Preparing for migrations
The installation of Ansible for OpenShift Virtualization Migration configured many of the primitives that are used to support the migration of Virtual Machines into OpenShift in an automated fashion.
As individual Migration Waves are defined and related applications are migrated into OpenShift, dedicated Projects/Namespaces are created to better organize and manage content. We saw this in prior exercises where a dedicated Project called vmexamples was used. To illustrate how the Ansible for OpenShift Virtualization Migration can be used to support migration activities, we will create a separate Project where we can demonstrate the capabilities of the Ansible for OpenShift Virtualization Migration.
Creating a Dedicated Project for Automation
Create a new Project called vmexamples-automation by navigating the OpenShift Web Console, expanding Home on the left hand navigation bar, and then selecting Projects.
Click the Create Project button and enter the name vmexamples-automation into the Name field. Feel free to optionally enter a Display name and Description. Click the Create button to create the new Project.
With a new Project in OpenShift created, let’s recall some of the steps that we preformed manually in the vmexamples project in prior exercises:
-
Creation of a
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionto enable connectivity of Virtual Machines to the previously created OVS bridge -
Creation of NetworkMaps and StorageMaps that are required to map source and destination Networks and Storage
Populating the Project
The activities that were previously performed manually can be automated with capabilities found within the Ansible for OpenShift Virtualization Migration.
Network Management
Nmstate is a declarative network manager and is responsible for many of the networking components of OpenShift and OpenShift Virtualization. Ansible for OpenShift Virtualization Migration includes functionality to automate the network configurations from a VMware environment or to define explicitly how networking configurations, like NetworkAttachmentDefinition resources are created in OpenShift.
