🛠️ Creating a Workbench
🚀 Launch a Workbench
-
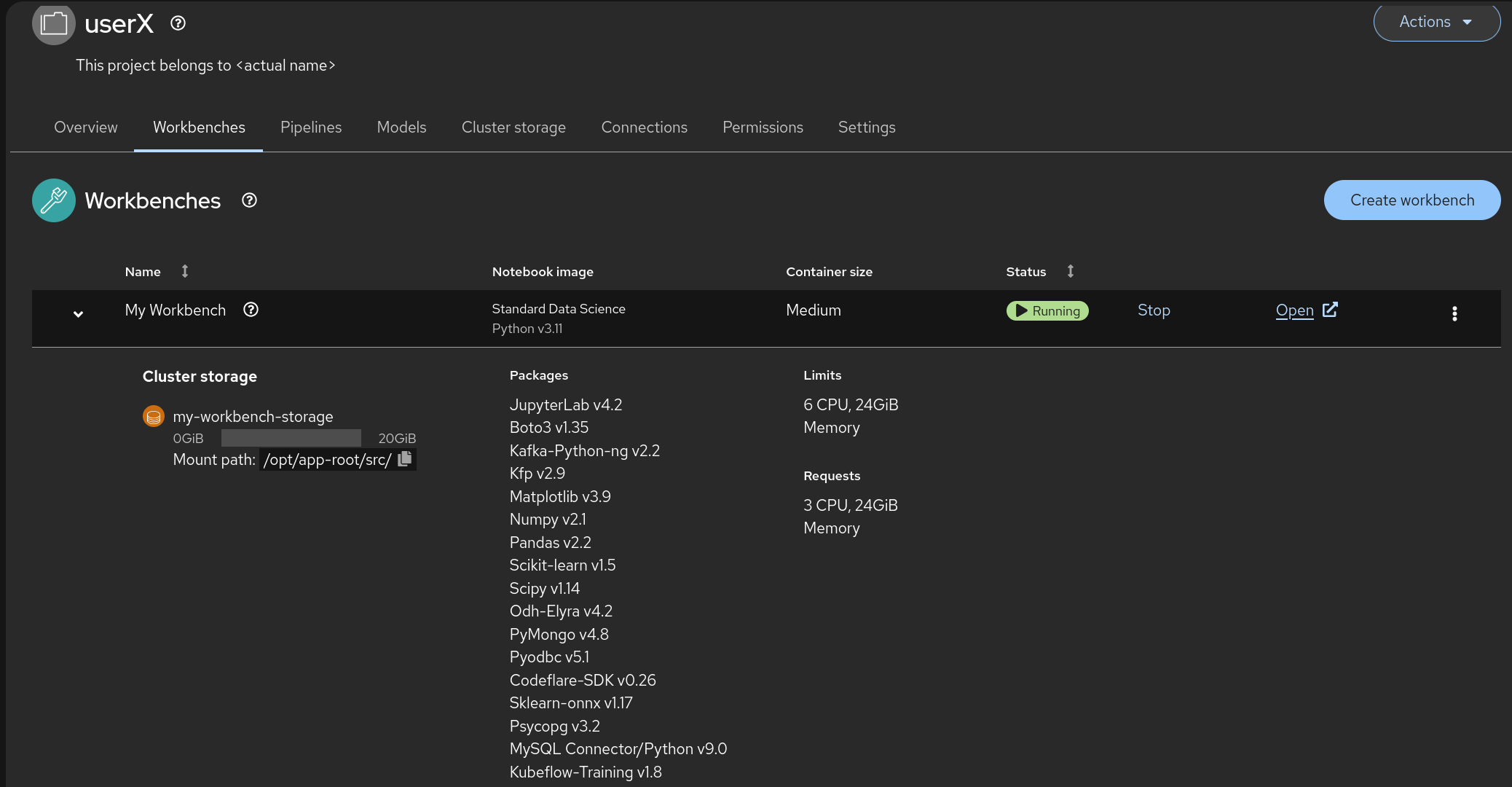
Once the Data Connection and Pipeline Server are fully created, it’s time to create your workbench! 🎉
-
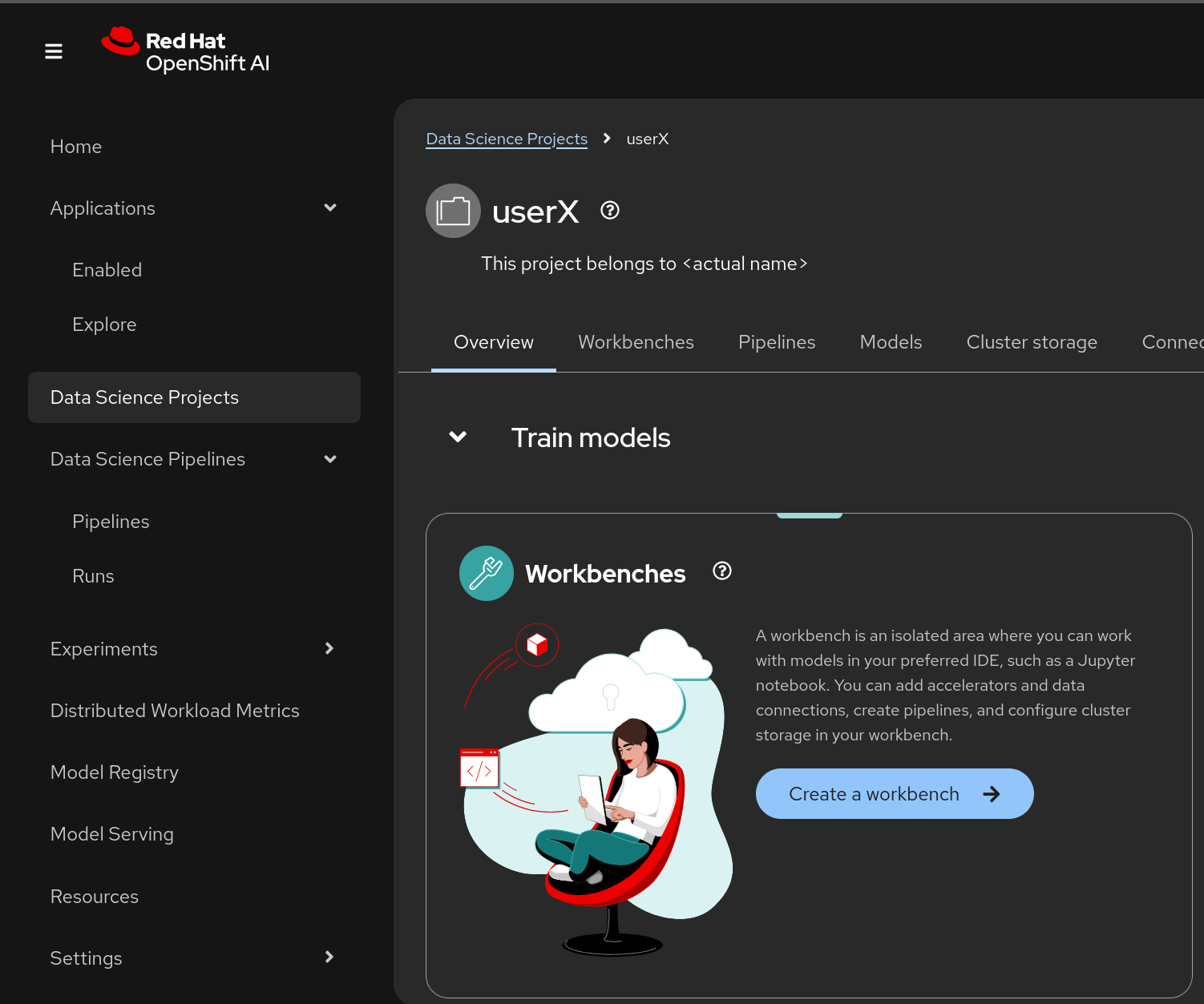
Go to Data Science Projects, select your previously created project (
