Snapshots with Openshift Virtualization
Scenario - Virtual Machine snapshots with Portworx
In this scerario, create a virtual machine snapshot.
We have created a new virtual machine that we will be using for this excercise.
Reminder: Accessing the Openshift Console
To connect to the console, click on the tab above.
IMPORTANT: The
Openshift Consoletab will open in a new browser window. Because we are using a self signed certificate, you will need to bypass your web browsers security features to connect.
We can then log in with the following credentials:
Username: kubeadmin Password: kubeadmin_password
Virtual Machine Snapshots
Task 1: Create a VolumeSnapshotClass
In order to take snapshots, we need to configure a VolumeSnapshotClass.
Run the following from our terminal tab:
cat << EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: VolumeSnapshotClass
metadata:
name: px-csi-snapclass
annotations:
snapshot.storage.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
driver: pxd.portworx.com
deletionPolicy: Delete
parameters:
csi.openstorage.org/snapshot-type: local
EOFTask 2: Take a snapshot of our new VM
Log in to the Openshift Console by following the instructions above.
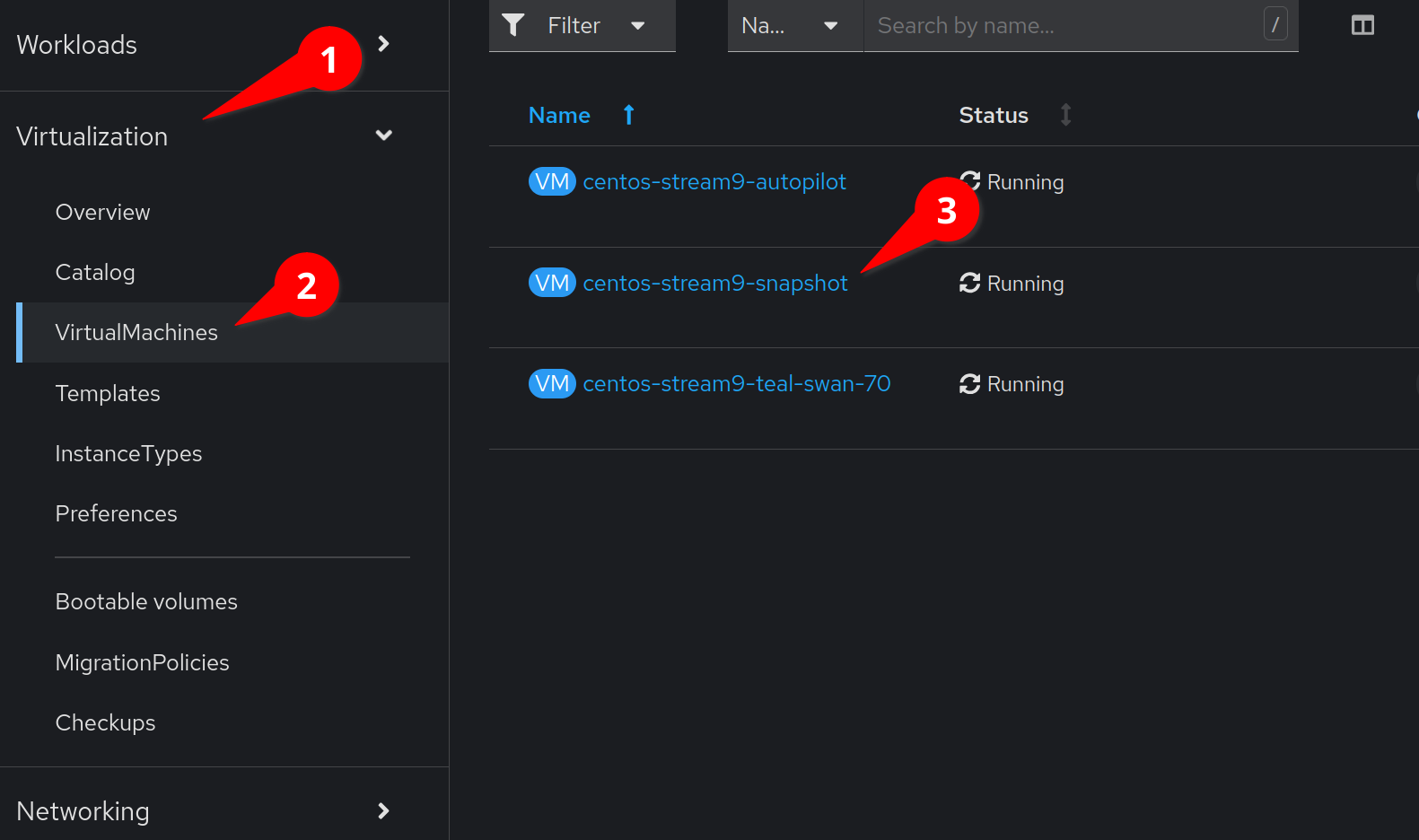
Click on the Virtualization menu item, followed by VirtualMachines.