An Ansible Automation Platform Job Template was created during the provisioning of the Ansible for OpenShift Virtualization Migration in the prior section to manage NMstate configurations.
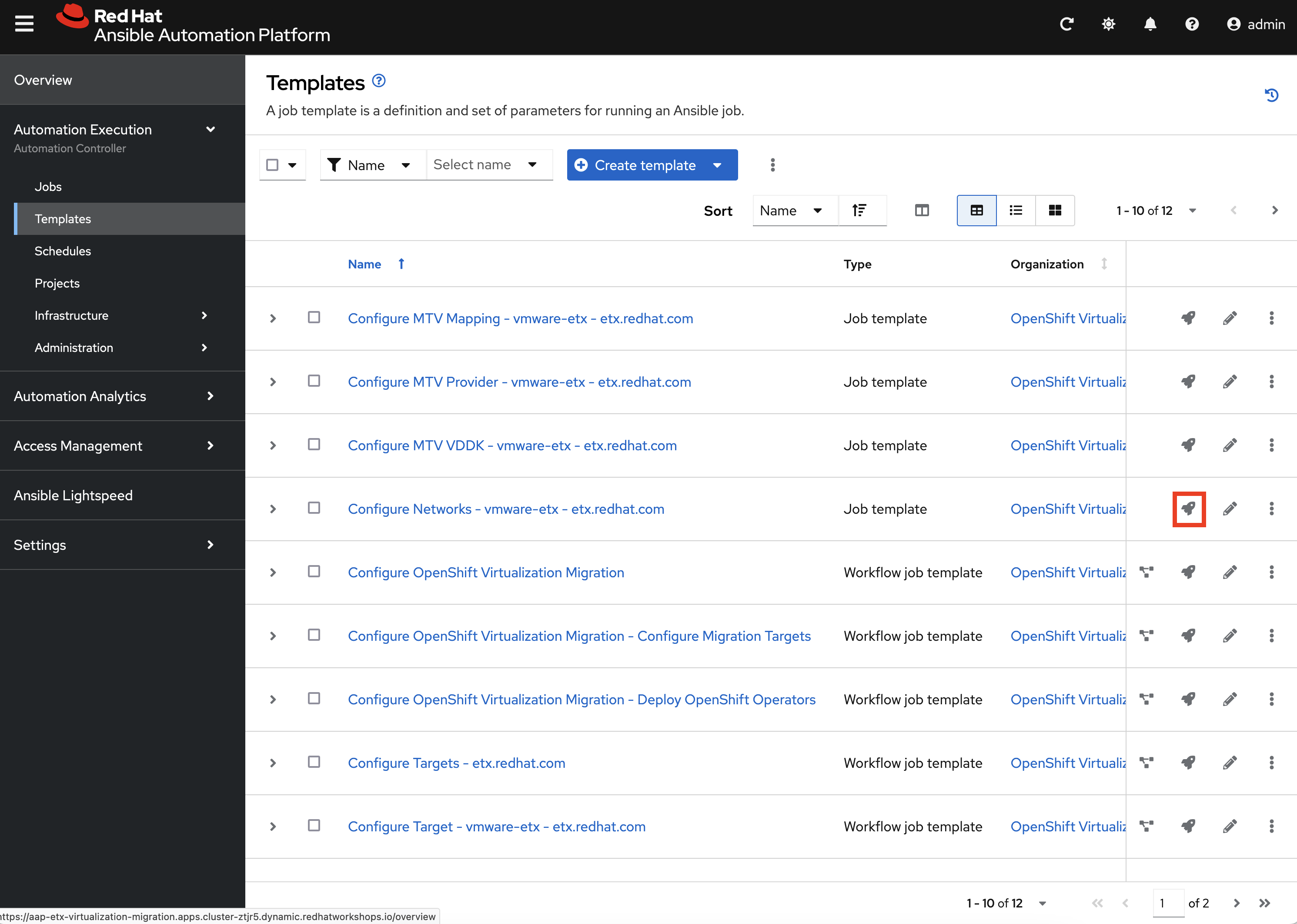
Open a web browser and navigate to Ansible Controller, expand Automation Execution and select Templates.
Locate the Job Template named Configure Networks - vmware-etx - etx.redhat.com and select the rocket icon.
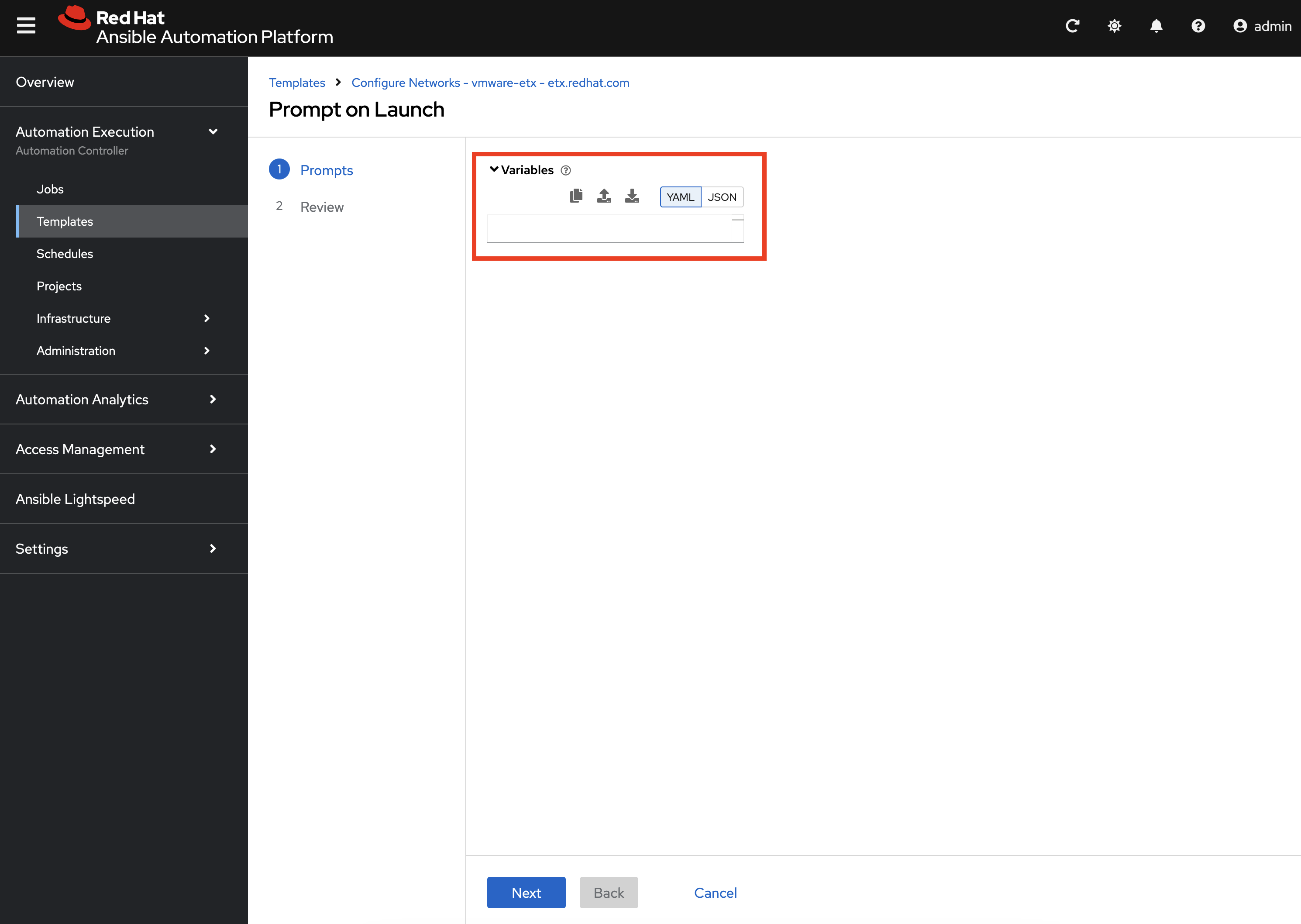
This job template is configured to allow additional variables to be specified at launch time. Since the ETX OpenShift environment includes a customized network set up, we will define how the automation creates the associated Nmstate resources.
Enter the following into the Variables dialog:
network_mgmt_manual_localnet_name: localnet2 (1)
network_mgmt_openshift_network_bridge_mode: ovs-bridge (2)
network_mgmt_manual_nad_list:
- name: vlan5 (3)
portgroup: segment-migrating-to-ocpvirt (4)
namespace: vmexamples-automation (5)
trunk: false (6)
vlan:
