Section 6 - Summary and Call to Actions
What You Accomplished
Throughout this lab, you experienced the power of AI-driven automation across two domains:
Summary of Job Templates
Here’s a recap of the job templates and rulebooks used in the lab: (in chronological order):
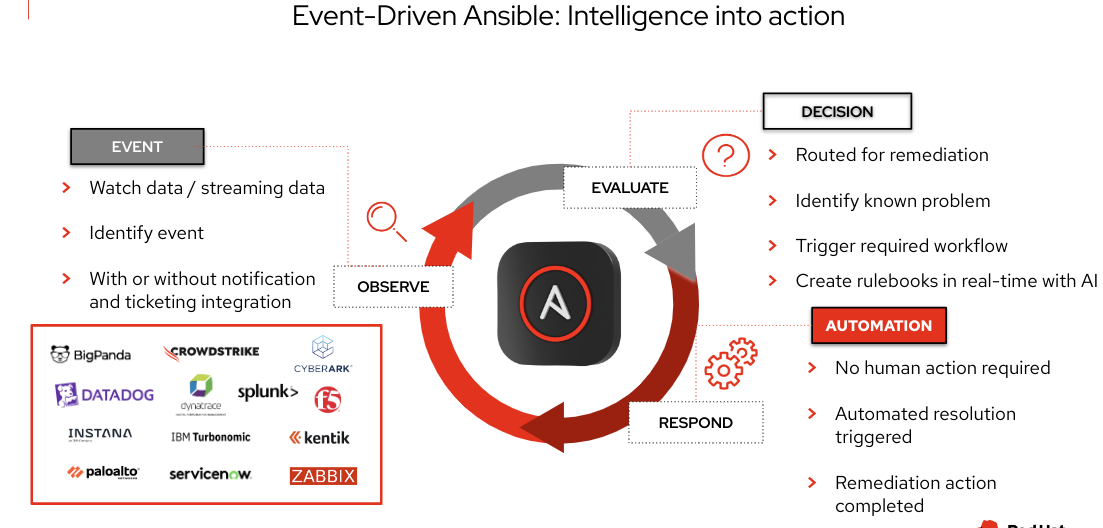
Glossary:
RB = Rulebook (for Event-Driven Ansible) JT = Job Template (for executing Ansible Playbooks)
Name |
Purpose |
|
JT simulates a failure in the Apache config |
|
RB that watches Kafka queue for httpd disruption |
|
JT that checks the current state of Apache |
|
JT that uses RHEL AI to understand the error |
|
JT sends incident details to a chat system |
|
JT that creates a JT to generate playbooks |
|
JT that uses Lightspeed to generate the fix |
|
JT pushes the generated playbook to Git |
|
Workflow node that syncs Gitea project with dynamically created playbooks |
|
JT that creates another JT to apply the AI-generated fix |
|
JT for Final fix (launched manually) |
|
JT that Restores Apache to a known-good config |
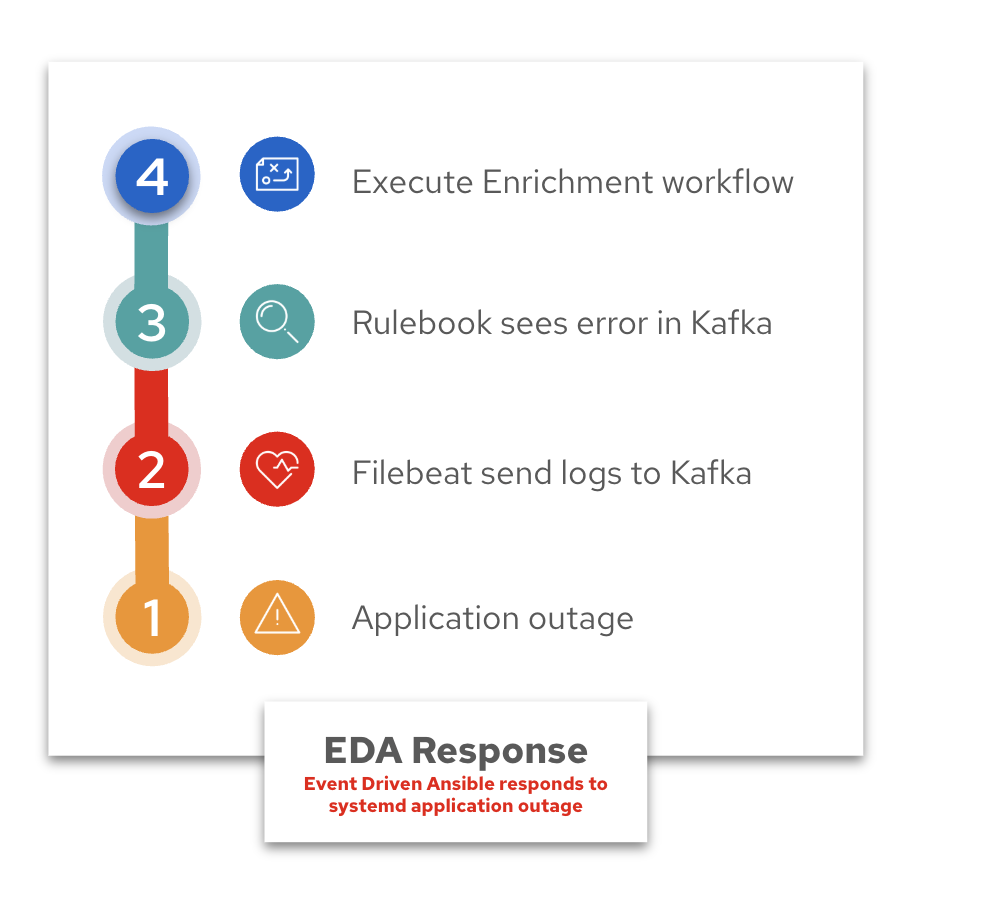
Now here is a walkthrough in the same chronological order:
❌ Break Apache
Purpose: Introduces a known bad directive in /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf to cause Apache failure
What happens next:
-
Filebeat detects the service issue
-
Kafka forwards the event
-
EDA rulebook matches and triggers
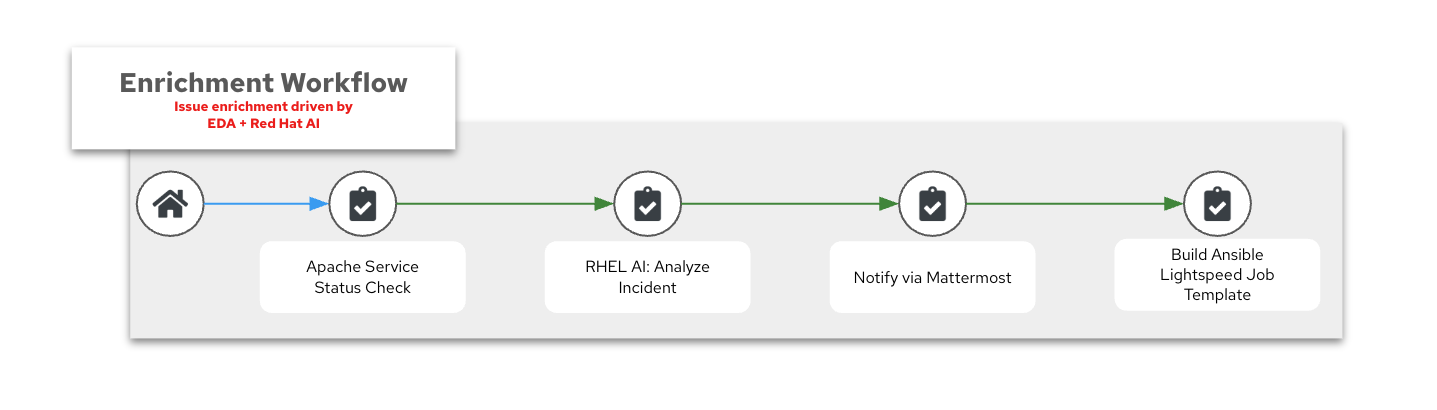