We can then find the virtual machine we will be using for this snapshot.
Click on the VM labeled centos-stream9-snapshot.
Navigate to the Snapshots tab and select Take Snapshot
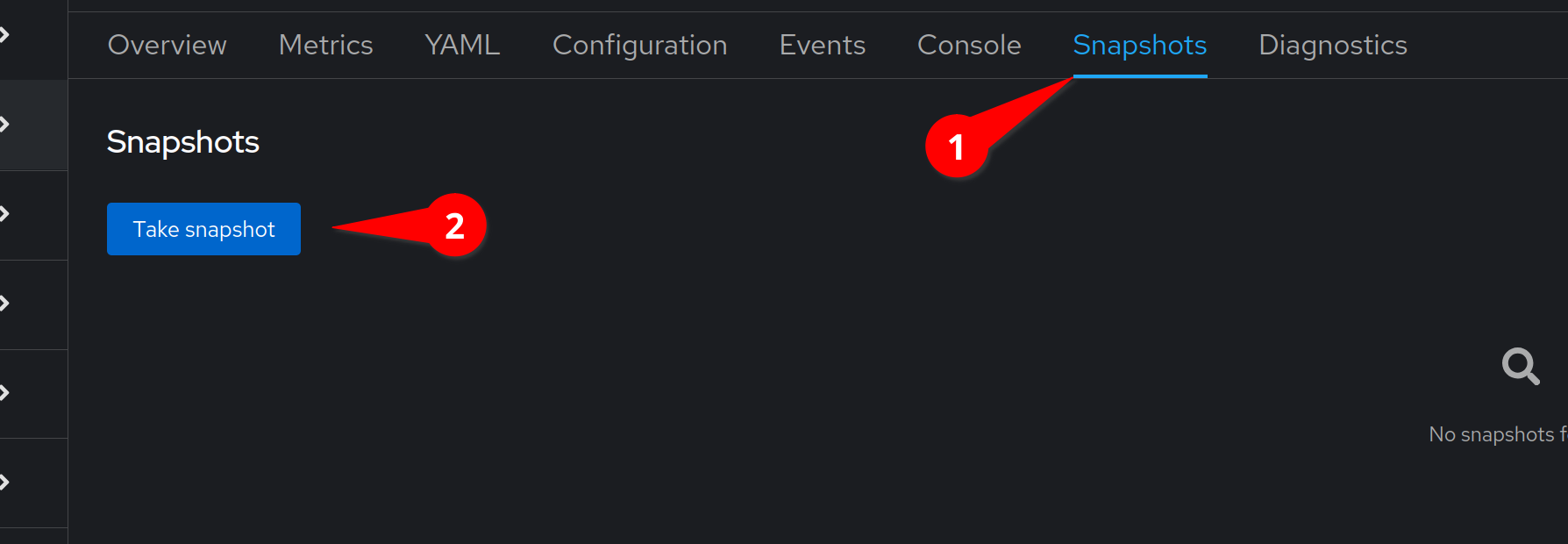
We can accept the default and select Save
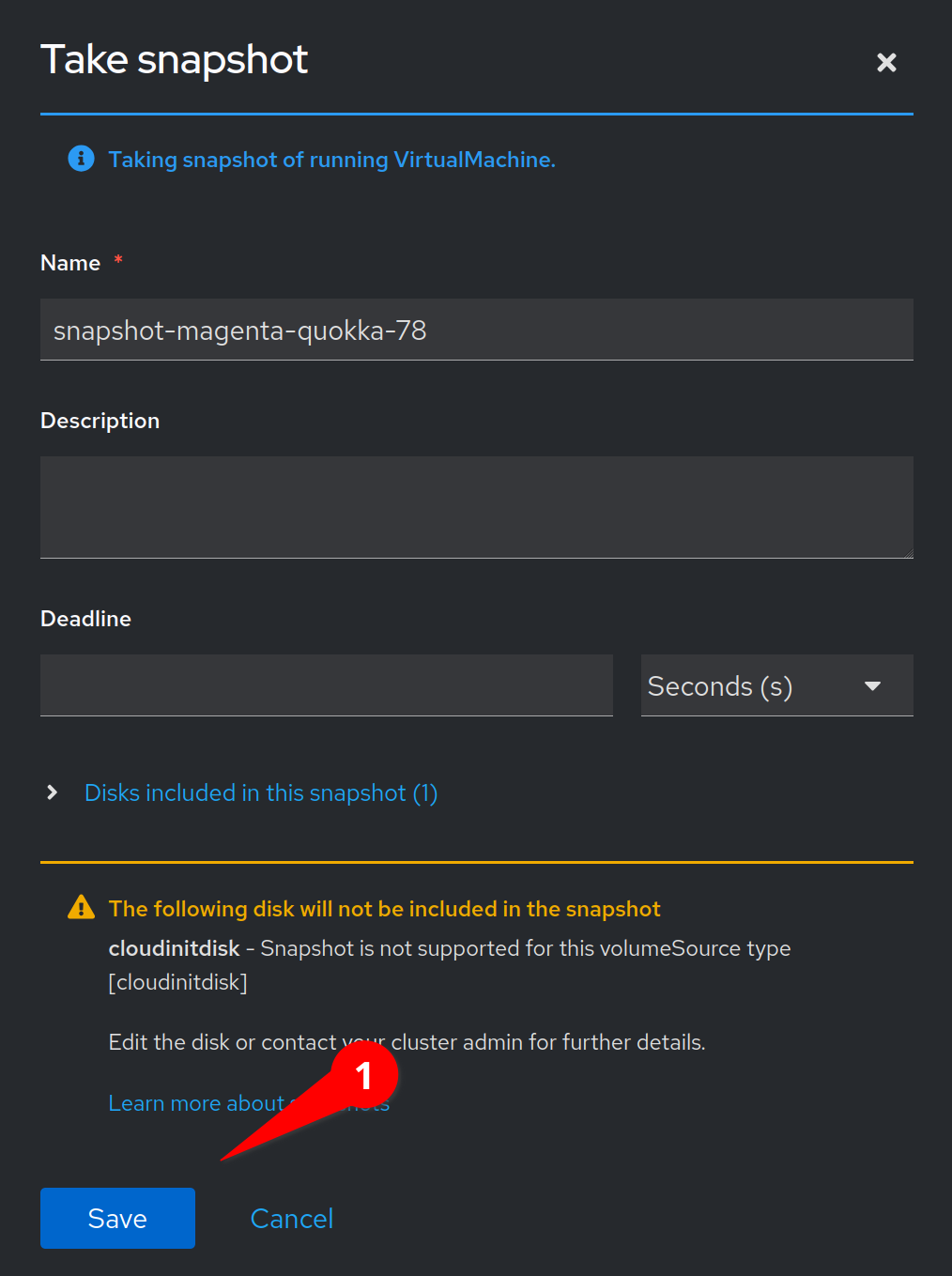
You will see a warning that our cloudinitdisk will not be included in this snapshot.
The cloudinitdisk is only used to configure our virtual machine and provide customizations.
We can safely ignore this warning.
|
Task 3: Make a change to our VM
Let’s switch back to the command line. To make a change, we are simply going to make a change to our running virtual machine.
Let’s accidently delete an important file:
virtctl ssh cloud-user@centos-stream9-snapshot -t "-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no" -c 'sudo rm /etc/fstab'Oh no! fstab is an important file for the operation of our linux system. We can verify that the file is indeed missing by running:
virtctl ssh cloud-user@centos-stream9-snapshot -t "-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no" -c 'cat /etc/fstab'Let’s fix our VM
Task 4: Restore our snapshot
Let’s log back in to the Openshift Console.
Click on the Virtualization menu item, followed by VirtualMachines.
We can then find the virtual machine we will be using for this snapshot.
Click on the VM labeled centos-stream9-snapshot.

