Fine‑Tuning & Customizing Model Responses
Fine‑tuning a large language model involves adapting a pre‑trained model by further training it on new, task‑specific data. This allows the model to produce more relevant, accurate, and context‑aware outputs that align precisely with enterprise‑specific use cases. Here’s where InstructLab comes in- by simplifying this traditionally complex process by providing a structured, synthetic data generation (SDG) method and fine-tuning process, all from a command line interface (CLI).
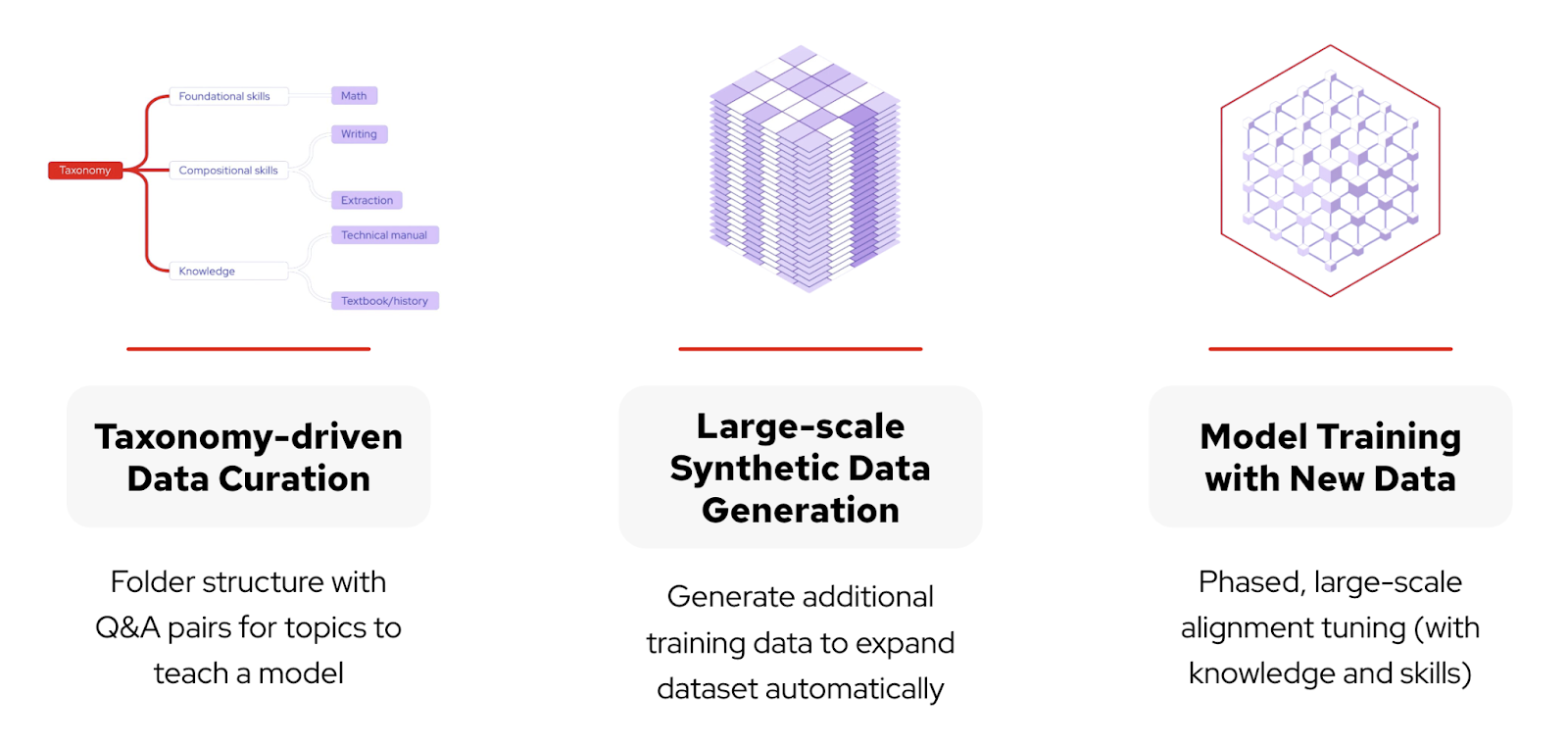
How InstructLab Helps Align Models
Originally started as a research project from the MIT-Watson lab and IBM Research, InstructLab addresses critical limitations in general‑purpose foundation models, particularly their inherent lack of domain‑specific expertise and tendency to hallucinate incorrect information, without needing full-retraining of the model. But, a large issue for model training is the large amount of data needed to train these large language models as well!