AI Insights and Lightspeed prompt generationworkflow
Ansible Playbook: Github Link
AI Insights and Lightspeed prompt generation workflow
Also known as the Enrichment Workflow for short!
⚙️ Apache Service Status Check
Purpose: Checks whether Apache is active and logs its status.
What it does:
-
Runs
systemctl status httpd -
Collects output and logs it
-
Output is consumed by the next steps (Red Hat AI and Mattermost)
Ansible Playbook: Github Link
🤖 RHEL AI: Analyze Incident
Purpose: Uses Red Hat AI inference service to understand the failure message.
What it does:
-
Sends logs
-
Returns a natural-language description of the error
-
Suggests what kind of automation could fix it
Ansible Playbook: Github Link
📣 Notify via Mattermost
Purpose: Sends a human-readable incident message to a Mattermost channel.
What it does:
-
Formats the AI response and Apache status
-
Pushes it to a channel using Mattermost Webhook
-
Simulates integration with a real ITSM tool like ServiceNow
Ansible Playbook: Github Link
⚙️ Build Ansible Lightspeed Job Template
Purpose: Creates a new job template for the second workflow
What it does:
-
Create a job template with a survey that includes:
-
A user-defined prompt field
-
A pre-filled prompt from Red Hat AI output
-
Why this is important:
This allows Ansible Lightspeed to generate a remediation playbook without writing code manually. The job template created here will be used in the second workflow.
