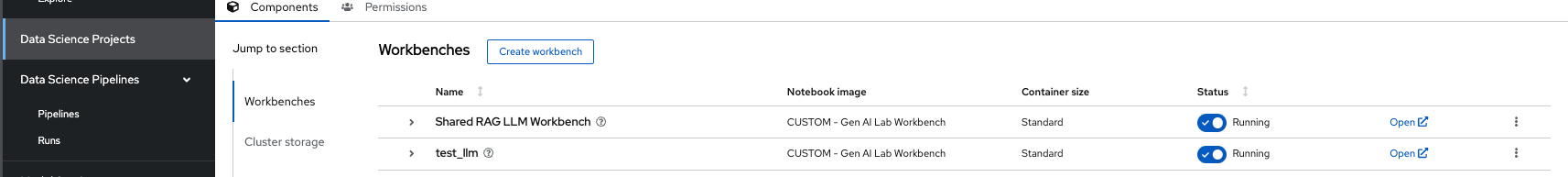
This will ask you to login if it’s for the first time. Use the same admin user/password as you have used previously and login to the workbench. Do Allow selected permissions before you access your workbench.
Wait for jupyterhub notebook to be launched (takes a minute for the first time) and then clone this git repository
https://github.com/ritzshah/llm-rag-deployment.git
Before you proceed further ensure that the Data Science Pipeline is referencing to right S3 storage route and not the local Kubernetes service. You need to change the service address to route for S3 storage access as shown below.
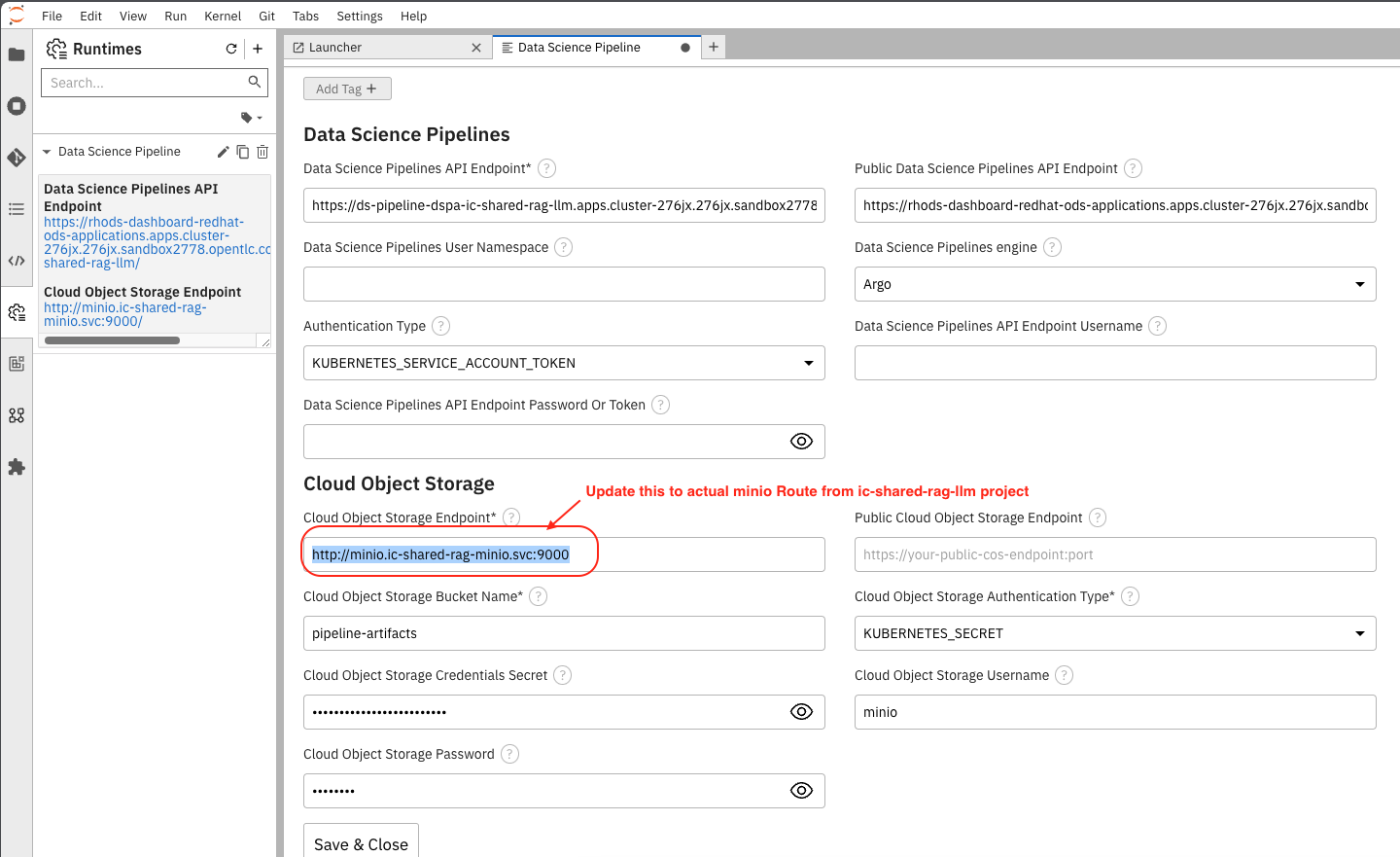
Use the route you get from the minio-s3 route component in the ic-shared-rag-minio project as shown below in the Example and the image if not already set.
