Welcome to Experience OpenShift Virtualization!
Introduction
OpenShift Virtualization enables you to bring virtual machines onto a modern, Kubernetes-based infrastructure. It enables the development and delivery of new applications as well as the modernization of existing ones and can create applications that consist of virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions - all managed together using Kubernetes-native tools and paradigms.
This roadshow event is organized to allow you to have a hands-on experience with Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization.
In this event we will explore many common management activities that virtualization administrators often encounter in their day to day workflows.
Who Will Benefit Most from attending a Roadshow?
Virtual Machine Administrators — Those responsible for day to day management of virtual guests in OpenShift Virtualization. These users will often find themselves responsible for provisioning virtual guests, and day to day management of the guests, and the applications running within.
Virtual Infrastructure Administrators — Those responsible for the physical infrastructure hosting the OpenShift Virtualization solution. These users will be responsible for physical hardware, storage, and networking changes to the environment, that will affect the day to day operations of the running virtual machines.
What Content Is Covered In The Roadshow?
These are the seven main sections that will be covered:
-
Virtual Machine Management: In this section we will provide a review of virtual machine management fundamentals, including creating a virtual machine, and modifying it’s allotted resources.
-
Migrating Existing Virtual Machines: In this section, we will use the Migration Toolkit for Virtualization (MTV) to migrate virtual machines from an existing VMware vSphere environment to OpenShift Virtualization.
-
Storage Management: The storage paradigm familiar to many administrators changes with OpenShift Virtualization. This section will explore many actions related to storage management for virtual machines.
-
Backup and Recovery for Virtual Machines: This unit introduces and demonstrates additional concepts around backing up VMs to external sites and restoring them in the event of a disaster.
-
Template and InstanceType Management: In order to streamline deployment of virtual machines, administrators will often create Templates or define InstanceTypes to ease deployment operations. This section will focus on those processes.
-
Working with Virtual Machines and Applications: In this section we will perform some day-2 activities with our imported virtual machines, by exposing our VM hosted applications through services and routes.
-
Network Management: By default VMs are connected to the pod network in OpenShift. In this section we will explore creating new L2 network mappings as well as making use of user defined networks (UDN) for direct network connectivity.
What is OpenShift Virtualization?
-
All current subscribers receive OpenShift Virtualization as part of their OpenShift subscription. It has been generally available since OpenShift 4.5.
-
OpenShift Virtualization is based on the “container-native virtualization” technology being developed upstream under the KubeVirt project, an incubating project in the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF).
-
It leverages the Red Hat Enterprise Linux KVM hypervisor (RHEL KVM), which is a mature and highly performant open-source hypervisor used by many organizations and cloud service providers globally and which has been under development for over 15 years.
-
OpenShift Virtualization leverages the RHEL KVM hypervisor and allows the VM to be managed by Kubernetes and KubeVirt. An OpenShift Virtualization VM uses Kubernetes scheduling, network, and storage infrastructure.
-
OpenShift Virtualization is SVVP certified with Microsoft for Windows guest support per the same rules that apply to Red Hat’s other KVM virtualization offerings.
-
OpenShift Virtualization is currently only supported on bare metal physical servers, typically on-premises or through supported cloud providers. Support for other topologies (OpenShift deployed on virtualized infrastructure like OpenStack or vSphere) is not available at this time.
-
OpenShift Virtualization allows OpenShift to deploy, manage, and connect virtual machines to resources in an OpenShift cluster. This includes the ability to connect to and manage those VMs using Kubernetes-native methods and take advantage of OpenShift features like Pipelines, GitOps, Service Mesh, and more.
Why switch from a traditional VM platform?
Adopt cloud-native development and/or cloud-native operations: Red Hat OpenShift helps your team build applications with speed, agility, confidence, and choice. Code in production mode, anywhere you choose to build. Get back to doing work that matters.
Complete app dev stack: Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces (formerly Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces), Runtimes, Integration and Process Automation, Serverless, Pipelines, and more with security throughout.
Shift infrastructure spend to innovation: OpenShift native architecture changes the heavyweight cost structure from SDDC legacy to lightweight container-native frameworks.
Risk mitigation: With OpenShift support for on-premises and public cloud options, OpenShift is insurance against public cloud lock-in.
Independent from infrastructure: Red Hat OpenShift runs consistently on bare metal, on-premises virtualization, or public cloud for ultimate choice and flexibility of deployment and updates.
Pure open source innovation: The innovation in Kubernetes, serverless, service mesh, Kubernetes Operators, and more powered by the velocity of open source, with Red Hat in the lead.