Taxonomy‑Driven Data Curation
Effective alignment begins with clearly structured data. InstructLab employs a taxonomy‑driven approach, organizing enterprise‑specific information into a logical, hierarchical folder structure. This taxonomy consists of distinct categories—foundational skills (e.g., math, writing), compositional skills (e.g., extraction from technical manuals), and specialized knowledge areas (e.g., historical texts).
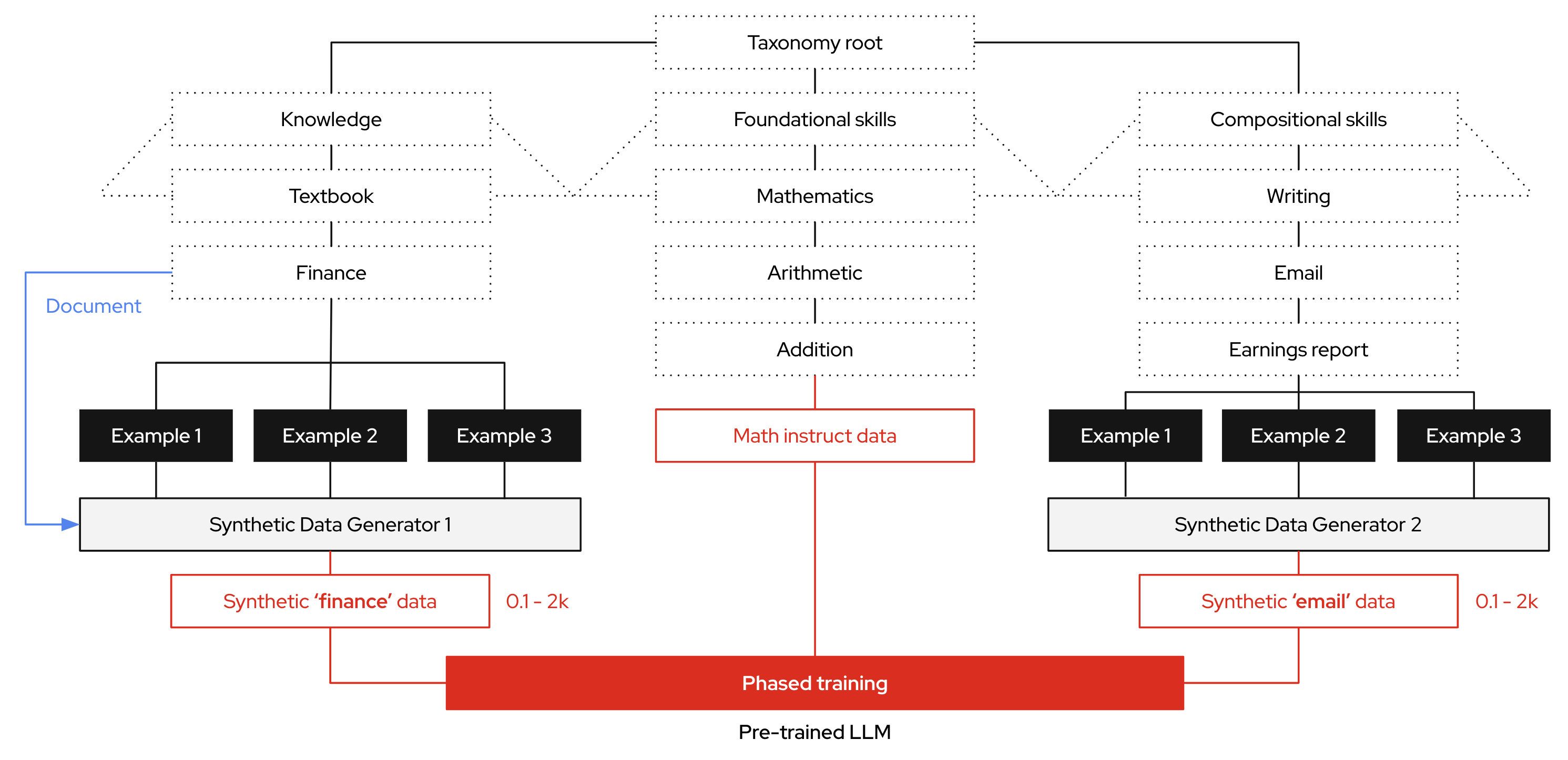
By structuring data in a clear, hierarchical format and pairing it with precise question‑and‑answer examples (qna.yaml), the synthetic data generation process is guided precisely, ensuring the produced training dataset closely mirrors your enterprise’s unique needs.
