Fencing and How to Handle Node Failure
Fencing is a vital mechanism, particularly in high-availability (HA) cluster configurations, for safeguarding cluster resources and ensuring data integrity. It works by isolating an unresponsive or failed node. This process is crucial to prevent the "split-brain" scenario, which occurs when multiple nodes try to write to shared storage simultaneously, inevitably leading to data corruption.
This lab demonstrates the capabilities of the Node Health Check Operator and the Self Node Remediation Operator. You will simulate a node failure to observe the virtual machine migration process and subsequent node recovery.
Accessing the OpenShift Cluster
{openshift_cluster_console_url}[{openshift_cluster_console_url},window=_blank]
oc login -u {openshift_cluster_admin_username} -p {openshift_cluster_admin_password} --server={openshift_api_server_url}{openshift_api_server_url}[{openshift_api_server_url},window=_blank]
{openshift_cluster_admin_username}{openshift_cluster_admin_password}Instructions
-
Ensure you are logged in to both the OpenShift Console and CLI as the admin user from your web browser and the terminal window on the right side of your screen and continue to the next step.
-
Navigate to Ecosystem → Installed Operators → Node Health Check Operator. Then click Node Health Check → Create NodeHealthCheck
Click the Create NodeHealthCheck button
-
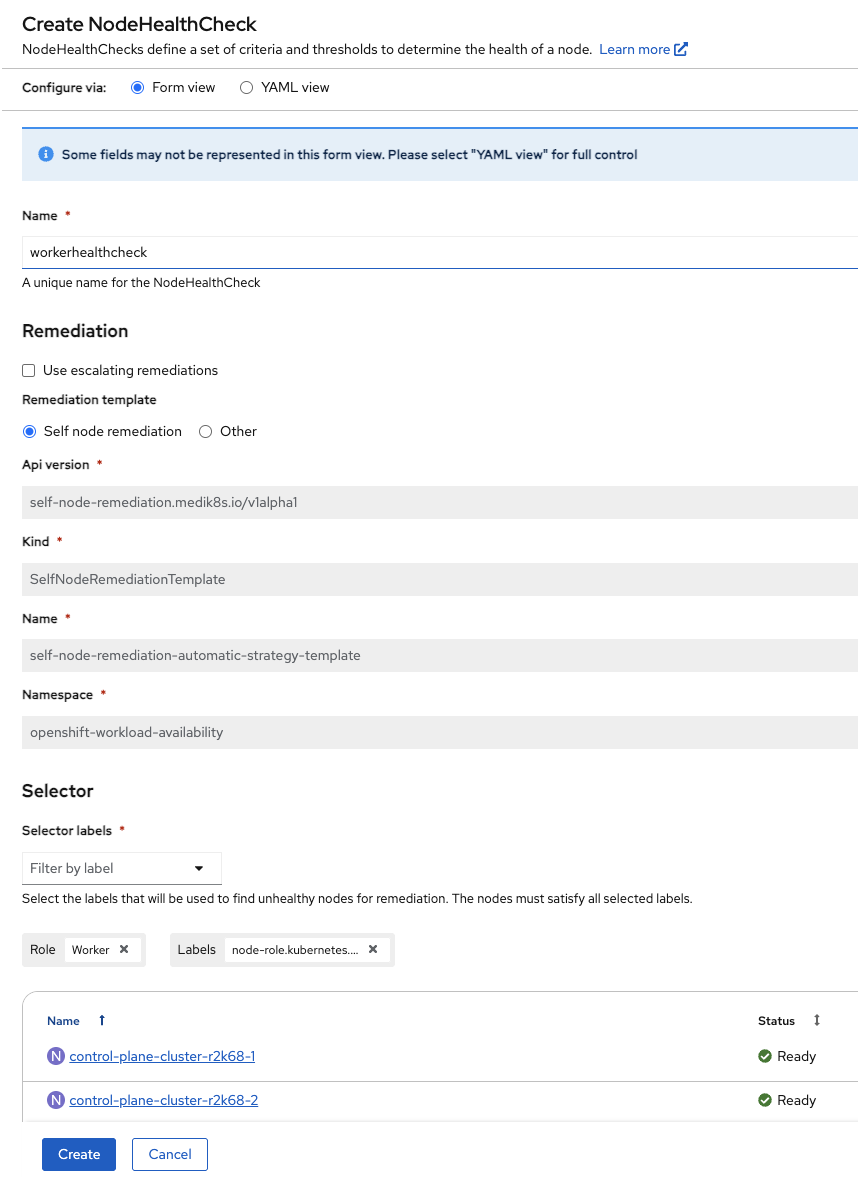
Name the NodeHealthCheck
workerhealthcheckand in the Selector labels menu, select worker.Change duration to 5s for both of the Unhealthy Conditions.
