Introduction
Red Hat OpenShift GitOps is an operator that provides a workflow that integrates git repositories, continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) tools, and Kubernetes to realize faster, more secure, scalable software development, without compromising quality.
OpenShift GitOps enables customers to build and integrate declarative git driven CD workflows directly into their application development platform.
There’s no single tool that converts a development pipeline to "DevOps". By implementing a GitOps framework, updates and changes are pushed through declarative code, automating infrastructure and deployment requirements, and CI/CD.
OpenShift GitOps takes advantage of Argo CD and integrates it into Red Hat OpenShift to deliver a consistent, fully supported, declarative Kubernetes platform to configure and use with GitOps principles.
OpenShift and OpenShift GitOps:
-
Apply consistency across cluster and deployment lifecycles
-
Consolidate administration and management of applications across on-premises and cloud environments
-
Check the state of clusters making application constraints known early
-
Rollback code changes across clusters
-
Roll out new changes submitted via Git
Deploying your Application with OpenShift GitOps
-
From the OpenShift Console Administrator view click through HOME -> Operators -> Operator Hub, search for "Red Hat OpenShift GitOps" and hit Install. Make sure to select the Channel
gitops-1.15.1. Accept all other defaults and click on Install.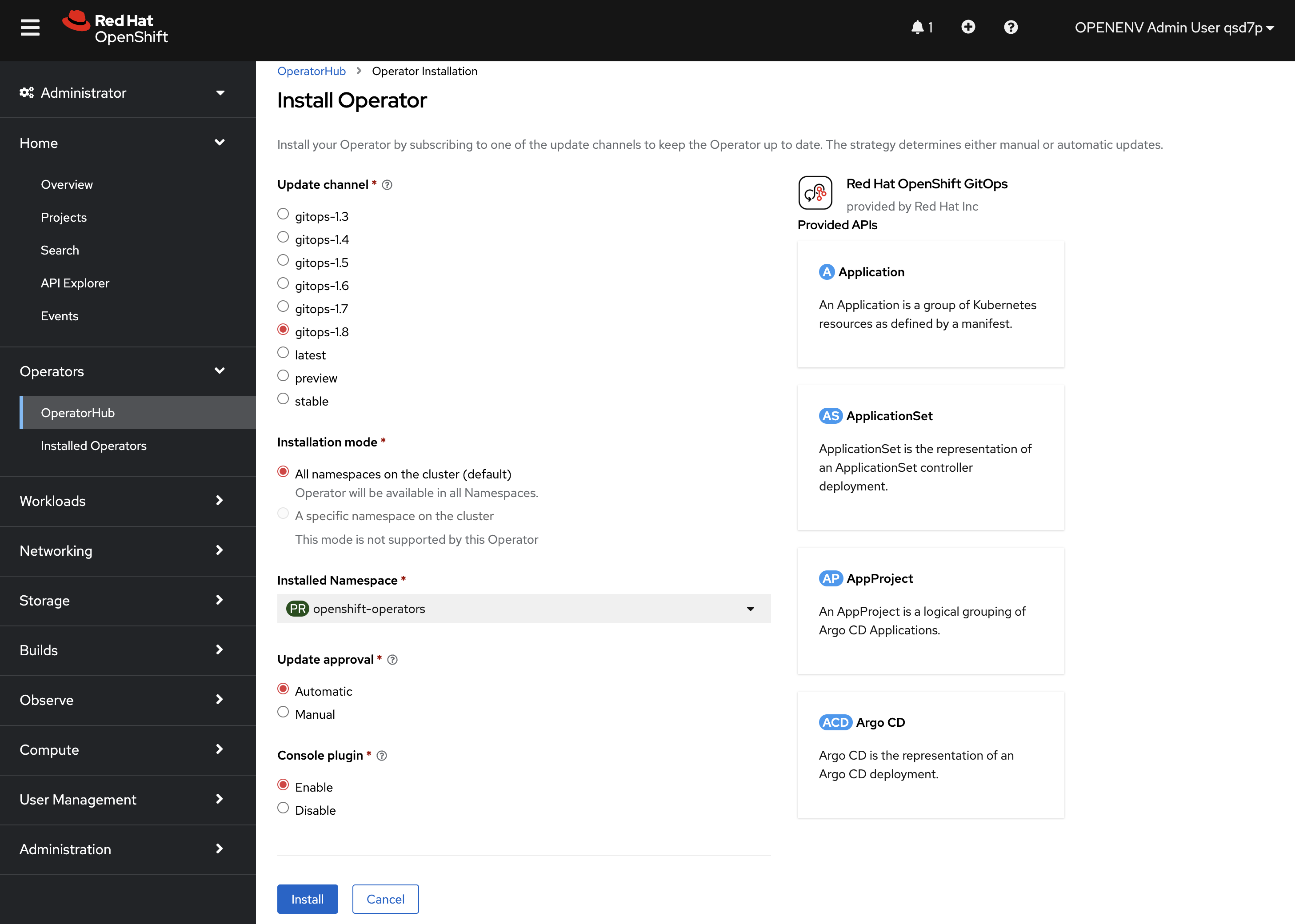
-
Create a new project
oc new-project bgdSample OutputNow using project "bgd" on server "https://api.c90qz1cy.eastus.aroapp.io:6443". You can add applications to this project with the 'new-app' command. For example, try: oc new-app rails-postgresql-example to build a new example application in Ruby. Or use kubectl to deploy a simple Kubernetes application: kubectl create deployment hello-node --image=k8s.gcr.io/e2e-test-images/agnhost:2.33 -- /agnhost serve-hostname -
