Introduction
When deploying your ARO cluster, you can configure many aspects of your worker nodes, but what happens when you need to change your worker nodes after they’ve already been created? These activities include scaling the number of nodes, changing the instance type, adding labels or taints, just to name a few.
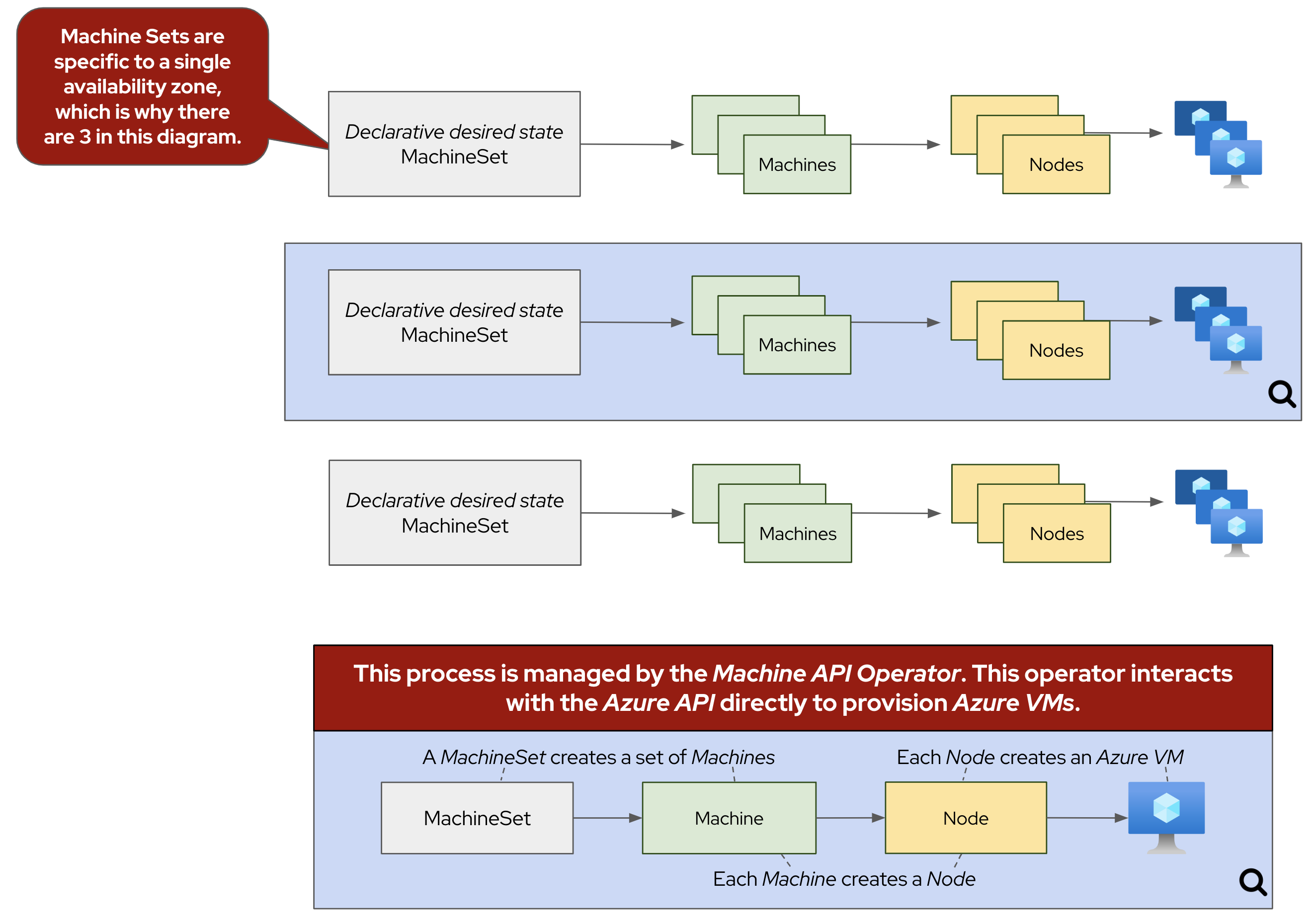
Many of these changes are done using MachineSets. MachineSets ensure that a specified number of Machine replicas are running at any given time. Think of a MachineSet as a "template" for the kinds of Machines that make up the worker nodes of your cluster. These are similar to other Kubernetes resources, like a ReplicaSet is to Pods. One important caveat, is that MachineSets allow users to manage many Machines as a single entity, but are contained to a specific availability zone. If you’d like to learn more, see the Red Hat documentation on machine management.
