Introduction to the Computate and Smart Aquaculture use case
Author: Christopher Tate
Overview
The Smart Aquaculture use case began when Professor B. Dewayne Branch reached out to me to learn the latest developments in open source for IoT and secure data standards. He shared with me some research about Smart Aquaculture solutions for sustainable fisheries and I was intruigued. I did some research as well, and determined that FIWARE has already been working on open source Smart Aquaculture solutions. I was already working with FIWARE smart IoT solutions on Red Hat OpenShift, so I put together the Smart Aquaculture use case.
About FIWARE
FIWARE is a non-profit organization, headquartered in Berlin. They have a mission of building an open, sustainable ecosystem around public, royalty-free, and implementation-driven software platform standards for the development of smart solutions in multiple sectors, following a digital twin approach. In 2022, I heard that the Red Hat Social Innovation Program started an innovative engagement with FIWARE to harness the power of open source technologies to solve global problems. I helped start the conversations with FIWARE and the Red Hat Social Innovation Program as the Social Innovation Architect. I also started a related research project with Boston University, the Red Hat Collaboratory with Boston University, and Smarta Byar in Veberöd, Sweden.
I also attended the 2022 FIWARE Global Summit in Gran Canaria, Spain, and presented about our FIWARE Innovation Hub on the way at Boston University. Because of the open source value for FIWARE provided for building smart solutions, I started a FIWARE iHub between Red Hat and Boston University.
In 2024, the FIWARE community reached out to me and other iHubs, to start some discussions about community building related to standards for IoT smart device computing. The target domains included smart cities, smart ports, and smart agriculture. The focus was on how the FIWARE community, including the FIWARE iHubs, can help.
I was asked to prepare a panel discussion with 4 other FIWARE iHubs at the upcoming FIWARE Global Summit. This would enhance community cooperation, contribution, and participation with FIWARE’s approach to "Think global, act local."
In addition to preparing for this upcoming panel discussion, I decided to focus on developing some new tools within my computate platform to support FIWARE use cases of Smart Data Models. I also developed a free course that runs on the Red Hat OpenShift Developer Sandbox. I was also building the Computate Smart Website Builder that allows software developers to build a custom data-driven website powered by FIWARE.
I wanted to put together a complete solution for the FIWARE community to deploy FIWARE microservices to the very best enterprise open source cloud environment, create Smart Data Models, register entities with the FIWARE Context Broker, and visualize their data in a Computate platform.
Use Case
The Smart Aquaculture use case is about building your own secure IoT smart platform for sustainable fisheries with generative AI, zero-trust access control, and interactive dashboards. It uses modern developer tools to access your VSCode developer workbench in the browser, it doesn’t matter your laptop’s operating system. Ansible automation automates the tedious tasks of generating all of the boilerplate code for your Smart Aquaculture site, and you can customize it along the way. Developers learn how to build reactive asynchronous Java code, OpenAPIs, database scripts, and Smart Aquaculture data. Users can visualize the Smart Aquaculture data in event-driven, interactive dashboards and maps.
The platform interacts with modern microservices in the cloud like:
-
PostgreSQL Database for transactional data storage
-
Apache Zookeeper Cluster Manager for event bus messaging
-
Apache Solr Search Engine for autosuggest and searchable APIs
-
Keycloak Single Sign-On for fine-grain access control to Smart Aquaculture data
-
FIWARE Context Broker for open source IoT edge device standards
What is the Smart Aquaculture Use Case?
Learn how to deploy open source smart device microservices to the cloud and try out your own secure IoT smart platform, including FIWARE Smart Data Models, and Context Broker, with built-in security provided by Keycloak fine-grained resource permissions.
Modern developer workbenches in the cloud
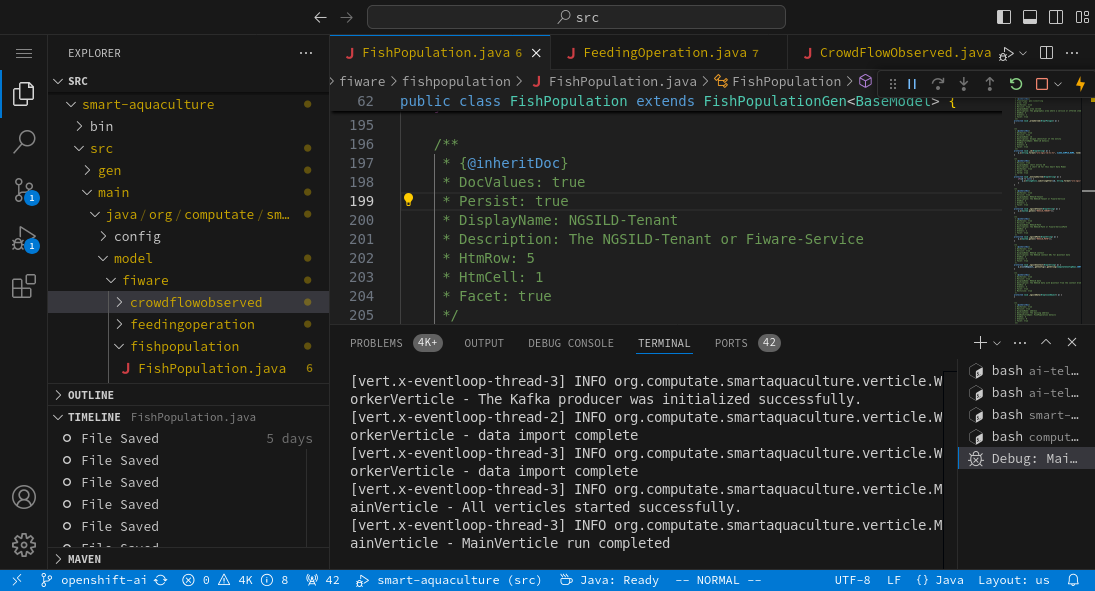
Use the latest cloud deployment tools like Jupyter, Ansible, Helm, and OpenShift command line interface from your browser, and start deploying microservices to the cloud like a modern cloud developer.