Deploy ArgoCD into your project
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f - --- apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1beta1 kind: ArgoCD metadata: name: argocd namespace: bgd spec: sso: dex: openShiftOAuth: true resources: limits: cpu: 500m memory: 256Mi requests: cpu: 250m memory: 128Mi provider: dex rbac: defaultPolicy: "role:readonly" policy: "g, system:authenticated, role:admin" scopes: "[groups]" server: route: enabled: true tls: insecureEdgeTerminationPolicy: Redirect termination: reencrypt EOFSample Outputargocd.argoproj.io/argocd createdArgoCD deployment will require additional Worker nodes. The MachineAutoscalers will create the Worker machines and nodes automatically. Watch progress of the MachineAutoscaler as follows: oc get pods -A | grep Pending; oc -n openshift-machine-api get machines; oc get nodesThis process will take about six minutes. -
Wait for ArgoCD to be ready
oc rollout status deploy/argocd-serverSample Outputdeployment "argocd-server" successfully rolled out -
Apply the gitops configuration
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f - --- apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1 kind: Application metadata: name: bgd-app namespace: bgd spec: destination: namespace: bgd server: https://kubernetes.default.svc project: default source: path: apps/bgd/base repoURL: https://github.com/rh-mobb/gitops-bgd-app targetRevision: main syncPolicy: automated: prune: true selfHeal: false syncOptions: - CreateNamespace=false EOFSample Outputapplication.argoproj.io/bgd-app created -
Find the URL for your Argo CD dashboard and log in using your OpenShift credentials
oc get route argocd-server -n bgd -o jsonpath='{"https://"}{.spec.host}{"\n"}'Sample Outputhttps://argocd-server-bgd.apps.c90qz1cy.eastus.aroapp.io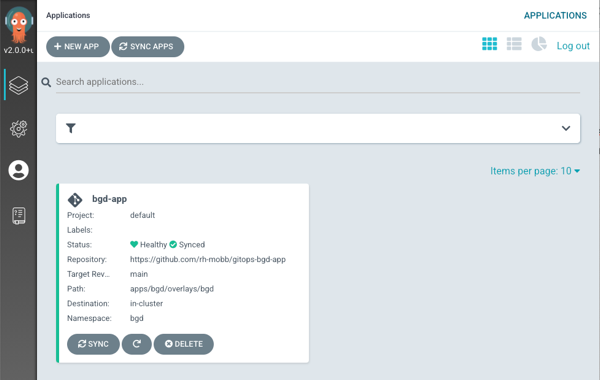