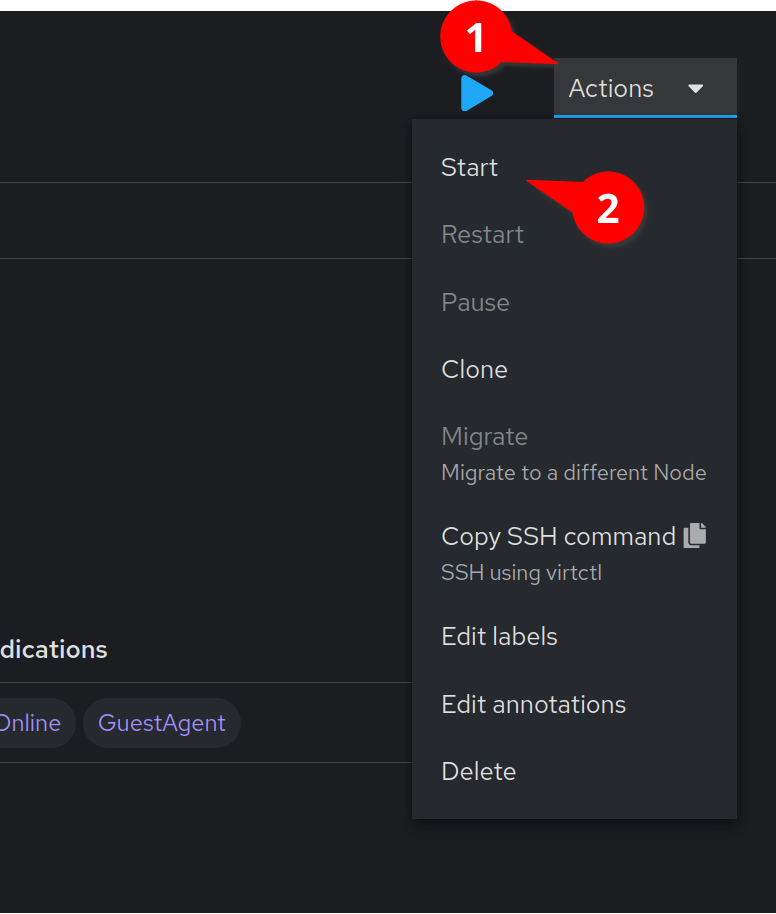
Click on the Actions menu, and select Stop
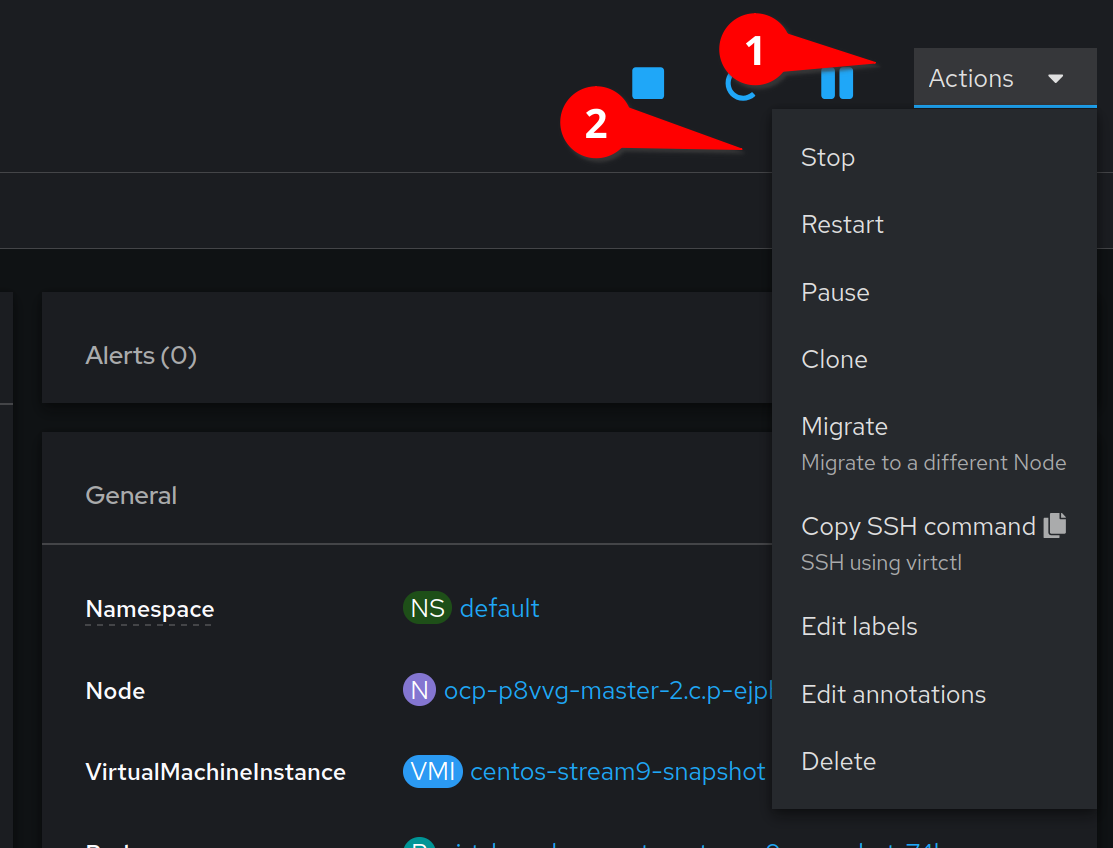
This will stop our running VM so that we can restore our snapshot.