vlan_id: 0 (7)| 1 | Name of the localnet as seen in the NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy |
| 2 | Bridge Mode type |
| 3 | Defining the NetworkAttachmentDefinition resources to create |
| 4 | Port group to associate |
| 5 | Namespace the NetworkAttachmentDefinition will be created in. If omitted, the default namespace will be used |
| 6 | Must either be omitted or set to false |
| 7 | Setting this value to 0 will omit the vlan configuration from being defined |
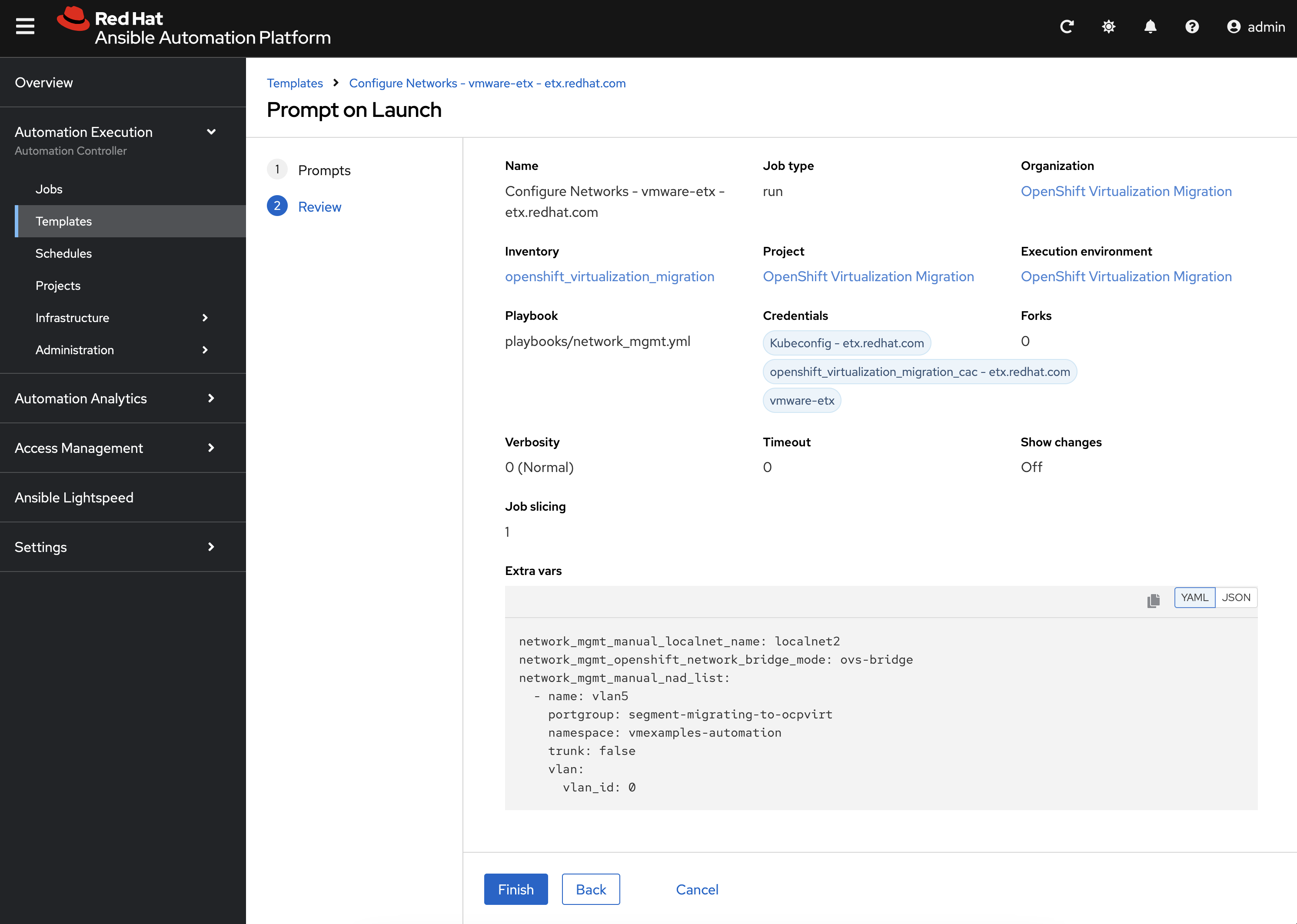
Click Next to review the settings.
Click Finish to launch the Job Template.
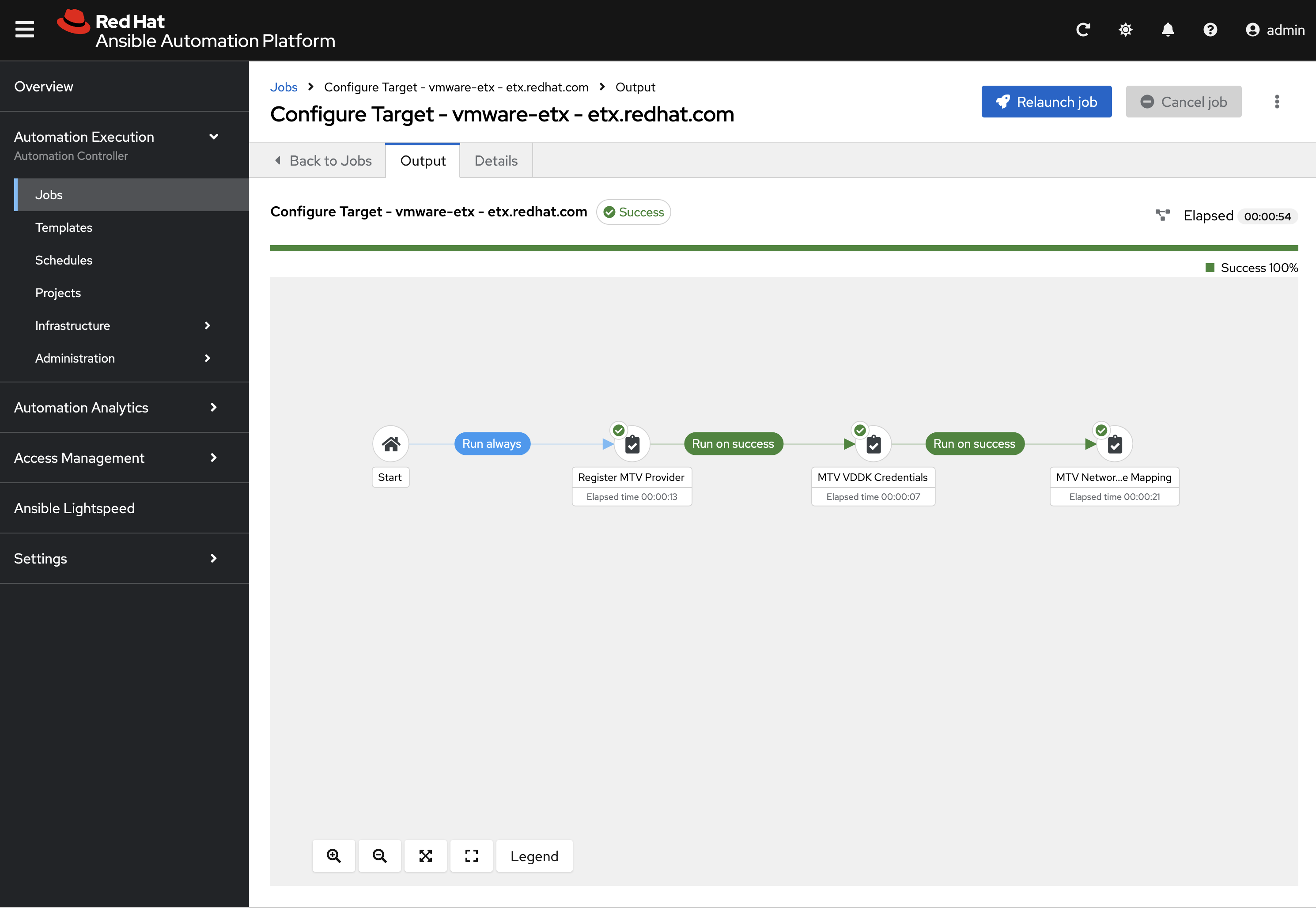
Monitor the output from the execution of the Job and confirm that it has completed successfully. Once complete a NetworkAttachmentDefinition will be created in the vmexamples-automation namespace.
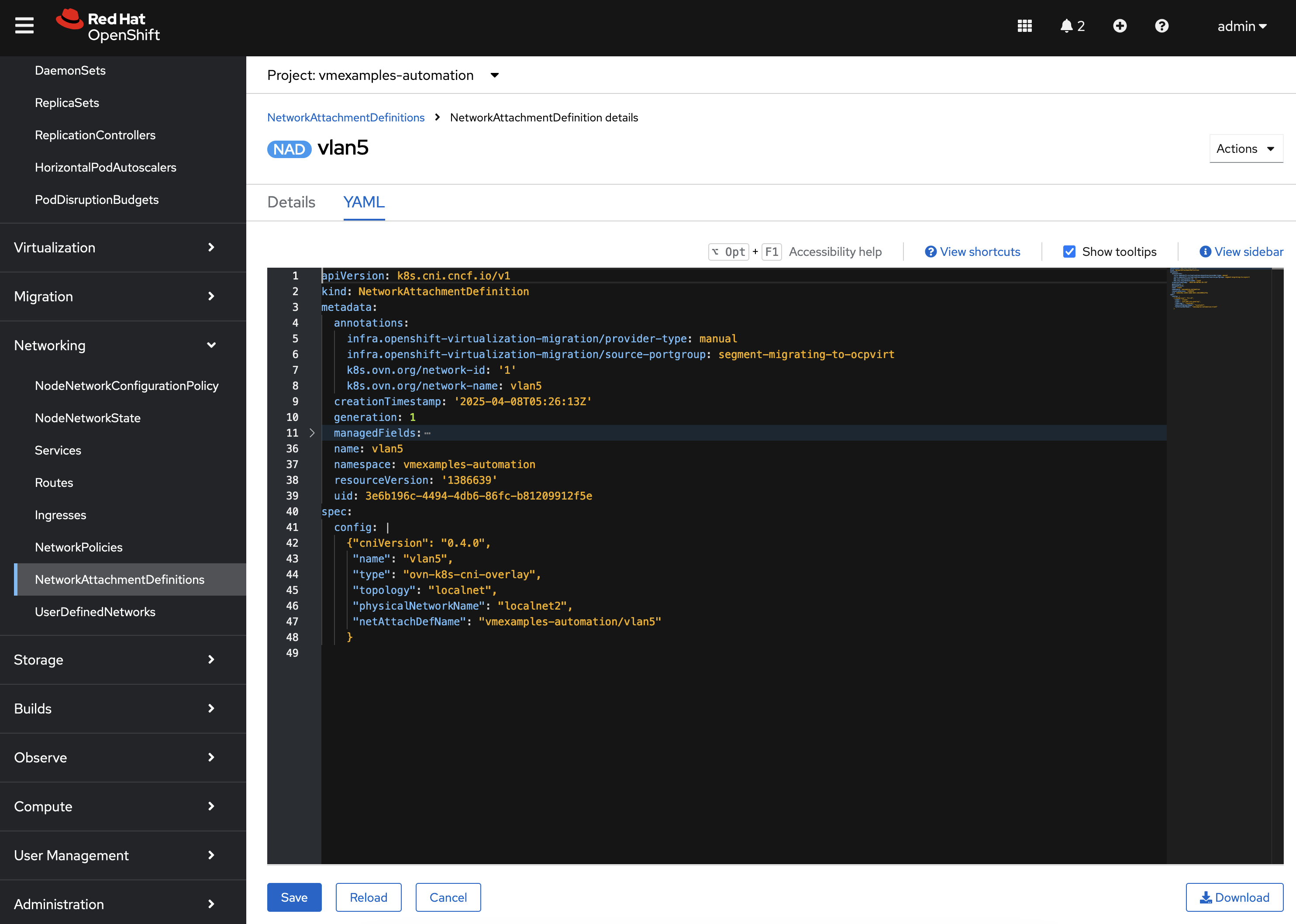
Confirm the NetworkAttachmentDefinition was created by navigating to the OpenShift Web Console and under Networking on the left hand navigation bar, select NetworkAttachmentDefinition.
