Security and Compliance
Introduction
The Mega-Sale was a success, but now, a critical security audit is looming. We need to demonstrate strict adherence to industry compliance standards for all our virtualized workloads. Our challenge is to ensure a unified approach to security across both VMs and containers. In this module we will be tasked with scanning our infrastructure with the OpenShift Compliance Operator and remediating any reported vulnerabilities to ensure that our cluster meets our strict security standards. We will also configure distinct user accounts and access roles for members of our team that need limited access to our virtualization infrastructure.
Scanning Infrastructure with the OpenShift Compliance Operator
This section of our lab will focus on making use of the OpenShift Compliance Operator to configure security scans in your OpenShift cluster. The compliance operator can help ensure that the hosts in your OpenShift environment meet specific security standards, and are deployed to meet those standards.
-
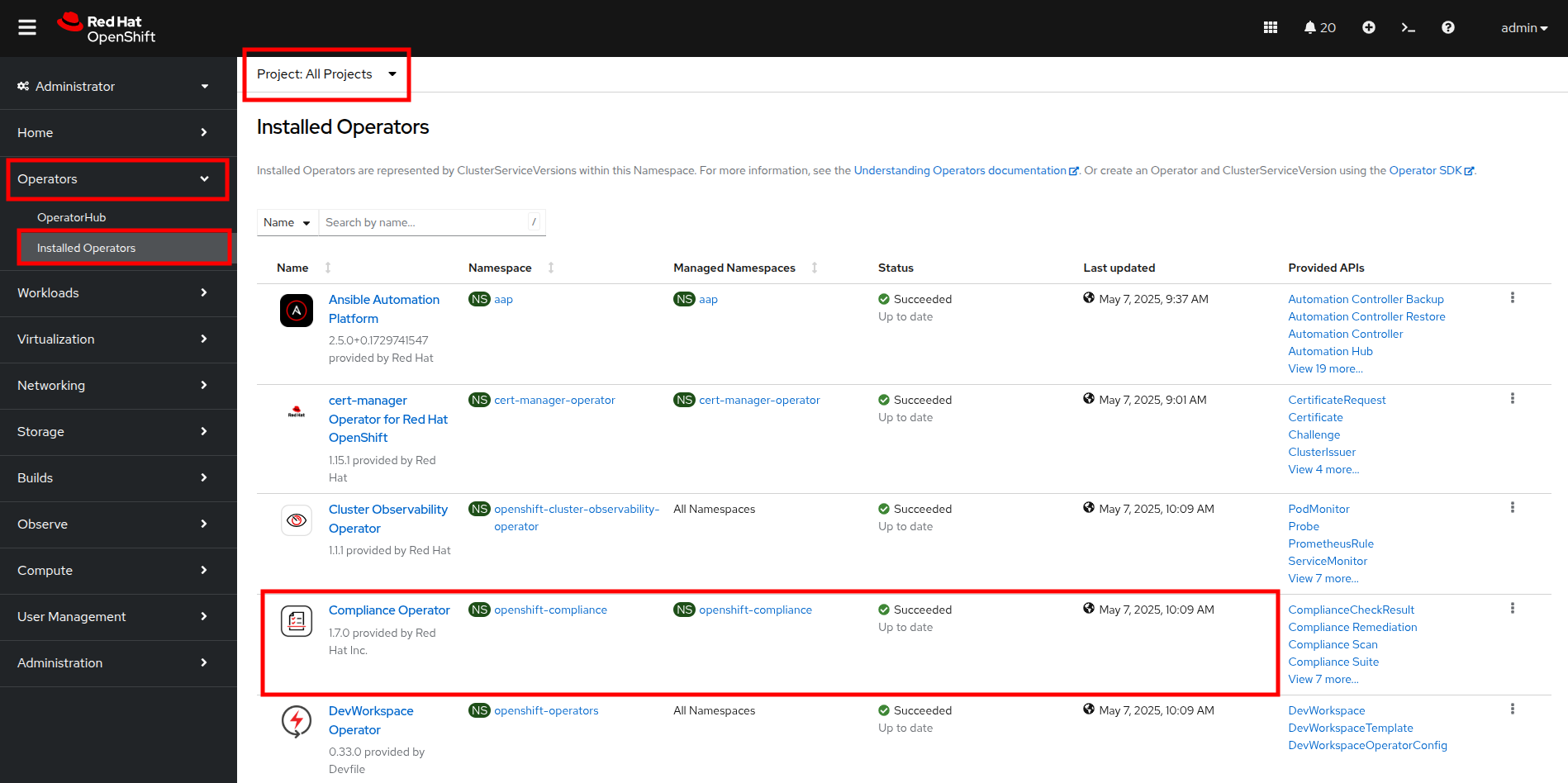
Select Operators and then Installed Operators from the left side navigation menu, confirm that you have selected All Projects and select the Compliance Operator.