Here are some of the advantages of using ARO MachineSets to manage the size of your cluster
-
Scalability - MachineSets enables horizontal scaling of your cluster. It can easily add or remove workers to handle the changes in workload. This flexibility ensures that your cluster can dynamically scale to meet the needs of your applications.
-
Infrastructure Diversity - MachineSets allow you to provision worker nodes of different instance type. This enables you to leverage the best kind of instance family for different workloads.
-
Integration with Cluster Autoscaler - MachineSets seamlessly integrate with the Cluster Autoscaler feature, which automatically adjusts the number of worker nodes based on the current demand. This integration ensures efficient resource utilization by scaling the cluster up or down as needed, optimizing costs and performance.
Scaling worker nodes
Via the CLI
-
First, let’s see what MachineSets already exist in our cluster. To do so, run the following command:
oc -n openshift-machine-api get machinesetSample OutputNAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AVAILABLE AGE aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1 1 1 1 1 108m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus2 1 1 1 1 108m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus3 1 1 1 1 108mBy default, ARO clusters have three MachineSets, one for each availability zone.
-
Now, let’s take a look at the machines that have been created according to the instructions provided by the above MachineSets. To do so, run the following command:
oc -n openshift-machine-api get machineSample OutputNAME PHASE TYPE REGION ZONE AGE aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-master-0 Running Standard_D8s_v3 eastus 1 107m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-master-1 Running Standard_D8s_v3 eastus 2 107m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-master-2 Running Standard_D8s_v3 eastus 3 107m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1-vgmng Running Standard_D4s_v3 eastus 1 102m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus2-m4dgh Running Standard_D4s_v3 eastus 2 102m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus3-k65k6 Running Standard_D4s_v3 eastus 3 102mFor this workshop, we’ve deployed your ARO cluster with six total machines (three workers machines and three control plane machines), one in each availability zone.
-
Now that we know that we have three worker nodes, let’s pick a MachineSet to scale up using the OpenShift CLI tools. To do so, run the following command:
MACHINESET=$(oc -n openshift-machine-api get machinesets -o name | head -1) echo ${MACHINESET}Sample Outputmachineset.machine.openshift.io/aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1 -
Now, let’s scale up our selected MachineSet from one to two machines. To do so, run the following command:
oc -n openshift-machine-api scale --replicas=2 ${MACHINESET}Sample Outputmachineset.machine.openshift.io/aro-cluster-vhtbl-8xd66-worker-westeurope1 scaled -
Now that we’ve scaled the MachineSet to two machines, we can see that the machine is already being created. First, let’s quickly check the output of the same command we ran in step 1:
oc -n openshift-machine-api get machinesetsSample OutputNAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AVAILABLE AGE aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1 2 2 1 1 108m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus2 1 1 1 1 108m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus3 1 1 1 1 108mNote, that the number of desired and current nodes matches the scale we specified, but only one is ready and available.
We can also run the same command we ran in step 2 to see the machine being provisioned:
oc -n openshift-machine-api get machineSample OutputNAME PHASE TYPE REGION ZONE AGE aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-master-0 Running Standard_D8s_v3 eastus 1 108m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-master-1 Running Standard_D8s_v3 eastus 2 108m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-master-2 Running Standard_D8s_v3 eastus 3 108m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1-8vzrw Provisioned Standard_D4s_v3 eastus 1 17s aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1-vgmng Running Standard_D4s_v3 eastus 1 104m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus2-m4dgh Running Standard_D4s_v3 eastus 2 104m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus3-k65k6 Running Standard_D4s_v3 eastus 3 104m
Via the Console
Now let’s scale the cluster back down to a total of 3 worker nodes, but this time, from the web console.