Example : https://minio-s3-ic-shared-rag-minio.apps.cluster-276jx.276jx.sandbox2778.opentlc.com
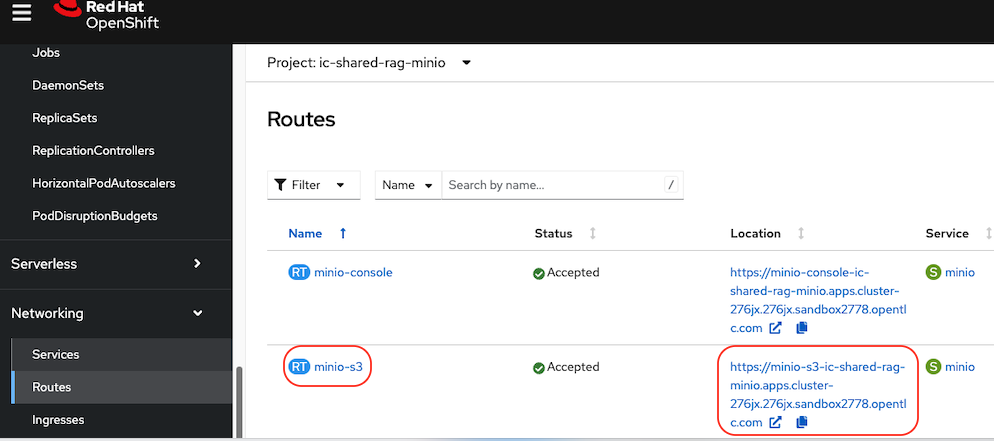
After route update image::demo/minio-route-update.png[]
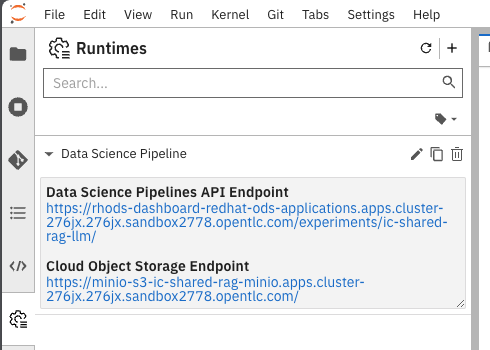
After updating the route, you need to Save & Close the above. Make sure that the Cloud Object Storage Endpoint is now reflecting the new updated route. Value.
