Introduction
The ARO Cluster Autoscaler is a feature that helps automatically adjust the size of an ARO cluster based on the current workload and resource demands. Cluster Autoscaler offers automatic and intelligent scaling of ARO clusters, leading to efficient resource utilization, improved application performance, high availability, and simplified cluster management. By dynamically adjusting the cluster size based on workload demands, it helps organizations optimize their infrastructure costs while ensuring optimal application performance and scalability. The cluster autoscaler does not increase the cluster resources beyond the limits that you specify.
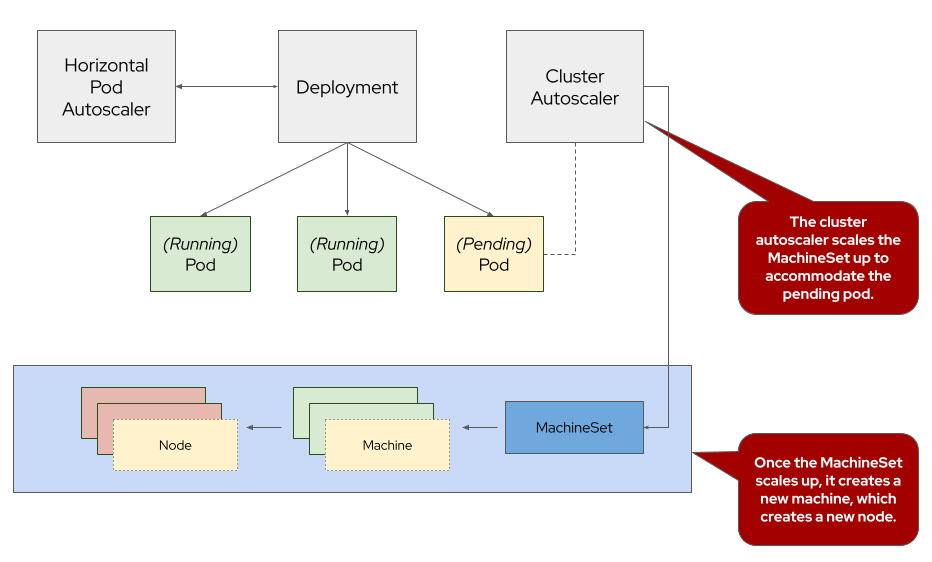
To learn more about cluster autoscaling, visit the Red Hat documentation for cluster autoscaling.
Create a Machine Autoscaler
Before we can configure cluster autoscaling, we first need to configure machine autoscaler to scale each of our MachineSets.
While this can be accomplished via the OpenShift Web Console or OpenShift CLI tools, we’ll be using the CLI for this part of the workshop.
-
Just like the last section, let’s pick a MachineSet to add a machine autoscaler. To do so, run the following command:
MACHINESET=$(oc -n openshift-machine-api get machinesets -o name \ | cut -d / -f2 | head -1) echo ${MACHINESET}Sample Outputaro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1 -
Next, let’s use that information to populate a manifest to create a machine autoscaler. To do so, run the following command:
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f - --- apiVersion: "autoscaling.openshift.io/v1beta1" kind: "MachineAutoscaler" metadata: name: "${MACHINESET}" namespace: "openshift-machine-api" spec: minReplicas: 1 maxReplicas: 3 scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: machine.openshift.io/v1beta1 kind: MachineSet name: "${MACHINESET}" EOFSample Outputmachineautoscaler.autoscaling.openshift.io/aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1 created -
Next, let’s check to see that our machine autoscaler has been created. To do so, run the following command:
oc -n openshift-machine-api get machineautoscalerSample OutputNAME REF KIND REF NAME MIN MAX AGE aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1 MachineSet aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1 1 3 16s
Create a Cluster Autoscaler
-
Next, we need to create the cluster autoscaler resource. To do so, run the following command:
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f - --- apiVersion: "autoscaling.openshift.io/v1" kind: "ClusterAutoscaler" metadata: name: default spec: podPriorityThreshold: -10 resourceLimits: maxNodesTotal: 10 cores: min: 8 max: 128 memory: min: 4 max: 256 scaleDown: enabled: true delayAfterAdd: 2m delayAfterDelete: 1m delayAfterFailure: 15s unneededTime: 1m EOFSample Outputclusterautoscaler.autoscaling.openshift.io/default created -
Next, let’s check to see that our cluster autoscaler has been created. To do so, run the following command:
oc get clusterautoscalerSample OutputNAME AGE default 22sFor a detailed explanation of each parameter, see the Red Hat documentation on the cluster autoscaler.