Confirm a NetworkAttachmentDefinition called vlan5 has been created in the vmexamples-automation Namespace with the parameters that were provided in the Job Template launch dialog.
StorageMaps and NetworkMaps
To migrate Virtual Machines using the Migration Toolkit for Virtualization (MTV), StorageMaps and NetworkMaps must be present within the Namespace the Plans and Migration resources will be created within.
In the prior section when the Ansible for OpenShift Virtualization Migration was deployed a set of activities were performed including the creation of StorageMaps and NetworkMaps within the openshift-mtv Namespace. The creation of these resources leverage information from the source and destination environments which has been captured and stored within the MTV Inventory.
Similar to the management of Nmstate resources, the creation of StorageMap and NetworkMap resources can be customized and their configurations can be influenced to achieve the desired results.
A Workflow Job Template called Configure Target - vmware-etx - etx.redhat.com is available to initialize individual Namespaces, such as the vmexamples-automation Namespace, with the remaining set of resources the is needed to support Migration activities including the NetworkMaps, StorageMaps, and credentials for the VDDK image.
Navigate to Ansible Automation Platform and select Templates underneath the Automation Execution section of the left hand navigation bar.
Click the Rocket icon next to the Configure Target - vmware-etx - etx.redhat.com Workflow Job Template which, like the Nmstate Job Template, allow for additional Ansible variables to be specified.
Within the Variables dialog, specify the mtv_management_migration_namespace variable to be vmexamples-automation so that any of the resources that are to be created are created within this namespace instead of the default openshift-mtv Namespace as shown below:
mtv_management_migration_namespace: vmexamples-automationClick Next to review the settings and then Finish to launch the Job Template.
Review the resources that were created in OpenShift by navigating back to the OpenShift Console.