Ansible Playbook: Github Link
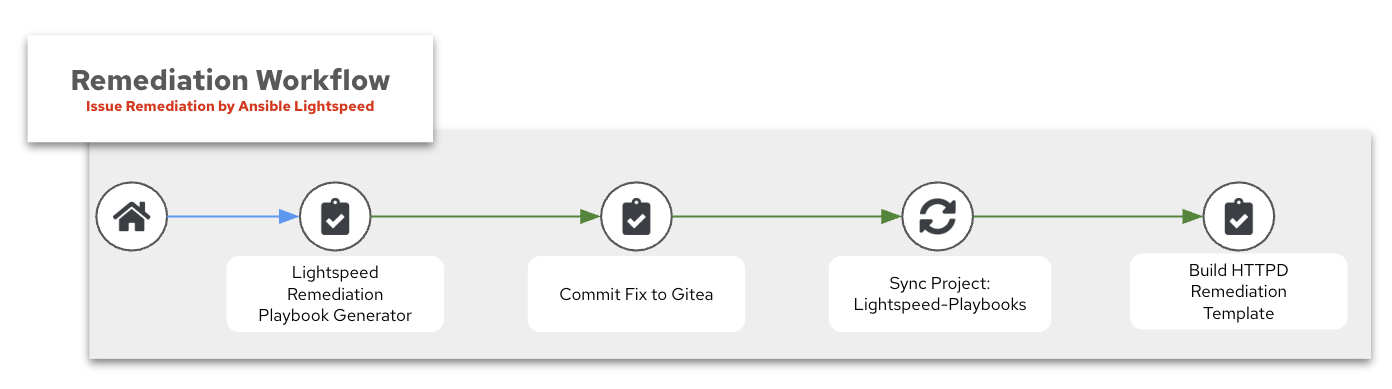
Remediation Workflow
🧠 Lightspeed Remediation Playbook Generator
Purpose:
Runs the job template created in the previous workflow AI Insights and Lightspeed prompt generation to generate a playbook from the AI prompt.
What it does:
-
Uses Lightspeed to turn a prompt into a YAML playbook
-
Stores the result locally as
lightspeed-response.yml
Ansible Playbook: Github Link
🧾 Commit Fix to Gitea
Purpose: Pushes the generated playbook to the Gitea Git repository.
What it does:
-
Authenticates with Gitea
-
Commits
lightspeed-response.yml -
Makes the playbook available for automation use
Ansible Playbook: Github Link
Sync Project to Lightspeed-Playbooks
Purpose: Syncs the git project from Gitea to Ansible Automation Platform
💡 This is not a Job Template, but a built-in node that will sync Git projects within the workflow visualizer
⚙️ Build HTTPD Remediation Template
Purpose: Creates a new job template that uses the playbook pushed by Ansible Lightspeed to fix the Apache (httpd) service.
What it does:
-
Creates a new Job Template called
Execute HTTPD Remediation -
Uses the dynamically generated
lightspeed-response.ymlplaybook -
Sets up the credentials, inventory and prompt for limit
Ansible Playbook: Github Link
Execute HTTPD Remediation
Purpose Fix httpd on the RHEL webserver
What is does
-
Removes the bad syntax from the httpd configuration file
-
Restarts the httpd service
Ansible Playbook: This Job Template is dynamically generated from Ansible Lightspeed and stored in your Gitea instance. The Ansible Playbook should look similar to this:
- name: Fix httpd
become: true
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Remove line that contains InvalidDirectiveHere
ansible.builtin.lineinfile:
path: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
regexp: ^InvalidDirectiveHere
state: absent
- name: Restart httpd
ansible.builtin.service:
name: httpd
state: restarted✅ Restore Apache
Purpose
If you want to return Apache to a good state (without running AIOps workflows), you can run the ✅ Restore Apache job template.
What it does
-
Should be mostly identical to what you see above for the
Execute HTTPD Remediation
Ansible Playbook: Github Link
Part 2: Network Automation Playbooks
Network-AIOps-Workflow Overview
The network automation portion of this lab follows the same AIOps principles as Part 1, but applies them to Cisco router OSPF troubleshooting scenarios.
Network-Router-Setup
Purpose: Configures the initial OSPF setup on both Cisco routers and enables syslog forwarding to Splunk.