Click Create
-
Next, locate the node hosting fencing-vm1 located within the fencing project section and record this information. In this example, the node name is worker-cluster-r2k68-1.
Get VM infooc get vmi -n fencingNAME AGE PHASE IP NODENAME READY fencing-vm1 169m Running 10.235.0.29 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 True
-
In the next steps, we will create a failure condition and monitor the effects on the OpenShift node. To monitor the process, open one additional terminal sessions and SSH into the bastion host as described above.
-
In second terminal run a command to continually monitor the state of the worker node you found above (e.g. worker-cluster-r2k68-1, but your node name will be different).
Monitor the worker nodesoc get nodes <worker from step 4> -w -
Using the original terminal you created, you will force the worker from step 4 to go into an unhealthy state by stopping the kubelet service.
Force the node into a unhealthy stateoc debug node/<worker from step 4> # chroot /host # systemctl stop kubeletRemoving debug pod ...
-
In your orginal terminal you opened, you will monitor the status of your virtual machine, fencing-vm1. Here you will see that self remediation is occurring on the node.
Get VM infooc get -n fencing vmi -w -
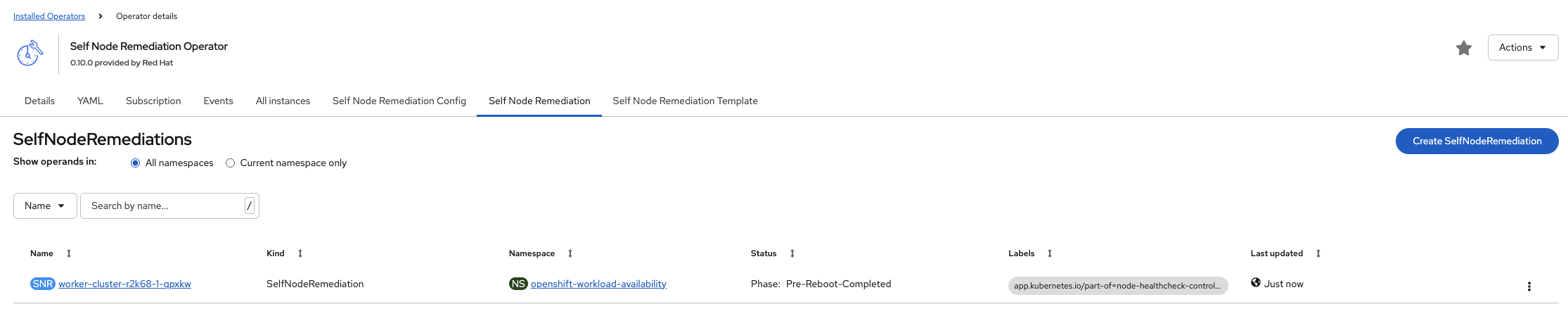
Navigate to Ecosystem → Installed Operators → Self Node Remediation Operator → Self Node Remediation Here you can see that self remediation is occurring on the node.
-
The VM will then proceed through scheduling and be scheduled onto a new node, where it will begin running. Concurrently, the original node will undergo remediation by the Self Node Remediation operator and be restored to a healthy state.
The node will be rebooted:
oc get nodes worker-cluster-r2k68-1 -w NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION worker-cluster-r2k68-1 Ready worker 4h15m v1.33.5 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 Ready worker 4h16m v1.33.5 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 NotReady worker 4h16m v1.33.5 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 NotReady worker 4h16m v1.33.5 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 NotReady,SchedulingDisabled worker 4h16m v1.33.5 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 NotReady,SchedulingDisabled worker 4h16m v1.33.5 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 Ready,SchedulingDisabled worker 4h17m v1.33.5 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 Ready,SchedulingDisabled worker 4h17m v1.33.5 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 Ready,SchedulingDisabled worker 4h17m v1.33.5 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 Ready worker 4h18m v1.33.5 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 Ready worker 4h18m v1.33.5
The VM will also be restarted on another node:
oc get -n fencing vmi -w NAME AGE PHASE IP NODENAME READY fencing-vm1 36m Running 10.235.0.14 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 True fencing-vm1 37m Running 10.235.0.14 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 False fencing-vm1 38m Failed 10.235.0.14 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 False fencing-vm1 38m Failed 10.235.0.14 worker-cluster-r2k68-1 False fencing-vm1 0s Pending fencing-vm1 1s Scheduling False fencing-vm1 10s Scheduled worker-cluster-r2k68-3 False fencing-vm1 10s Running 10.232.2.41 worker-cluster-r2k68-3 True