Large‑Scale Synthetic Data Generation
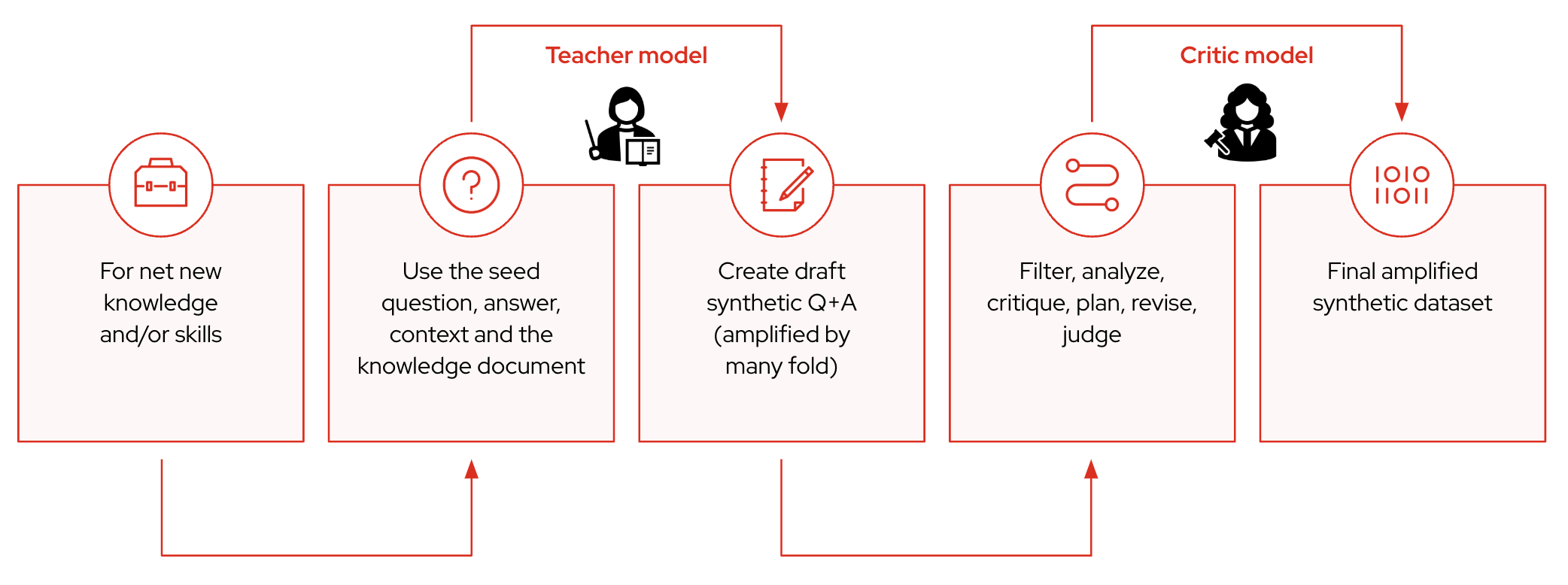
To effectively fine‑tune models, you need extensive, high‑quality training data. InstructLab uses an automated synthetic data generation strategy that deeply aligns the model with enterprise‑specific knowledge and skills. The synthetic data process leverages a local teacher model to help generate high‑quality synthetic data based on enterprise documents and carefully curated seed examples (in the format of a qna.yaml text document). This significantly expanding your training datasets based on initial Q&A seed examples and becomes the training set to fine‑tune foundation models, such as the Mistral or Granite, to address specialized tasks with enhanced precision and context‑awareness.