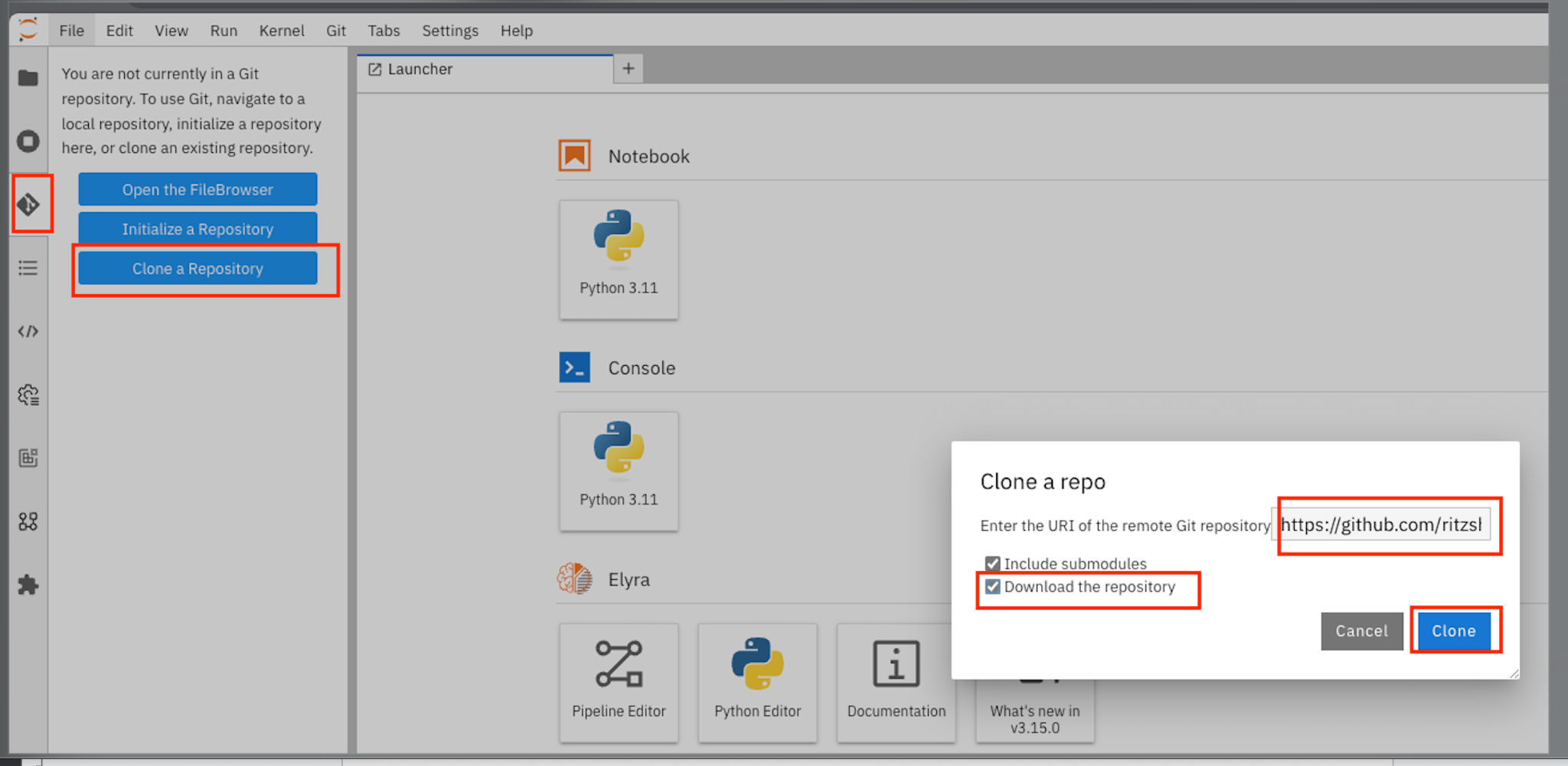
From the left side panel select the icon to clone the git repository and use the above git repo (https://github.com/ritzshah/llm-rag-deployment.git). Select Clone. This will download and add this git repository to your jupyterhub notebook..
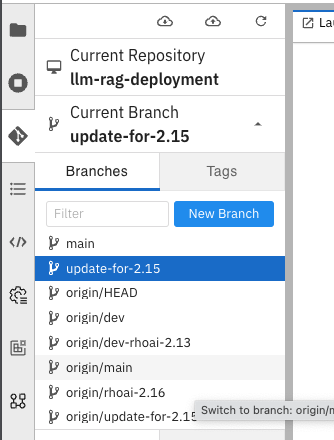
IMP : *Once you clone the repo ensure that you switch the *branch to “update-for-2.15”, as the pipeline we create is in this branch. Go to llm-rag-deployment branch and select the branch. See image below for reference.
In llm-rag-deployment/examples go to pipelines folder and select “data_ingestion_response_check.pipeline” file.
This will open the file in elyra editor and you will see those 4 tasks which you saw earlier as well. Now as a data scientist you can add or delete the tasks (just drag a python code and it gets added as a task into the pipeline, it’s that simple for a data scientist and you do not need to know how the pipeline works).
Task 1’s code can be updated to point to new data and that should push new data to vectordb.