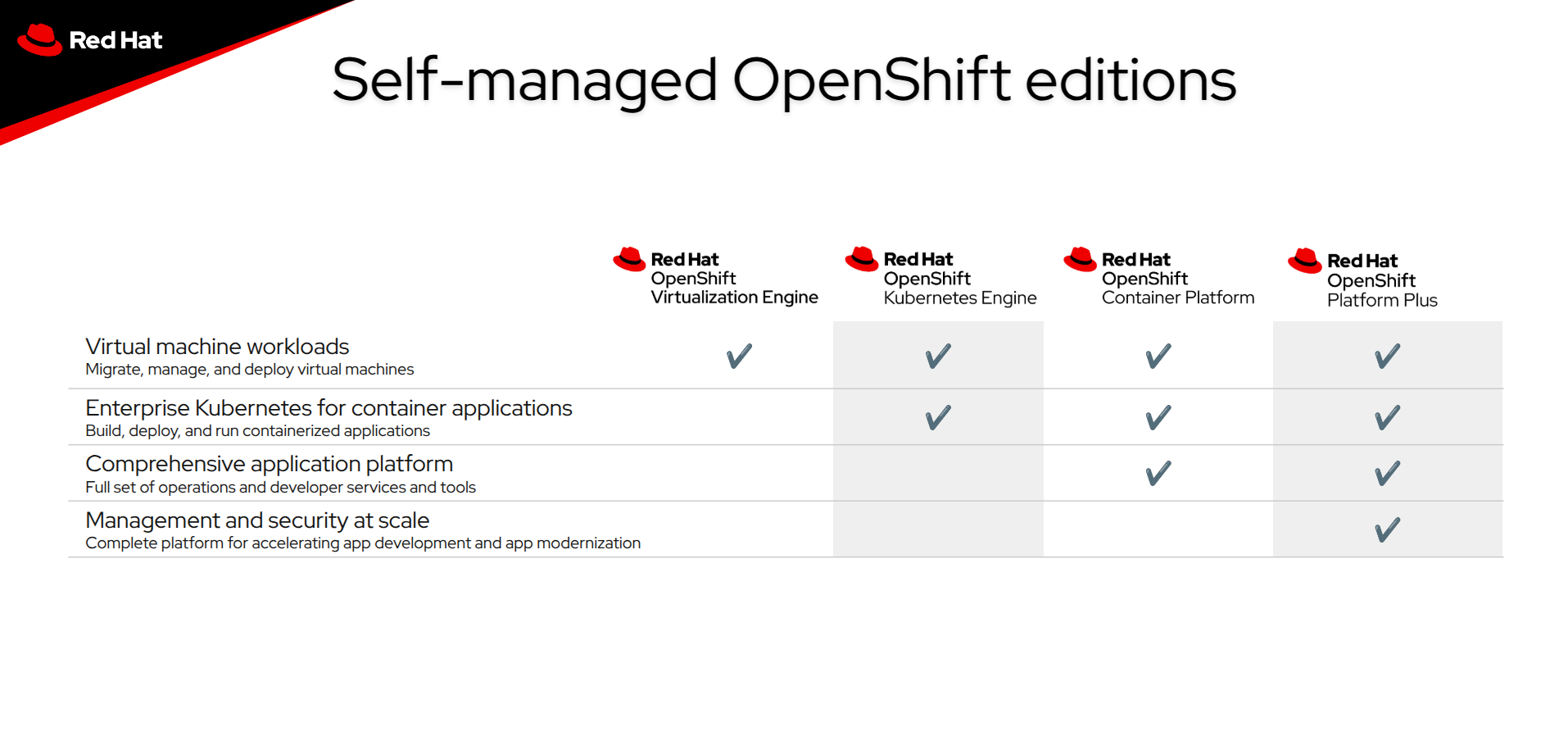
Which OpenShift Subscription is right for me?
OpenShift is an inclusive platform wherein all of the features are accesible to end users at any time, but their usage is governed by the subscription that that user has purchased.
Subscriptions for OpenShift fall into one of four categories, all of which provide access to OpenShift Virtualization:
Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus is a unified platform to build, modernize, and deploy applications at scale. Multicluster security, compliance, application and data management work across infrastructures to provide consistency throughout the software supply chain. Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus helps you work smarter and faster with a complete set of services for bringing apps to market on your hybrid cloud.
Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform is a trusted, comprehensive, and consistent platform to develop, modernize, and deploy applications at scale, including today’s AI-enabled apps. Innovate faster with a complete set of services for bringing apps to market on your choice of infrastructure.
Red Hat OpenShift Kubernetes Engine provides you with the basic functionality of Red Hat OpenShift. It offers a subset of the features that Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform offers, like full access to an enterprise-ready Kubernetes environment and an extensive compatibility test matrix with many of the software elements that you might use in your datacenter.
Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization Engine provides the proven virtualization functionality of Red Hat OpenShift to deploy, manage, and scale virtual machines (VMs). Only pay for what you need with a streamlined solution focused exclusively on VM workloads.
The following chart explains the features that are entitled with each subscription and may help you decide which version of OpenShift is best for your environment.
A full feature breakdown across all OpenShift editions can be found in the subscription guide.
Next steps
If you would like to learn more about OpenShift Virtualization, please visit the landing page, review the documentation, enjoy one of our interactive experiences, or view some of our demo videos on YouTube.
Requirements for the Lab Environment
-
Participant needs to have their own computer with a web browser and internet access.
-
Chromium based browsers are recommended as some copy/paste functions don’t work in Firefox for the time being.
-
Remote access console uses the US keyboard layout by default, so it’s good to know where special characters reside for other country’s layouts, or to use the copy/paste function in a supported browser.
Credentials for the OpenShift Console
Your OpenShift cluster console is available {openshift_console_url}[here^].
Your login is available with:
-
User: {user}
-
Password: {password}
vCenter Access
In the migration chapter of the lab, you will be asked to login and examine a VMware vSphere environment.
For access, please use the following credentials:
-
vcenter_user: {vcenter_full_user}
-
vcenter_password: {vcenter_password}
Version Information
This edition of the OpenShift Virtualization Roadshow has been developed using the following software versions:
-
Red Hat OpenShift 4.18.20
-
Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization 4.18.8
-
Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation 4.18.6
-
Red Hat OpenShift API for Data Protection (OADP) 1.4.5
-
Red Hat Migration Toolkit for Virtual Machines 2.8.5
(Accurate as of August 7, 2025)