-
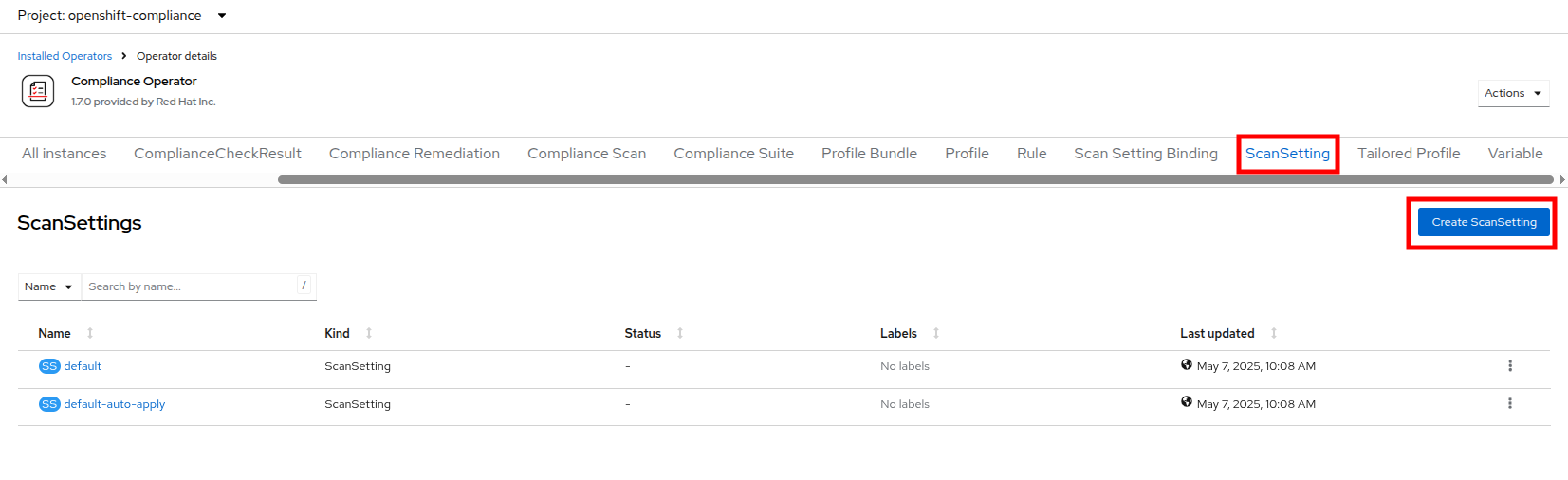
This takes you to the Operator details page, use the horizontal scrollbar to move across and locate the ScanSetting tab.
-
Click the Create ScanSetting button.
-
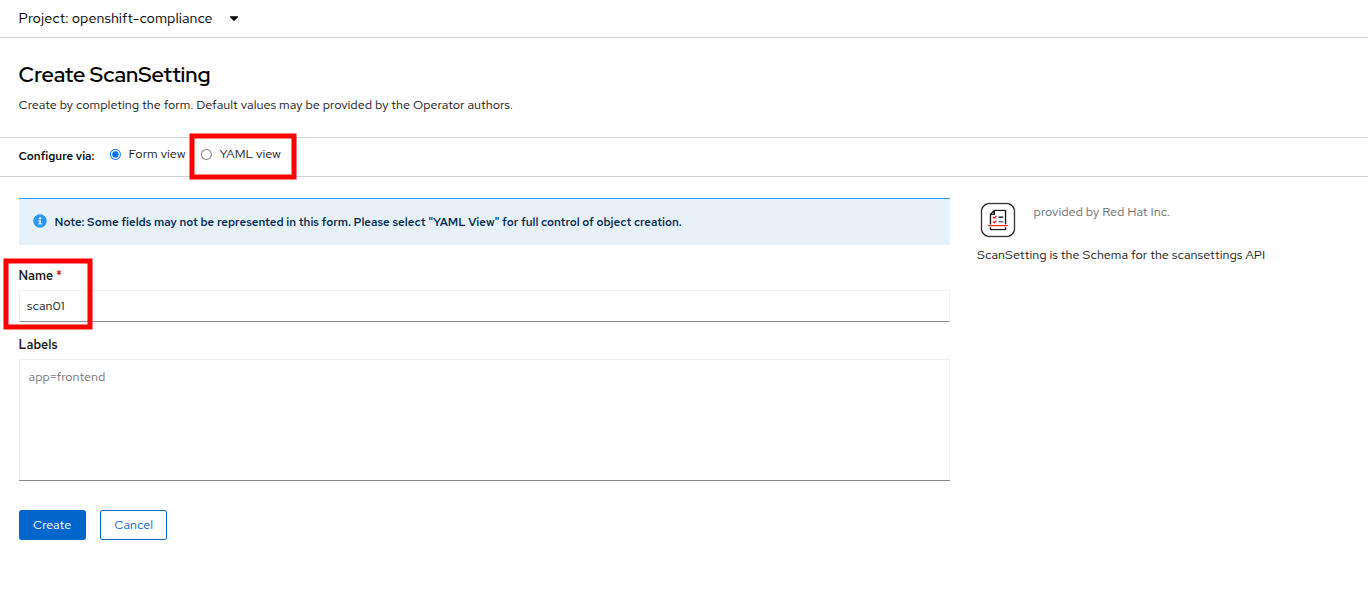
On the Create ScanSetting page, set the name of the scan to
scan01. Then click the YAML view radio button. -
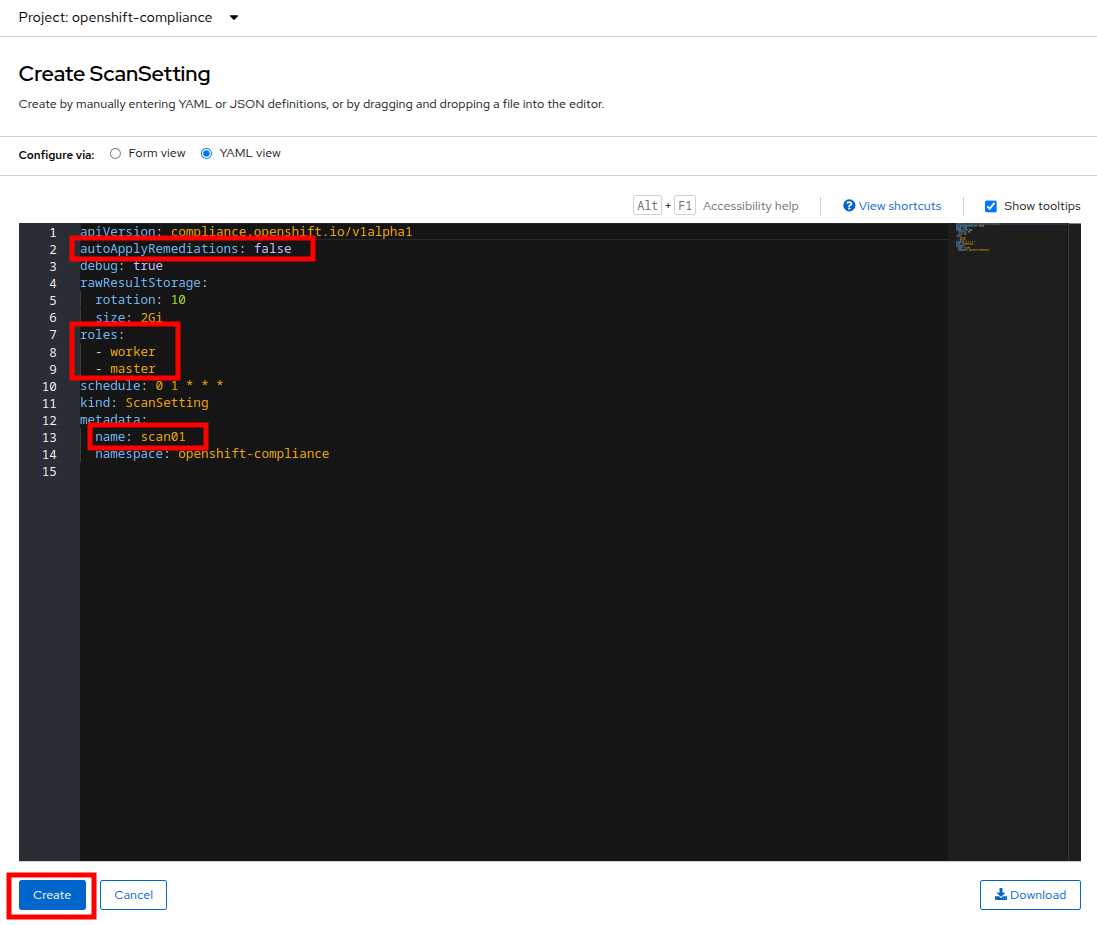
In the ScanSetting YAML details, make note of the following values that are set by default:
-
The autoApplyRemediations field is set to false.
-
The roles to be scanned by default include both worker and master nodes.
-
The name field is set to scan01 which you entered on the form view.
-
-
Click the Create button to create this simple scansetting definition.