What it does:
-
Establishes OSPF routing on Tunnel0 interfaces
-
Configures syslog forwarding to Splunk on TCP port 5514
-
Sets up the baseline OSPF neighbor adjacency
Ansible Playbook: Github Link
Network EDA Response
OSPF Neighbor
Purpose: Listens for OSPF neighbor state changes from Splunk webhook alerts.
What it does:
-
Monitors TCP port 5000 for webhook events
-
Triggers when search_name matches 'ospf-neighbor'
-
Launches the Network-AIOps-Workflow with webhook payload
Ansible Rulebook: Github Link
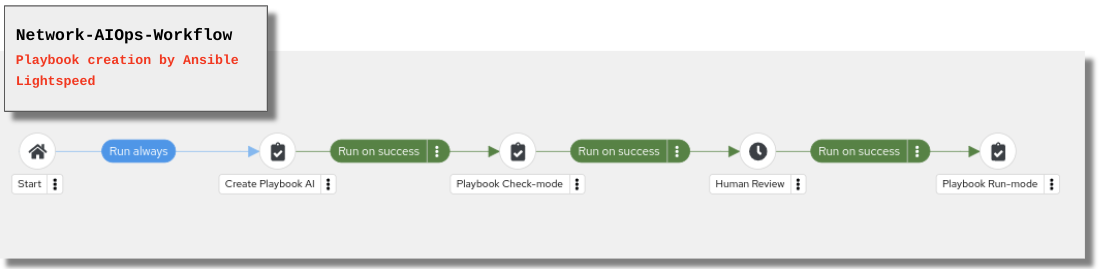
Network-AIOps-Workflow
This workflow is triggered by the OSPF Neighbor rulebook activation when an OSPF adjacency fails.
Create Playbook AI
Purpose: Uses Ansible Lightspeed to generate a network remediation playbook based on the OSPF failure scenario.
What it does:
-
Receives the webhook payload containing OSPF event details
-
Constructs a detailed prompt for Ansible Lightspeed that includes:
-
Scenario-specific troubleshooting logic (interface status, network type, hello timers)
-
Cisco IOS command requirements
-
Conditional checks for different failure modes
-
-
Generates a playbook with tasks to diagnose and fix the specific OSPF issue
-
Commits the generated playbook to Gitea as
lightspeed-response.yml
Ansible Playbook: Github Link
Sync Project to Lightspeed-Playbooks
Purpose: Syncs the Gitea project containing the AI-generated network playbook to Ansible Automation Platform.
This is a built-in workflow node that performs a Git sync operation.
Playbook-Check-Mode
Purpose: Runs the AI-generated playbook in check mode to preview changes before applying them to production routers.
What it does:
-
Executes the
lightspeed-response.ymlplaybook with--checkflag -
Shows what changes would be made to the router configuration
-
Allows human review of AI-generated changes before actual execution
-
Pauses the workflow for approval
Why this is important:
Network changes can have significant impact. Running in check mode first provides a safety gate to validate the AI-generated remediation before applying it.
Playbook-Run-Mode
Purpose: Applies the validated remediation to fix the OSPF neighbor adjacency issue.
What it does:
-
Executes the same
lightspeed-response.ymlplaybook without check mode -
Makes actual configuration changes to cisco-rtr1
-
Restores OSPF neighbor adjacency based on the failure scenario:
-
Scenario 1: Brings up the shutdown Tunnel0 interface
-
Scenario 2: Corrects the OSPF network type to point-to-point
-
Scenario 3: Fixes the OSPF hello timer interval
-
Example AI-Generated Playbook (Scenario 1 - Interface Shutdown):
- name: OSPF Neighbor Remediation
hosts: all
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: Check if Tunnel0 interface is administratively down
cisco.ios.ios_command:
commands:
- show ip interface brief | include Tunnel0
register: interface_status
- name: Bring up Tunnel0 interface if down
cisco.ios.ios_config:
lines:
- no shutdown
parents:
- interface Tunnel0
when: "'administratively down' in interface_status.stdout[0]"
- name: Verify OSPF neighbor adjacency
cisco.ios.ios_command:
commands:
- show ip ospf neighbor
register: ospf_neighborNetwork Remediation Summary
The network automation workflows demonstrate:
-
Observability: Splunk captures syslog messages from Cisco routers
-
Inference: Ansible Lightspeed generates scenario-specific remediation playbooks
-
Automation: Event-Driven Ansible triggers workflows that validate (check mode) and execute (run mode) fixes
This creates a complete closed-loop automation system for network troubleshooting that codifies expert knowledge into reusable, AI-generated playbooks.
Call to action
Here are some recommended next steps in your Ansible AIOps journey:
-
-
Check out the AI + Ansible YouTube playlist
-
-
Check out developers.redhat.com and get a home lab license.
Are you ready to implement now? - Contact Red Hat