Test the Cluster Autoscaler
Now let’s test the cluster autoscaler and see it in action. To do so, we’ll deploy a job with a load that this cluster cannot handle. This should force the cluster to scale to handle the load.
-
First, let’s create a namespace (also known as a project in OpenShift). To do so, run the following command:
oc new-project autoscale-exSample OutputNow using project "autoscale-ex" on server "https://api.rbrlitrg.westeurope.aroapp.io:6443". You can add applications to this project with the 'new-app' command. For example, try: oc new-app rails-postgresql-example to build a new example application in Ruby. Or use kubectl to deploy a simple Kubernetes application: kubectl create deployment hello-node --image=k8s.gcr.io/e2e-test-images/agnhost:2.33 -- /agnhost serve-hostname -
Next, let’s deploy our job that will exhaust the cluster’s resources and cause it to scale more worker nodes. To do so, run the following command:
cat << EOF | oc create -f - --- apiVersion: batch/v1 kind: Job metadata: generateName: maxscale namespace: autoscale-ex spec: template: spec: containers: - name: work image: busybox command: ["sleep", "300"] resources: requests: memory: 500Mi cpu: 500m restartPolicy: Never backoffLimit: 4 completions: 50 parallelism: 50 EOFSample Outputjob.batch/maxscale7s6c6 created -
After a few seconds, run the following to see what pods have been created.
oc -n autoscale-ex get podsSample OutputNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE maxscale7s6c6-2z67x 1/1 Running 0 31s maxscale7s6c6-45th7 1/1 Running 0 31s maxscale7s6c6-4kd92 0/1 Pending 0 31s maxscale7s6c6-4vcqq 1/1 Running 0 31s maxscale7s6c6-6jhc6 0/1 Pending 0 31s maxscale7s6c6-6zl86 0/1 Pending 0 31s maxscale7s6c6-96vdc 0/1 Pending 0 31s maxscale7s6c6-9k68x 1/1 Running 0 31s maxscale7s6c6-9nkkp 0/1 Pending 0 31s [... Output Omitted ...]Notice that we see a lot of pods in a pending state. This should trigger the cluster autoscaler to create more machines using the MachineAutoscaler we created.
-
Let’s check to see if our MachineSet automatically scaled. To do so, run the following command:
oc -n openshift-machine-api get machinesetsSample OutputNAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AVAILABLE AGE aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1 3 3 1 1 111m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus2 1 1 1 1 111m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus3 1 1 1 1 111mIf you see READY and AVAILABLE at 1 still, don’t panic! It can take a few minutes for the workers to instantiate. Try checking again after 3-5 minutes.
This shows that the cluster autoscaler is working on scaling the MachineSet up to 3.
-
Now let’s watch the cluster autoscaler create and delete machines as necessary. To do so, run the following command:
watch oc -n openshift-machine-api get machines \ -l "machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machine-role=worker"Sample OutputEvery 2.0s: oc -n openshift-machine-api get machines -l machine.openshift... bastion-lwqq8: Tue Dec 19 09:04:00 2023 NAME PHASE TYPE REGION ZONE AGE aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1-6qt5v Provisioned Standard_D4s_v3 eastus 1 53s aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1-8vzrw Provisioned Standard_D4s_v3 eastus 1 3m46s aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus1-vgmng Running Standard_D4s_v3 eastus 1 107m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus2-m4dgh Running Standard_D4s_v3 eastus 2 107m aro-cluster-lwqq8-8mkmr-worker-eastus3-k65k6 Running Standard_D4s_v3 eastus 3 107mWatch will refresh the output of a command every two seconds. Hit CTRL and c on your keyboard to exit the watch command when you’re ready to move on to the next part of the workshop.
-
When all the pods have run to completion the cluster autoscaler will scale the MachineSet back to just one worker node. This will take a while so we are not waiting for that to happen.
You can continue with the next lab while the cluster does its work.
Congratulations!
You’ve successfully demonstrated cluster autoscaling.