-
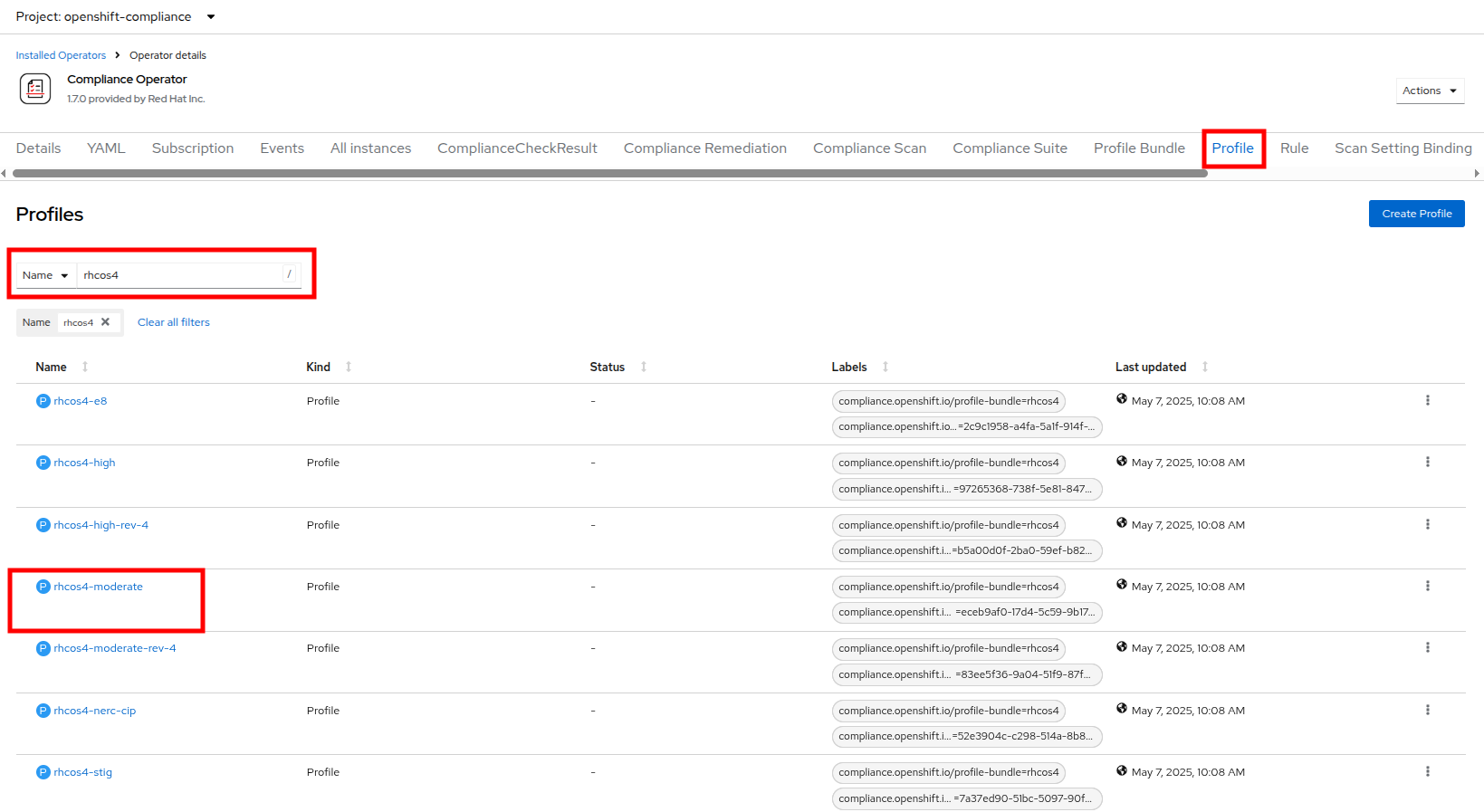
Now click on the Profile tab where there are a number of pre-defined scanning profiles.
-
In the search box, type
rhcos4and locate the FedRamp moderate profile rhcos4-moderate in the list. -
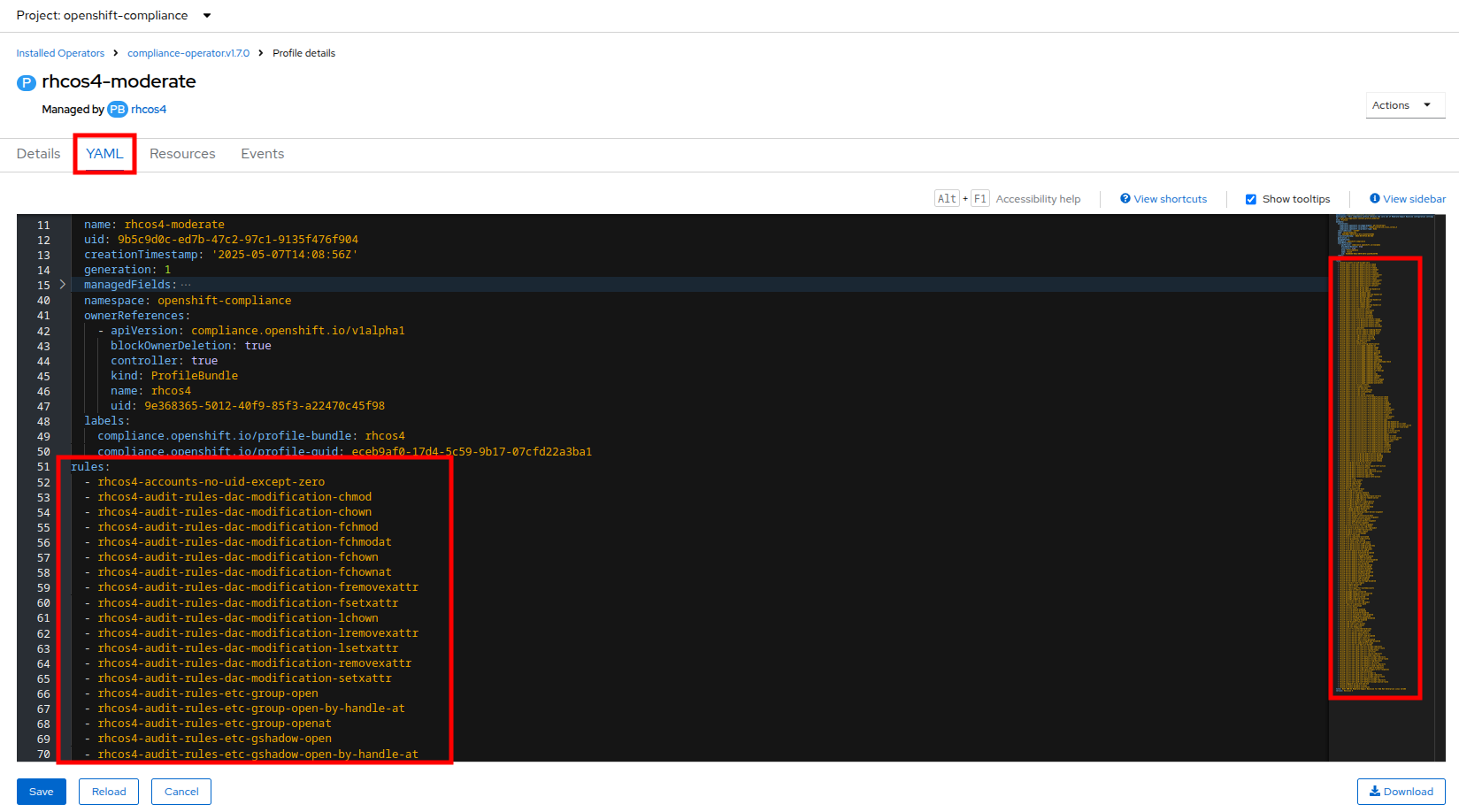
Click on rhcos4-moderate and then on the YAML. Scroll down the output to browse the rules that are enforced as a part of this scan. A quick glimpse at the side panel shows that there are quite a few of them.
-