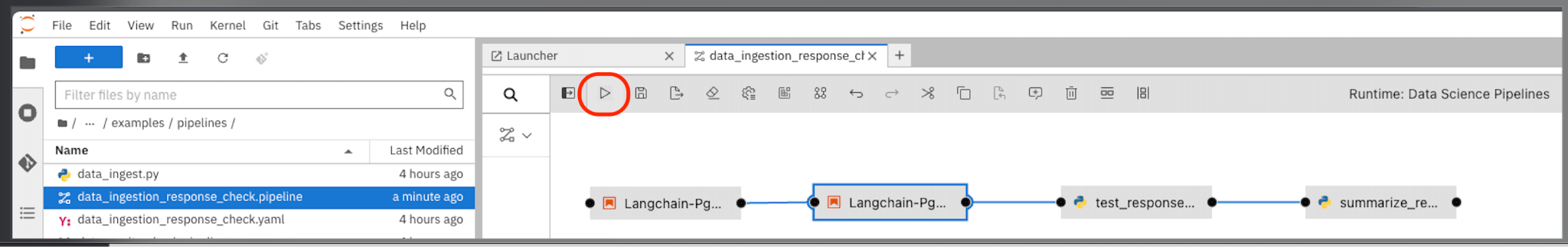
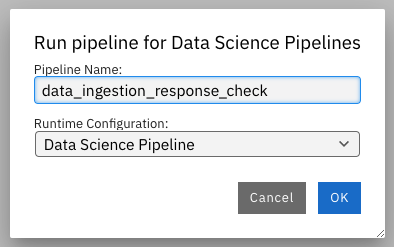
Press the Run button as you see in the above screenshot. Select the defaults and say OK and then again press OK. Ensure that you update the Pipeline Name with a different name as the same name already exists from the previous run.
Once the pipeline is created, you should see this output:
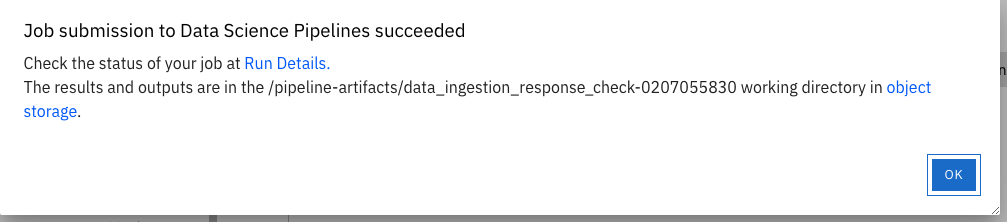
Select Run Details to review the run. This will open a new tab/screen. Once it loads, you will see the following on screen. Alternatively you can go to Experiments → Experiments and runs on OpenShift AI Dashboard to review the run directly.
Check the pipeline created with Elyra.
Select View Runs :
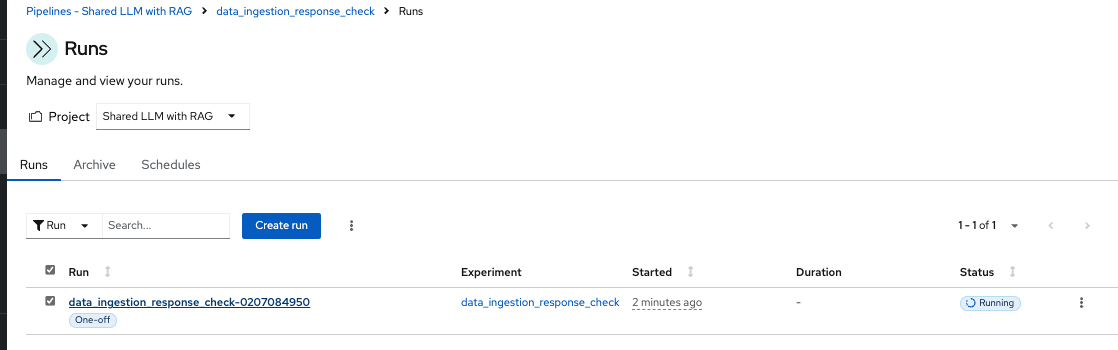
Once you open the above Run, it will show the same pipeline you saw earlier when you ran as admin persona.
Let’s say you created a python code to check the quality of the response and want to add it alongside test_response. You can do this right in the elyra editor and this will create additional tasks in the pipeline run automatically for you.

Isn’t that !!
This next section is to show that you can add new tasks and execute. Currently this new task is not executed correctly in the pipeline and so do not show the complete output or wait for it to finish. Just execute and show that it’s running and close the discussion for now.