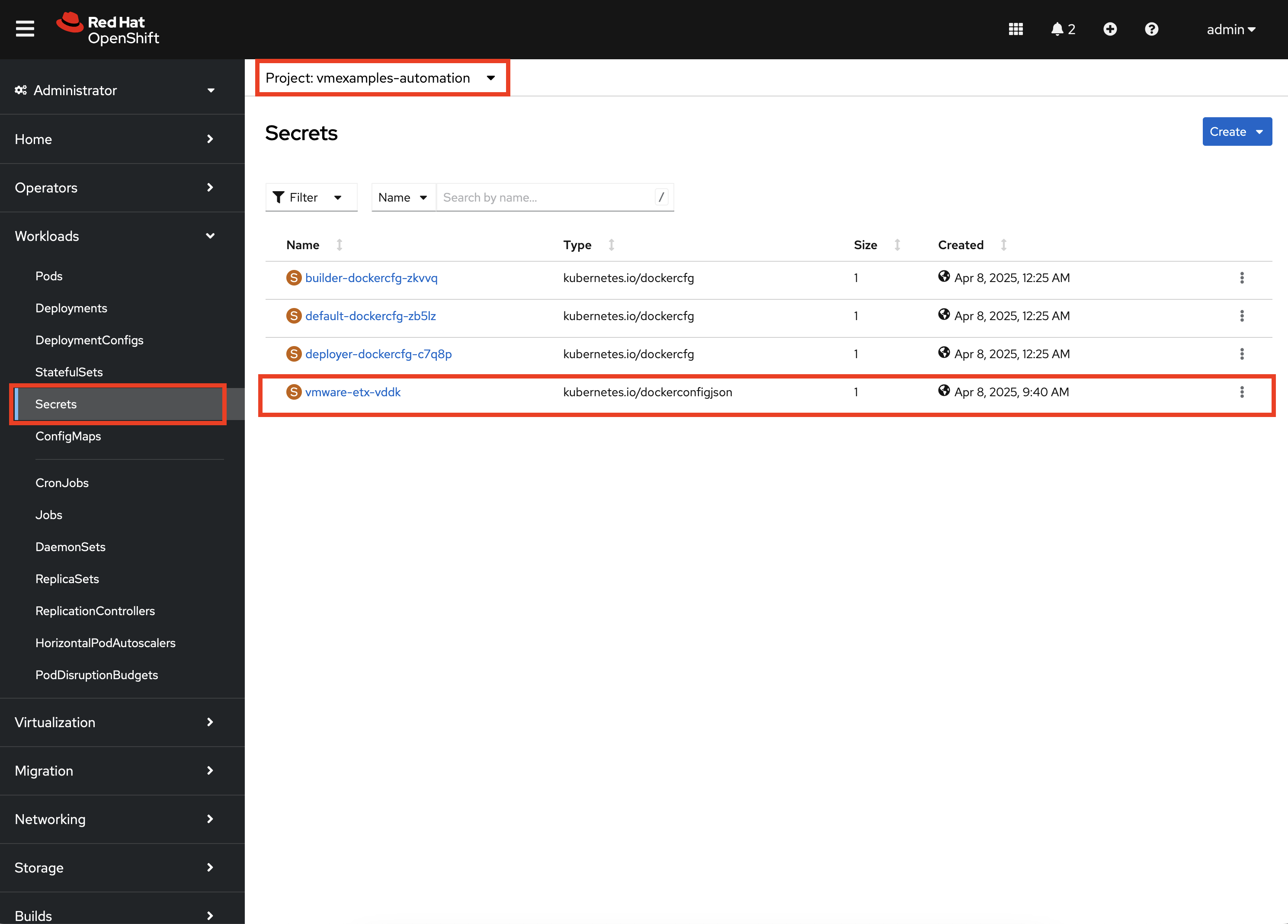
On the left hand navigation bar, expand Workloads and select Secrets. Confirm that you are in the vmexamples-automation namespace by confirming that the vmexamples-automation Project is selected at the Project dropdown at the top of the screen.
Confirm the vmware-etx-vddk Secret is present in the namespace.