When you are done reviewing the rules, return to the Operator details page by clicking your browser’s back button twice.
Additional details on the profiles available can be found here. -
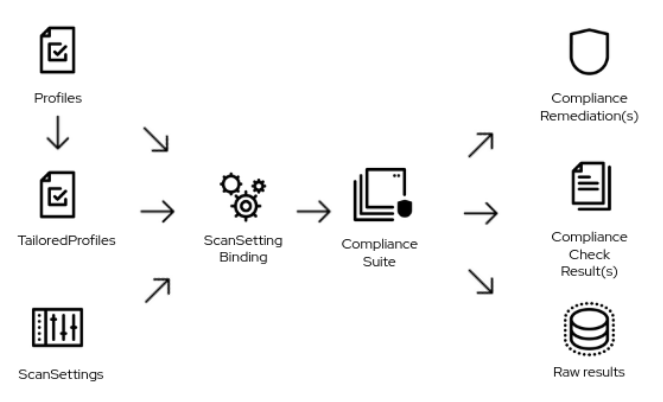
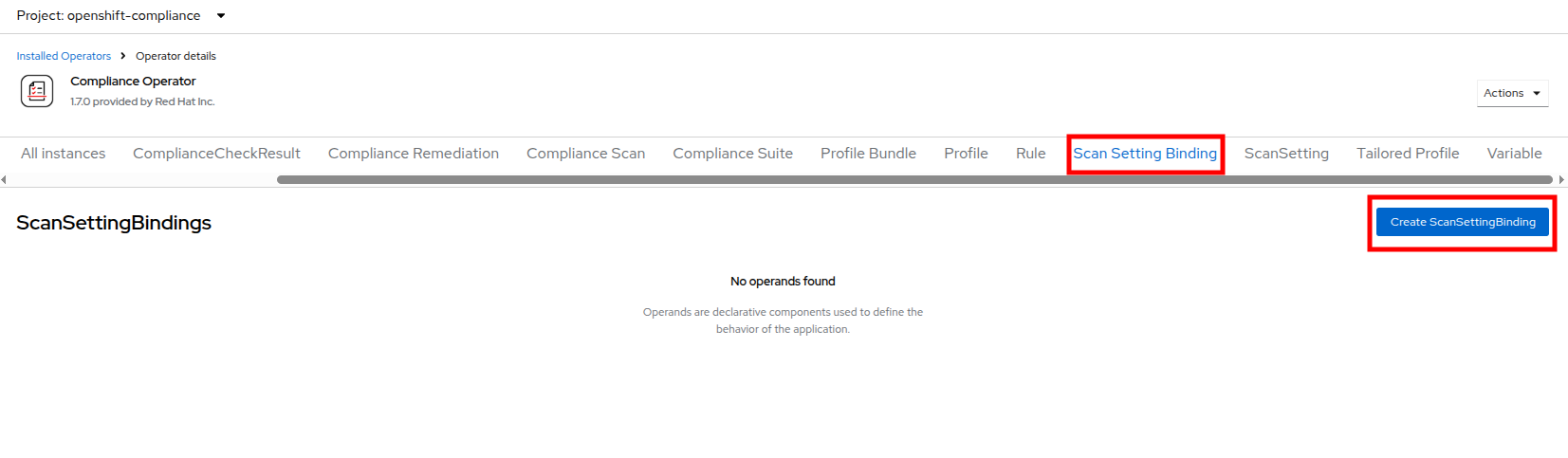
Next we want to create a ScanSettingBinding, pairing a Profile with our ScanSetting definition we created. We do this by navigating to the Scan Setting Binding tab, and clicking the Create ScanSettingBinding button.