-
Return to your tab with the OpenShift Web Console.
-
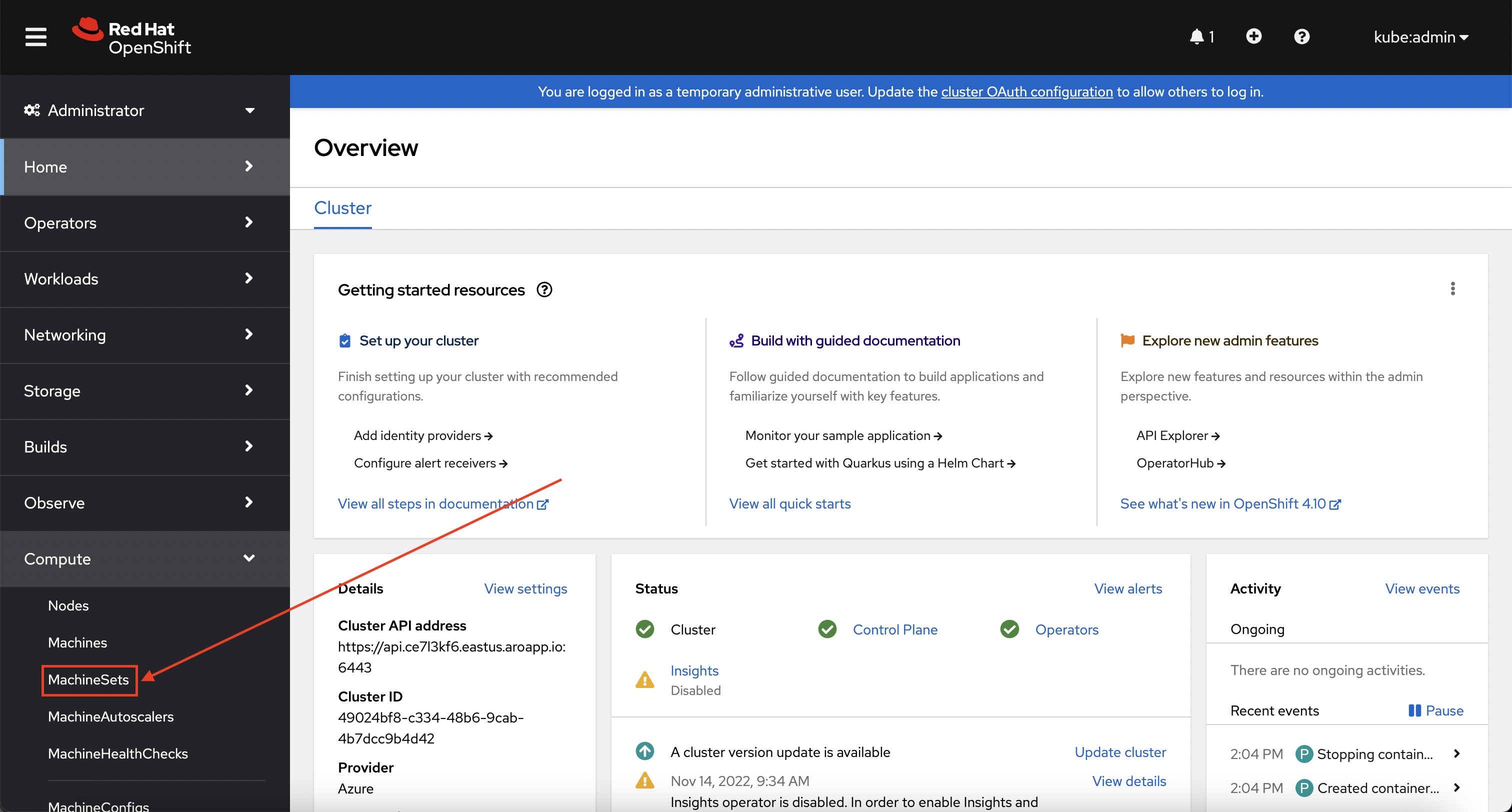
Using the menu on the left Select Compute -> MachineSets.