Model Training with New Data
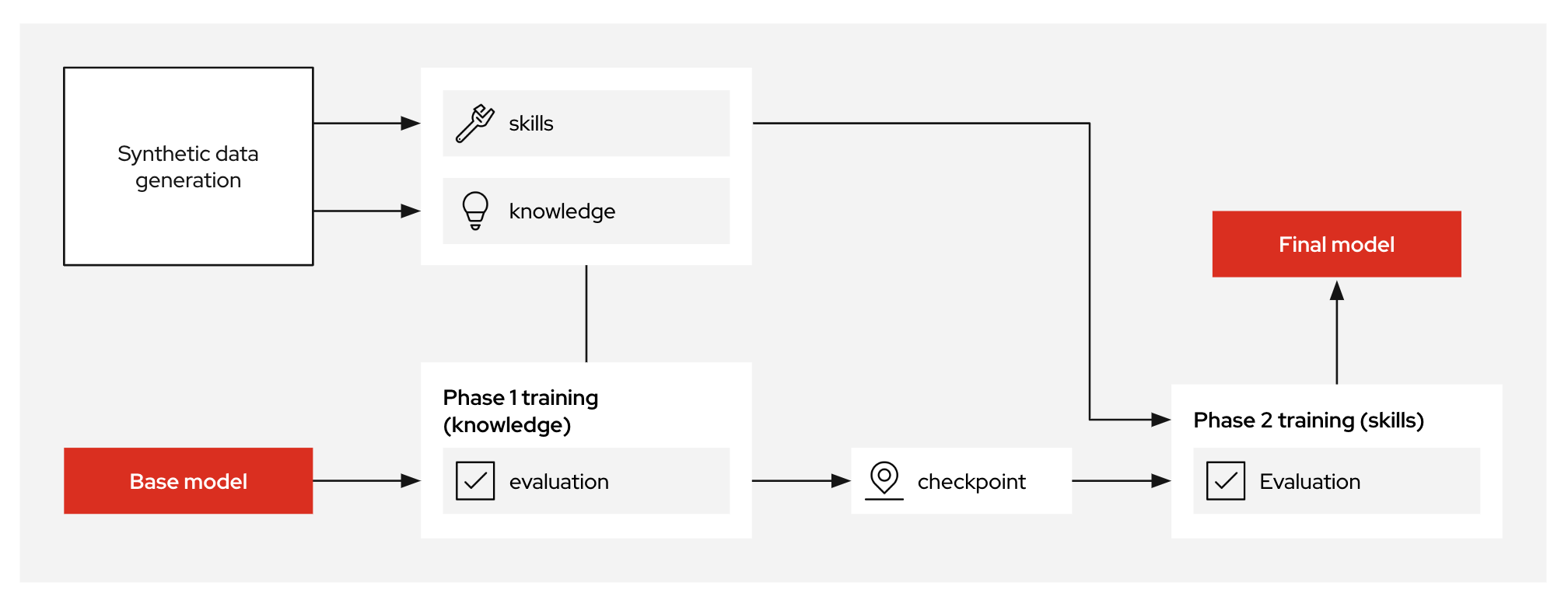
Once synthetic data is curated and generated, InstructLab utilizes phased, large‑scale alignment tuning—training your model iteratively in multiple stages, first on general knowledge and then refining it with specialized enterprise skills. This structured training approach ensures models not only understand broad concepts but can also perform specific, nuanced tasks effectively.