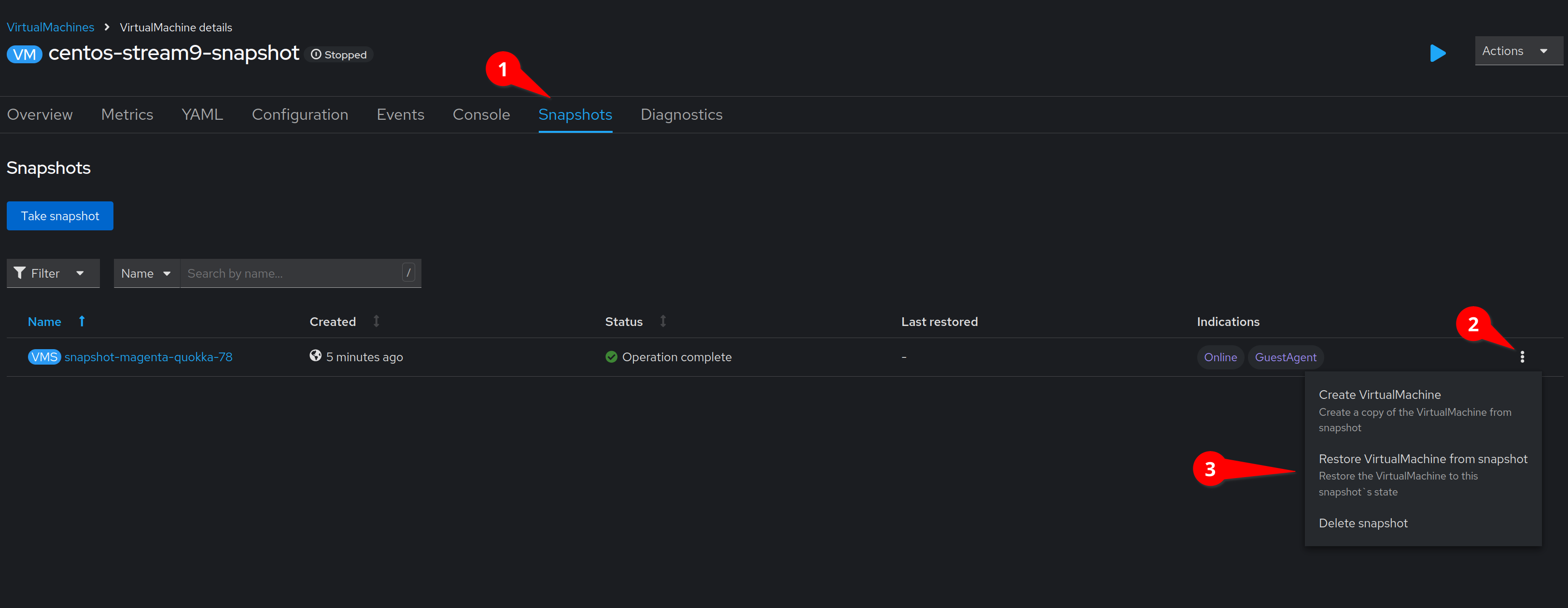
Click on the Snapshots tab.
Then click on the kebab menu by the snapshot we created earlier and click Restore VirtualMachine from snapshot
[!Important] Restoring a snapshot is a distructive operation as it discards all changes that were made to a virtual machine since the snapshot was taken. To avoid loosing data, it is possible to take a snapshot before restoring our virtual machine.
Confirm the restore by clicking the Restore button.
We can now start our virtual machine by clicking on the Action menu and clicking Start
We can check on the progress of our virtual machine’s boot by clicking on the Console or Overview tab.
Task 5: Verify our restore
After a couple of minutes, our VM should be running. Let’s verify that our fstab file is back in place:
virtctl ssh cloud-user@centos-stream9-snapshot -t "-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no" -c 'cat /etc/fstab'We can now see the contents of the fstab file!