-
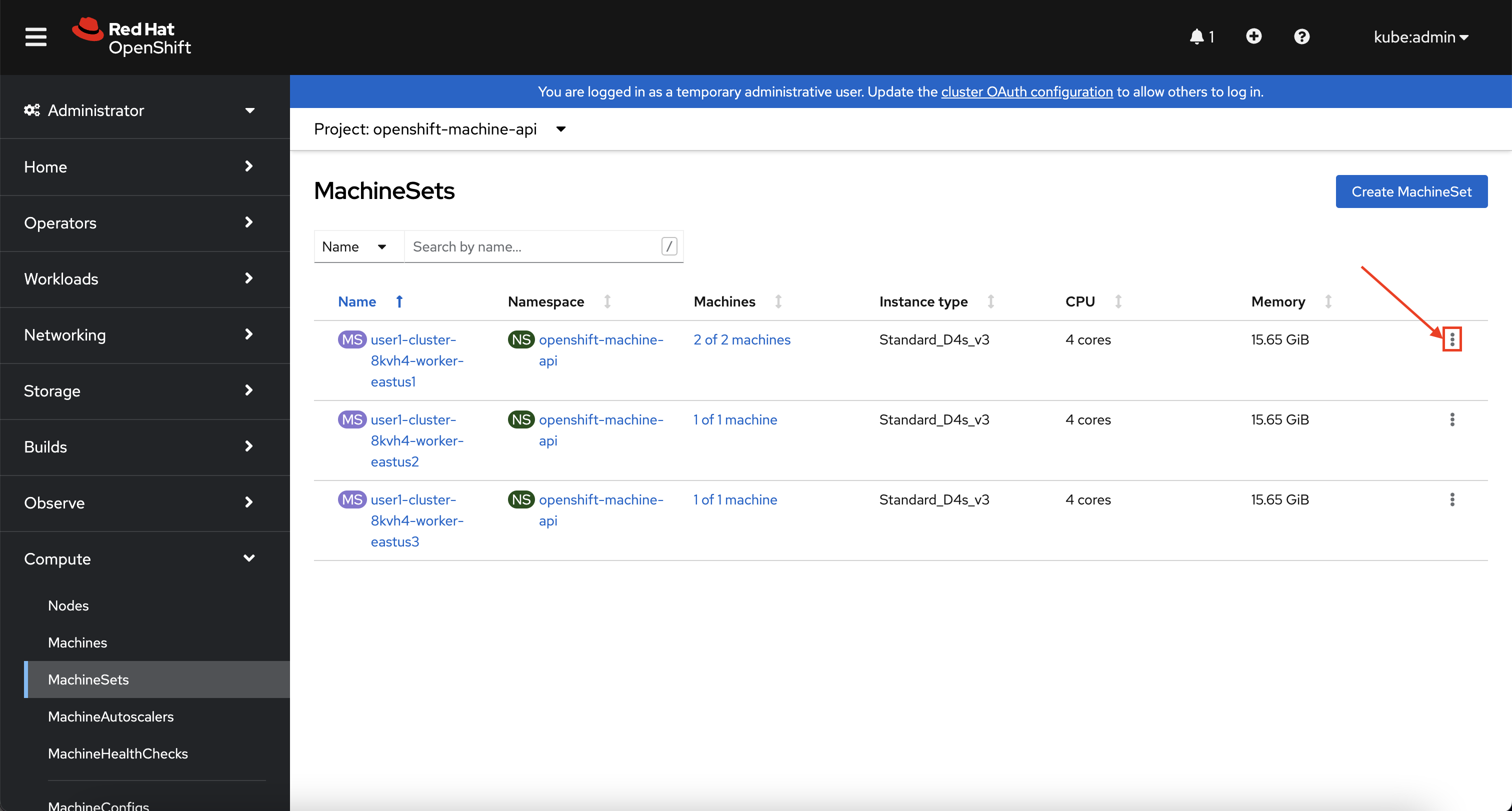
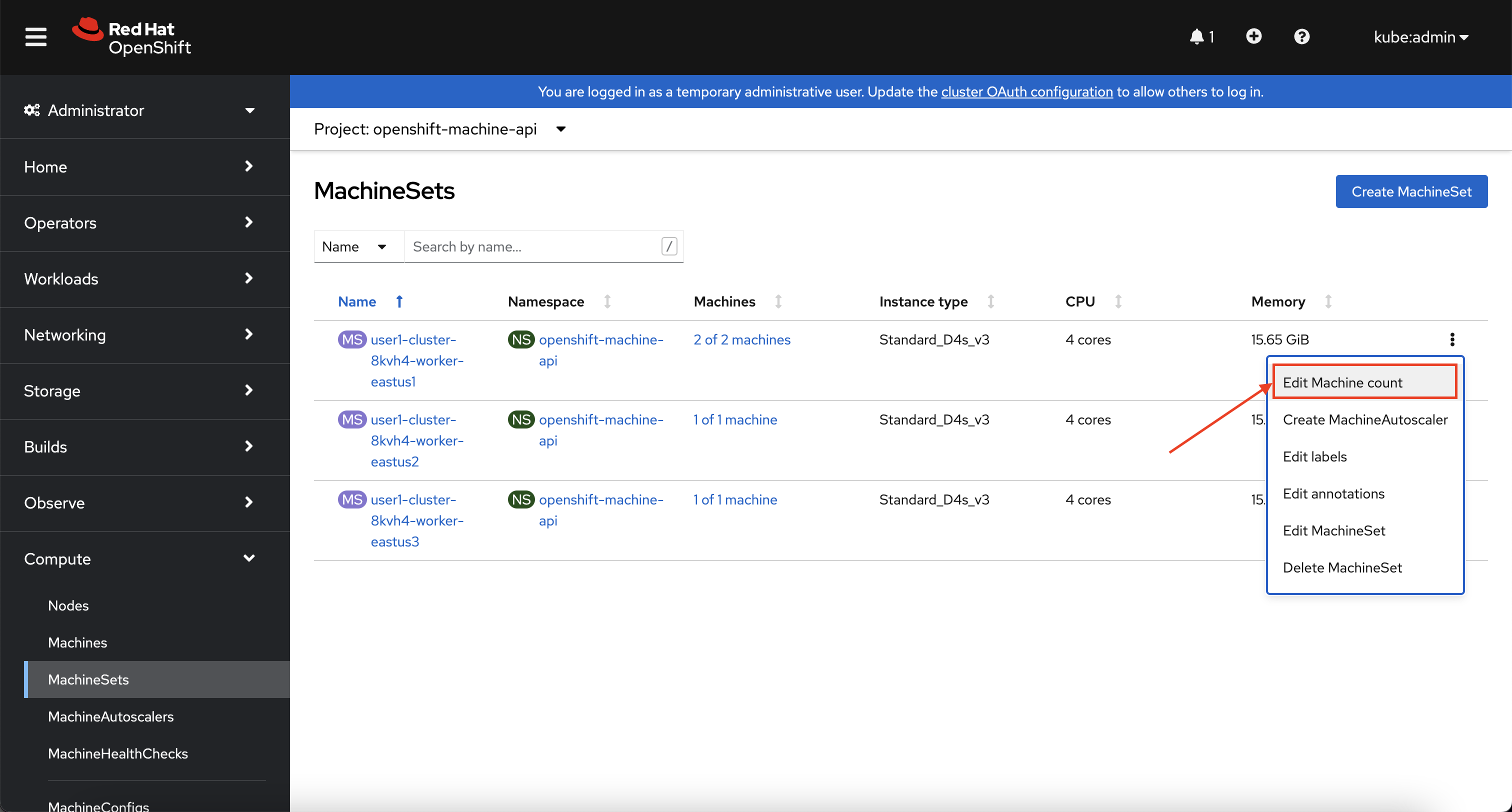
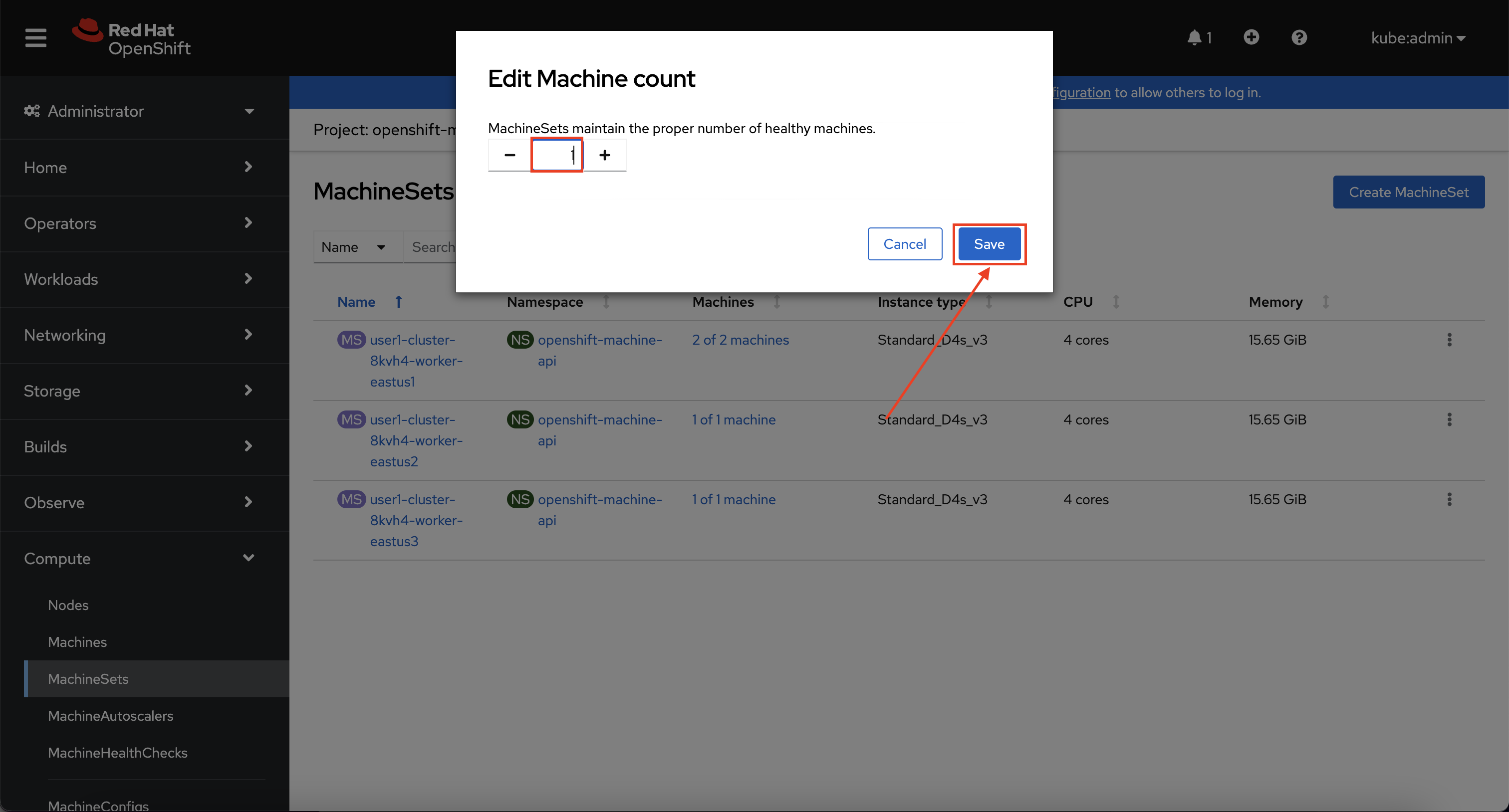
In the overview you will see the same information about the MachineSets that you saw on the command line. Now, locate the MachineSet which has "2 of 2" machines, and click on the ⋮ icon, then select Edit machine count.
It may take up to 5 minutes for the MachineSet to scale to 2 nodes while the underlying machine provisions and becomes ready. Until this time, the machine count will read "1 of 2".
-
Next, reduce the count from "2" to "1" and click Save to save your changes.
Congratulations!
You’ve successfully scaled your cluster up and back down to three nodes.