-
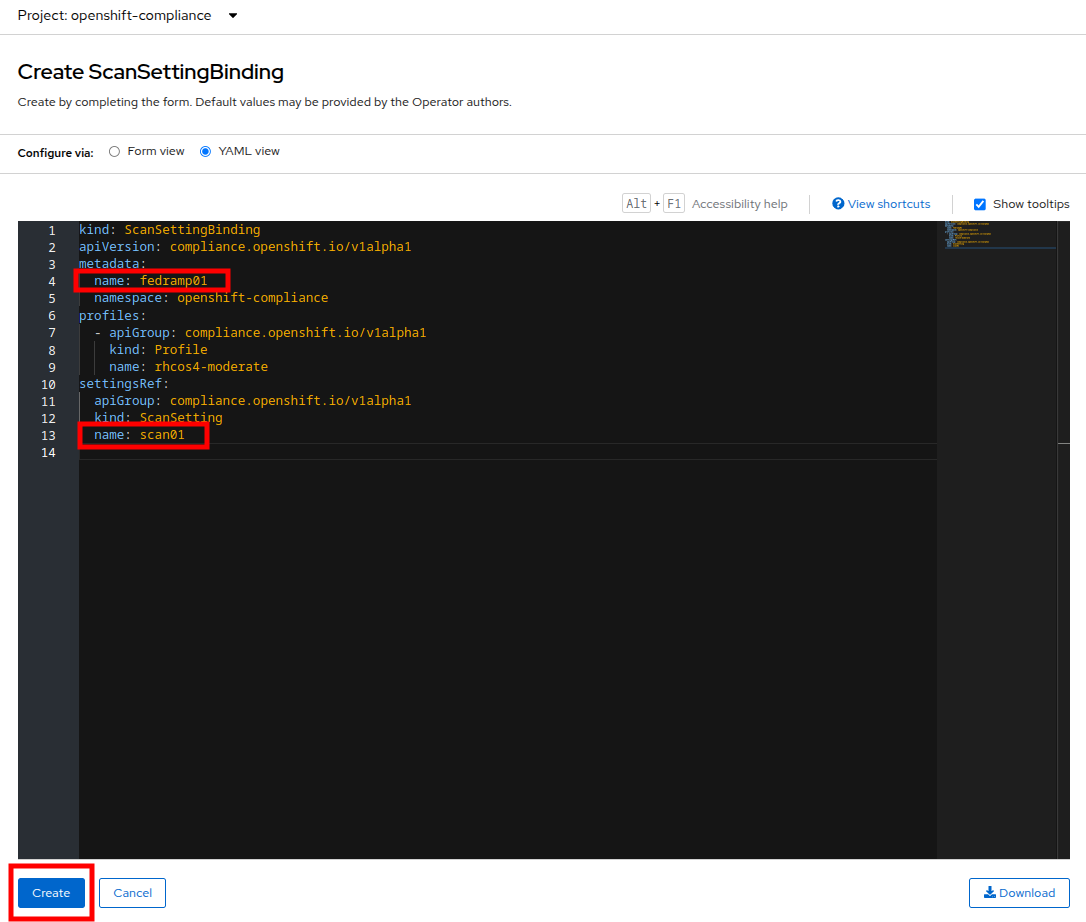
In the ScanSettingBinding YAML details, let us make a few changes:
-
The metadata/name value should be set to
fedramp01 -
The settingsRef/name field is set to
scan01which we created earlier.
-
-
Click the Create button.