Cloud-native microservices that cluster and scale

Deploy modern open source microservices including Apache Zookeeper cluster manager, Apache Solr search engine, PostgreSQL relational database, MongoDB No-SQL database, RabbitMQ message broker, Keycloak single sign-on authentication and authorization, and reactive—event bus driven applications.
Fine-grain zero-trust authorization to data
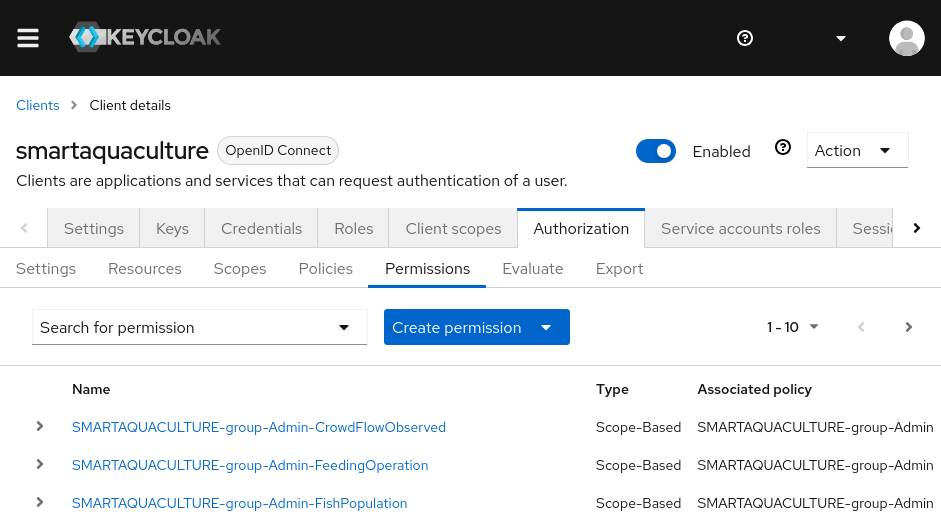
Create authentication realms, clients, OAuth identity providers, and fine-grain resources, scopes, policies, and permissions to data and dashboards.
FIWARE IoT services and Smart Data Models
Connect your databases and message broker to a FIWARE Context Broker — utilize NGSI-LD standards and Smart Data Models to manage your own smart device data.
Getting started building a Smart Aquaculture platform
To begin working on a use case like Smart Aquaculture, you need to be working in a supported environment. This Red Hat OpenShift Demo environment is already to go with all the dependencies and source code to get started. The Computate platform is public and open source, so it runs on Linux. Linux is different than proprietary computer operating systems like Microsoft and Apple. It’s best suited to run on a computer with the x86_64 architecture, in place of Microsoft. I wouldn’t recommend installing Linux on an Apple computer because it is a different ARM64 based architecture and incompatible with some cloud container images that are required. The Linux operating systems best suited for developing a Smart Aquaculture platform are Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9, CentOS Stream 9, and Fedora 34+.
Building a Smart Aquaculture platform in the cloud
Thanks to the powerful cloud developer tools built into Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform, Developers can log into a VSCode workbench directly in the browser and start developing a Smart Aquaculture platform. The OpenShift AI workbenches provided by Red Hat allow developers to write code in the browser, it doesn’t matter what your computer’s architecture or operating system is.
Sovereign generative AI behind the Smart Aquaculture platform
Because developing microservices is hard, and requires a lot of tedious configuration of databases, OpenAPI specs, and code, it really helps to write down your ideas in a logical way and have the code generated for you. This is how Computate software powering the Smart Aquaculture platform works. You define a logical list of variables to decide how your platform will be customized for your organization and your use case. Then the boilerplate code that you need is automatically generated for you to jumpstart your project. Then you work on building specific models for your specific use case. Then you can create articles that explain your project.
Developing smart data models in your platform
A model in a platform powered by Computate is generally composed of Java code comments describing the whole model. You create a Java Class in a unique Java Package, then write a description for your model, write some language context for your model because it’s meant to be internationalized, add a Font Awesome icon for your model, add an API URI where your JSON REST API for your model will be, add a search page URI where you can search for the model, add an edit page URI where you can edit the model, add API methods you wish to provide in your API (like GET, POST, PATCH, DELETE, PUTImport) then create any number of authorization groups who can access the various API methods for your model.
Developing model persistent fields
The next step to develop your model is to create fields that are either persisted in the database, or calculated and returned by the search engine in the API for your model. To develop this kind of special field into the model with the Computate platform, you create a new protected void method in your class that starts with an _ (underscore) character, followed by the field name. Next, if the field can be null, you will want to create one parameter in the method with the Wrap class that comes from the computate-search project. The Wrap class is a Generic class where you can specify the actual Java Class of the field as a Generic type of the Wrap class. If you wish to leave the field null when you initialize the class, you can leave the method empty. If you wish to populate the field with a default value, then construct the value and wrap it in the Wrap by typing w.o("field value goes here");