-
Click on the Application bgd-app to show its topology
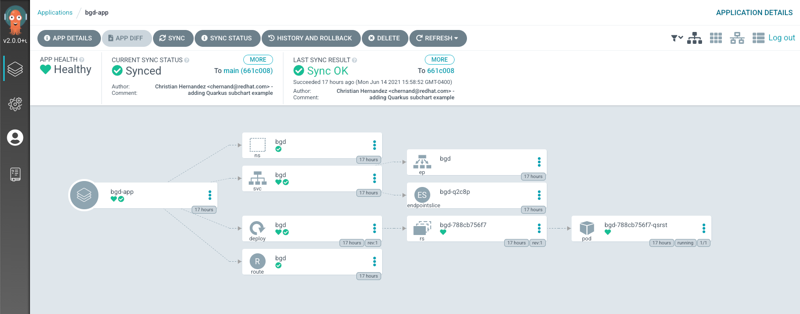
-
Verify that OpenShift sees the Deployment as rolled out
oc rollout status deploy/bgd -n bgdSample Outputdeployment "bgd" successfully rolled out -
Get the route and browse to it in your browser
oc get route bgd -n bgd -o jsonpath='{"https://"}{.spec.host}{"\n"}'Sample Outputhttps://bgd-bgd.apps.c90qz1cy.eastus.aroapp.io -
You should see a green box in the website like so
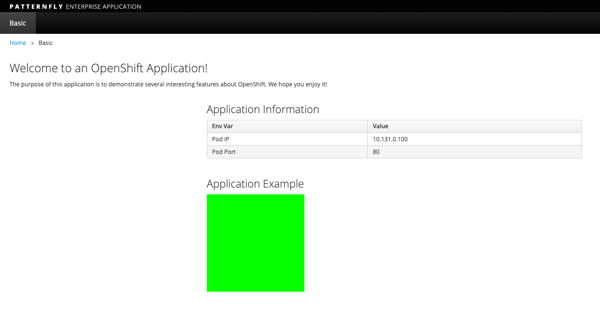
-
Patch the OpenShift resource to force it to be out of sync with git
oc patch deploy/bgd --type='json' \ -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/template/spec/containers/0/env/0/value", "value":"blue"}]'Sample Outputdeployment.apps/bgd patched -
Refresh your browser and you should see a blue box in the website like so
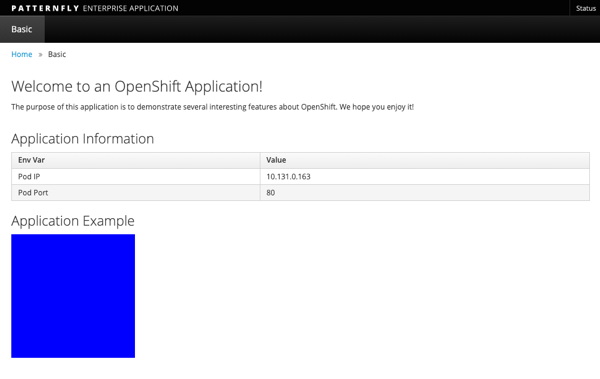
-
Meanwhile check ArgoCD it should show the application as out of sync. Click the Sync button and then click on Synchronize to have it revert the change you made in OpenShift

-
Check again, you should see a green box in the website like so

-
Patch the ArgoCD application to automatically self heal
oc patch application bgd-app --type merge \ -p='{"spec":{"syncPolicy":{"automated":{"selfHeal": true}}}}'Sample Outputapplication.argoproj.io/bgd-app patched -
Change the Application again and watch the ArgoCD web gui, you should see the change made in the cluster get quickly reverted back to match what is in github.
oc patch deploy/bgd --type='json' \ -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/template/spec/containers/0/env/0/value", "value":"blue"}]'Sample Outputdeployment.apps/bgd patchedThe self healing may happen so fast you don’t even see it happen. If you missed just run the command again and be sure to have the Argo CD view up and ready!