The profile is set to rhcos4-moderate (the fedramp moderate profile) by default. -
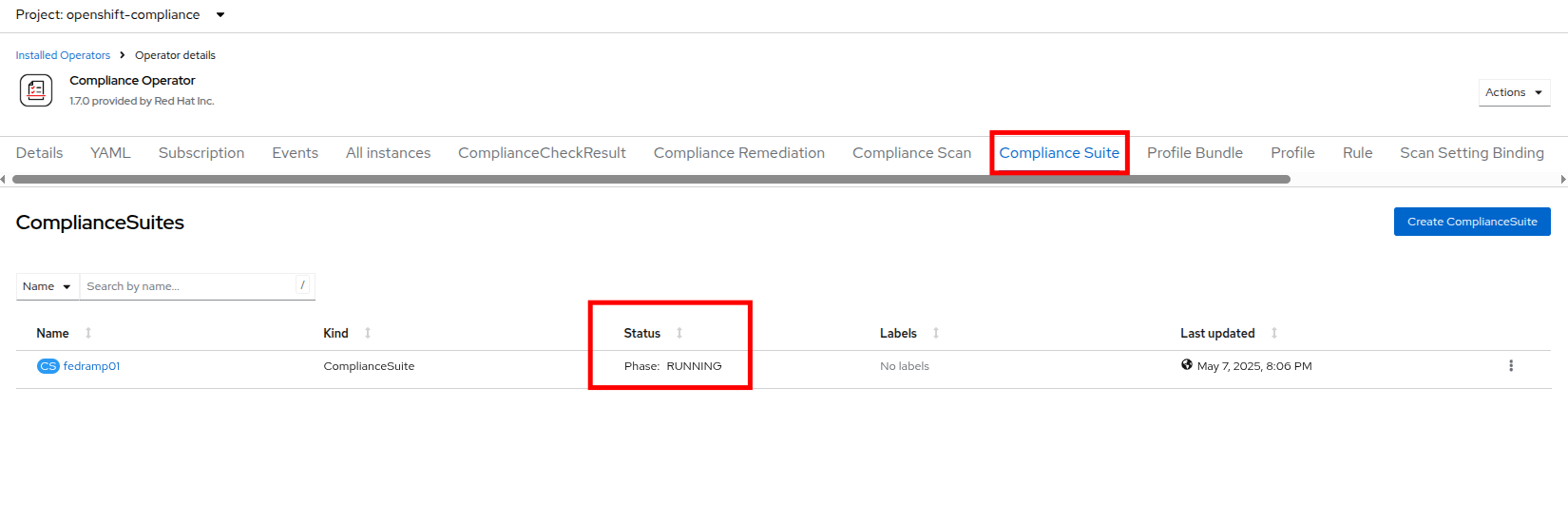
After the ScanSettingBinding is created, the fedramp01 scan will be run automatically. You can view this on the Compliance Suite tab.
-
This Compliance Suite runs the defined scans against the specified nodes, in our case the masters and the workers defined in scan01.
-
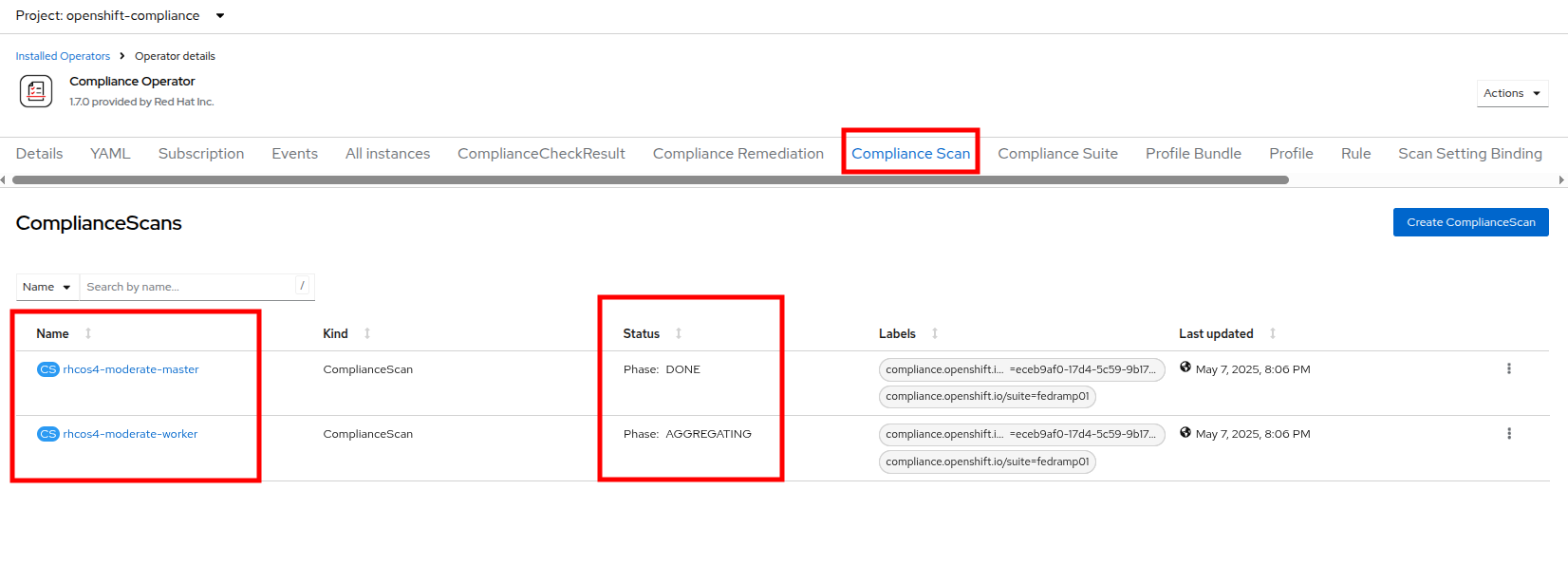
You can watch as the scan proceeds through the steps of RUNNING, AGGREGATING, and DONE by clicking on the Compliance Scan tab.