The Value in Enterprise Data
It is estimated that only about 1% of enterprise data is represented in popular large language models. This minimal coverage significantly restricts the models' capability to understand and interact meaningfully within specific organizational contexts. For example, at 404 Airlines, we know our internal policies and guidelines, but models are likely to not know or be trained on this information. For example our policies state the following:
- **Standard Allowance:** Each passenger is permitted one piece of carry-on baggage.
- **Size Limitations:** Maximum dimensions are 22 inches (length) x 14 inches (width) x 9 inches (height). Items must fit in the overhead bin or under the seat.
- **Weight Limit:** Total weight must not exceed 15 lbs (6.8 kg).Now, this is important information that our models should always know, and so fine-tuning this information into the model is critical to having an AI assistant which is actually helpful. But, what do language models actually know?
-
Let’s actually test this out with model that has been pre-downloaded for you, specifically the Merlinite model from Hugging Face, by running the following command in the uppper Terminal window.
ilab model serve
This command points to the default model in InstructLab’s config.yaml, but you can download and serve others using ilab model download and ilab model serve -–model-path as an argument to point to specific models.
|
Once the model is served and ready, you will see the following output:
INFO 2024-09-10 18:12:09,459 instructlab.model.serve:145: Using model '/home/developer/.cache/instructlab/models/granite-7b-lab-Q4_K_M.gguf' with -1 gpu-layers and 4096 max context size.
INFO 2024-09-10 18:12:09,459 instructlab.model.serve:149: Serving model '/home/developer/.cache/instructlab/models/granite-7b-lab-Q4_K_M.gguf' with llama-cpp
INFO 2024-09-10 18:12:16,023 instructlab.model.backends.llama_cpp:250: Replacing chat template:
{% for message in messages %}
{% if message['role'] == 'user' %}
{{ '<|user|>
' + message['content'] }}
{% elif message['role'] == 'system' %}
{{ '<|system|>
' + message['content'] }}
{% elif message['role'] == 'assistant' %}
{{ '<|assistant|>
' + message['content'] + eos_token }}
{% endif %}
{% if loop.last and add_generation_prompt %}
{{ '<|assistant|>' }}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
INFO 2024-09-10 18:12:16,026 instructlab.model.backends.llama_cpp:193: Starting server process, press CTRL+C to shutdown server...
INFO 2024-09-10 18:12:16,026 instructlab.model.backends.llama_cpp:194: After application startup complete see http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs for API.Because you are serving the model in one terminal window, we provided a separate terminal window for interactions.
-
In the bottom terminal window, you can begin a chat session with the
ilab chatcommand:
ilab model chatYou should see a chat prompt like the example below.
╭───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ Welcome to InstructLab Chat w/ GRANITE-7B-LAB-Q4_K_M.GGUF (type /h for help)
╰───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
>>>-
At this point, you can interact with the model by asking it a question. Example:
What are the maximum dimensions (length, width, and height) for carry-on baggage on 404 Airlines?The answer will almost certainly be incorrect, as shown in the following example output:
The maximum dimensions for carry-on baggage on 404 Airlines are 55 cm × 38 cm × 25 cm (approximately 21.6 in × 14.9 in × 9.8 in) in length, width, and height, respectively. This information is accurate as of April 2023 and may be subject to change, so it’s always a good idea to double-check with the airline directly for the most up-to-date information.| LLMs by nature are non-deterministic. This means that even with the same prompt input, the model will produce varying responses. So, your results may vary. |
Wow, that was both pretty awesome and sad at the same time! Kudos for it generating a response that appears to be very accurate and it was very confident in doing so. However, it is incorrect. The policies that were given look detailed but are wrong, and this can be misleading for both our agents and customers at 404 Airlines. These errors are often referred to as “hallucinations” in the LLM space.
Model alignment and fine-tuning (like you’re about to do) is one of the ways to improve a model’s answers and avoid hallucinations. In this workshop, we are going to focus on adding a new knowledge to the model so that it can be helpful for the team of customer service agents. Let’s get to work!
-
When you are done exploring the model, exit the chat by issuing the exit command within in the chat session:
exitNow, it’s time to use InstructLab to begin customizing our model, and align it to Parasol’s policies so we have a domain-specific language model, ready to be used in our application and provide real value to our employees.