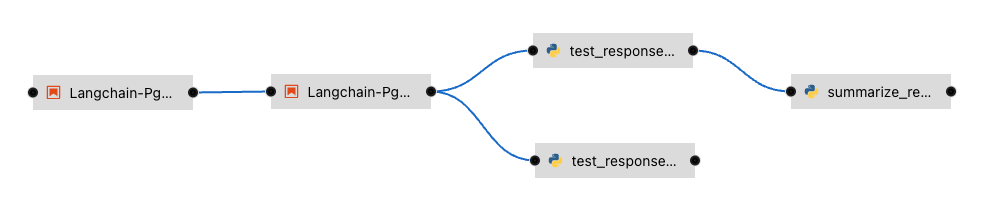
Let’s add a task, say we want to check the quality of the response output from LLM. We can add that as a task through the elyra editor. Drag the python code which does response quality check.
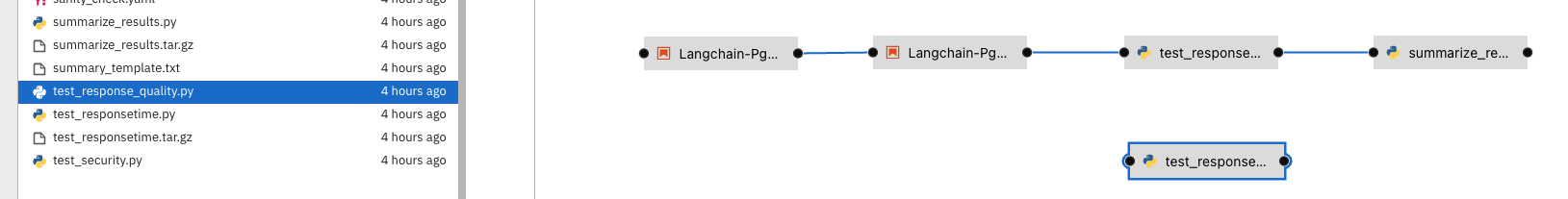
Then connect the lines from the second task to this new task and from this new task to summarize task. This should run both the response tasks in parallel.
Step 1
&
Step 2

Now re-run the complete pipeline again and this time it should include the new task as well.
Check AI dashboard
You will see this new pipelinerun. Select the run and this should take you here:
You can view the run and this is what you will see.
You as a data scientist do not need to know about the underlying pipeline implementation but just use elyra editor and drop your code as tasks , connect it the way you want to create workflow and run. That’s it.
Troubleshooting
-
If you do not see the following pods running in our ic-shared-rag-llm project you need to delete the dspa and resync with the prune option the ds-rag-pipelines project from ArgoCD to get this fixed.
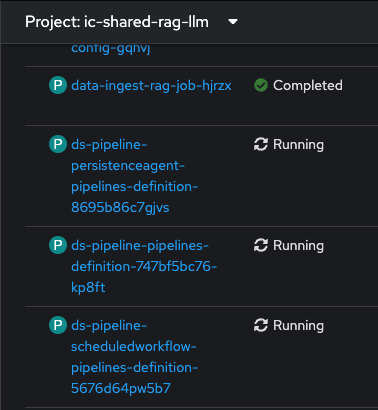
&
in ArgoCD create-ds-pipeline-config pod should be healthy
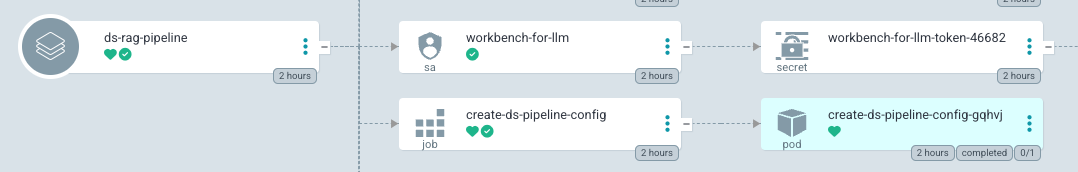
If you do not see the above, do the following to fix it.
On your OpenShift UI, start the OpenShift Terminal and run the following:
Welcome to the OpenShift Web Terminal. Type "help" for a list of installed CLI tools.
bash-4.4 ~ $ oc get dspa -n ic-shared-rag-llm
NAME AGE
pipelines-definition 129m
bash-4.4 ~ $ oc delete dspa pipelines-definition -n ic-shared-rag-llm
datasciencepipelinesapplication.datasciencepipelinesapplications.opendatahub.io "pipelines-definition" deleted
Go to ArgoCD and sync with the prune option the following application.