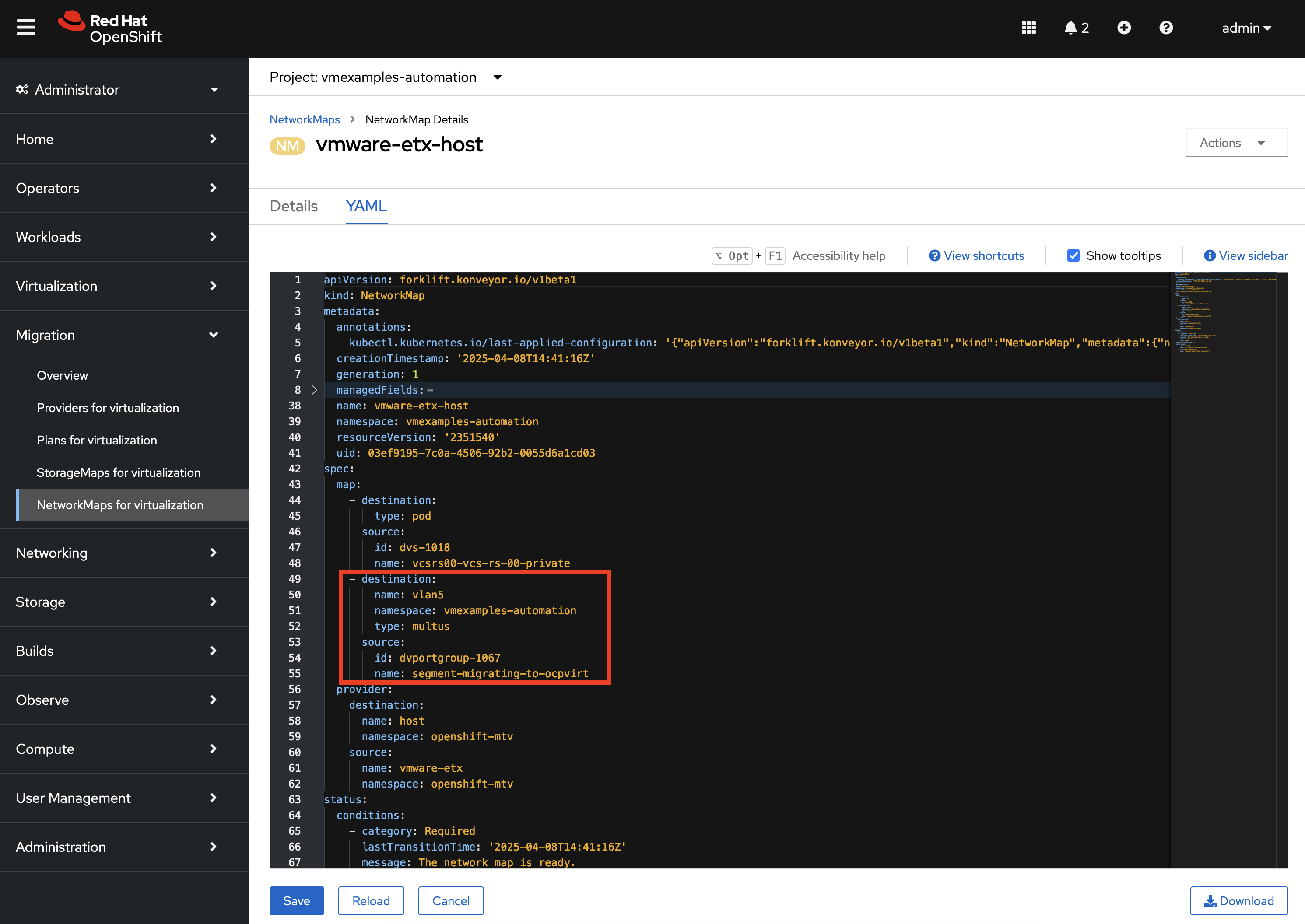
Review the NetworkMaps and StorageMaps that were also created in the vmexamples-automation Namespace. If you look at the vmware-etx-host NetworkMap within the NetworkMaps for Virtualization page under the Migration section of the left hand navigation bar, select the YAML tab to view the details of the resource.
Notice how the NetworkMap was configured with the connection to the NetworkAttachmentDefinition automatically. This is due an annotation present on the NetworkAttachmentDefinition matching the name of the VMware network that is being mapped.
The vmware-etx-host StorageMap on the NetworkMaps for Virtualization page was configured with the connection to the ocs-external-storagecluster-ceph-rbd as it is the default StorageClass in the cluster.
Thanks to the Ansible for OpenShift Virtualization Migration, many of the steps that were previously configured manually have now been automated.