-
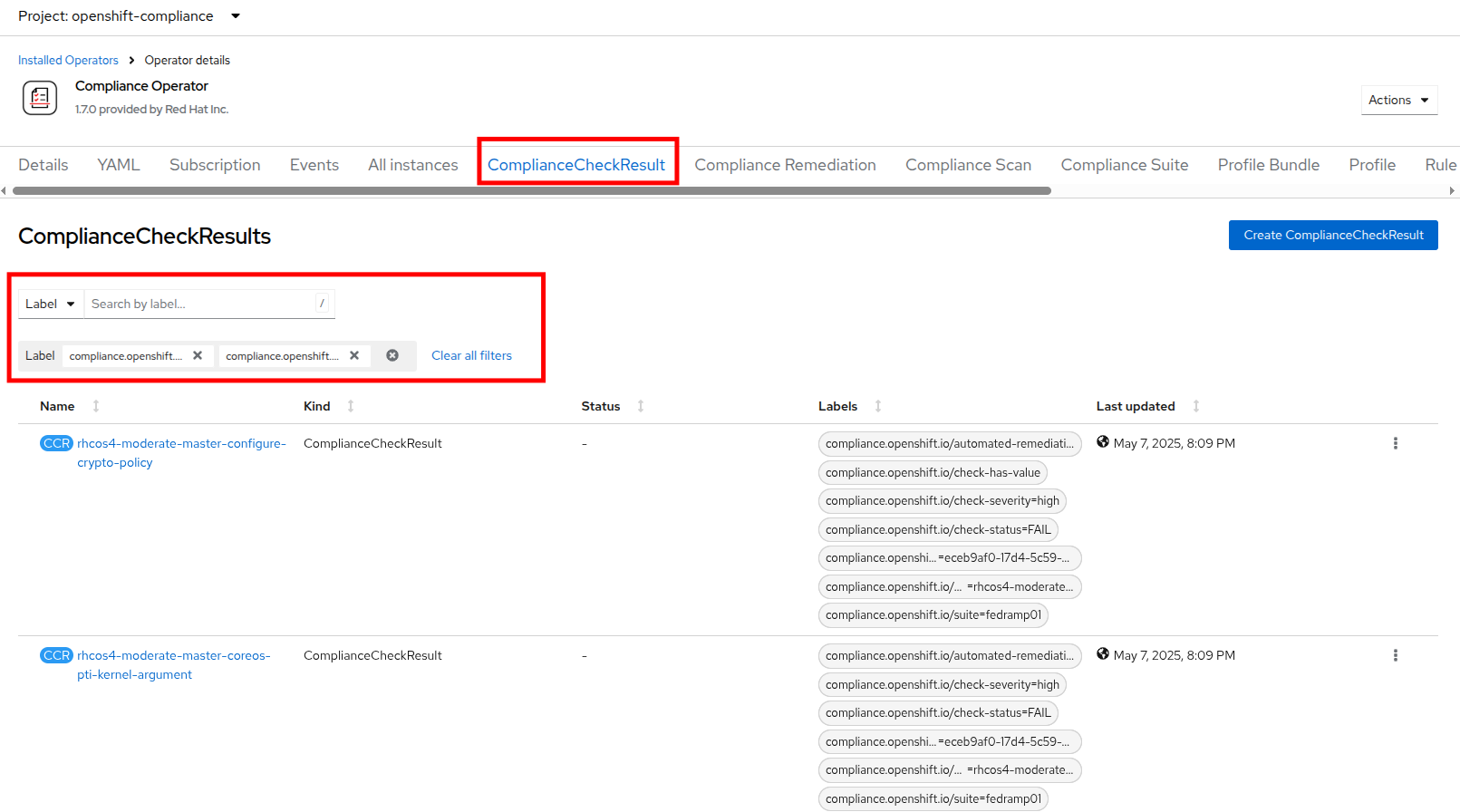
Once the scan completes (3-4 minutes on average) you can check your results by clicking on the ComplianceCheckResult tab.
-
Change the search bar to Label and apply the following labels:
-
Twelve high severity checks have a failed status:
ComplianceCheckResult |
Check-Severity |
Check-Status |
rhcos4-moderate-master-configure-crypto-policy |
high |
FAIL |
rhcos4-moderate-master-coreos-pti-kernel-argument |
high |
FAIL |
rhcos4-moderate-master-disable-ctrlaltdel-burstaction |
high |
FAIL |
rhcos4-moderate-master-disable-ctrlaltdel-reboot |
high |
FAIL |
rhcos4-moderate-master-enable-fips-mode |
high |
FAIL |
rhcos4-moderate-master-no-empty-passwords |
high |
FAIL |
rhcos4-moderate-worker-configure-crypto-policy |
high |
FAIL |
rhcos4-moderate-worker-coreos-pti-kernel-argument |
high |
FAIL |
rhcos4-moderate-worker-disable-ctrlaltdel-burstaction |
high |
FAIL |
rhcos4-moderate-worker-disable-ctrlaltdel-reboot |
high |
FAIL |
rhcos4-moderate-worker-enable-fips-mode |
high |
FAIL |
rhcos4-moderate-worker-no-empty-passwords |
high |
FAIL |