userX), and click on Create a workbench -
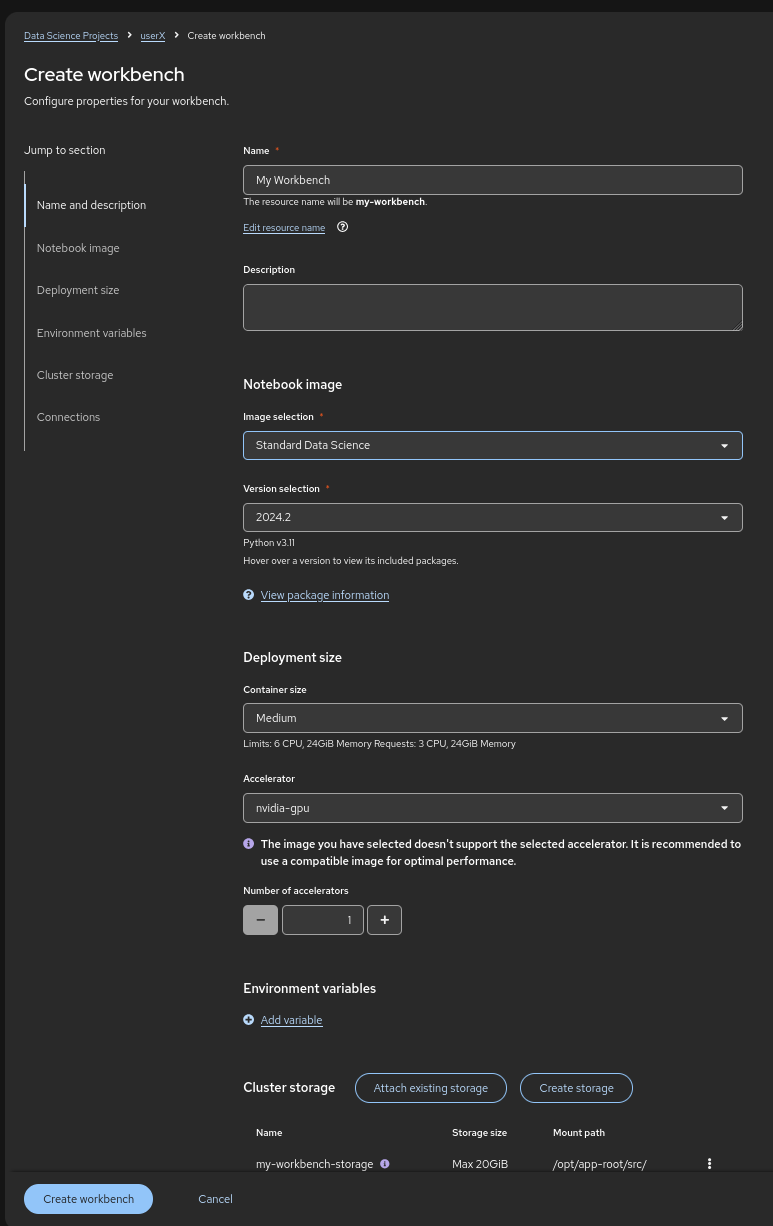
Make sure it has the following characteristics:
-
Choose a name for it, like:
My Workbench🌟 -
Image Selection:
Minimal PythonorStandard Data Science🐍 -
Container Size:
Medium📦 -
Accelerator:
NVIDIA-GPU💻
-
-
That should look like:
-
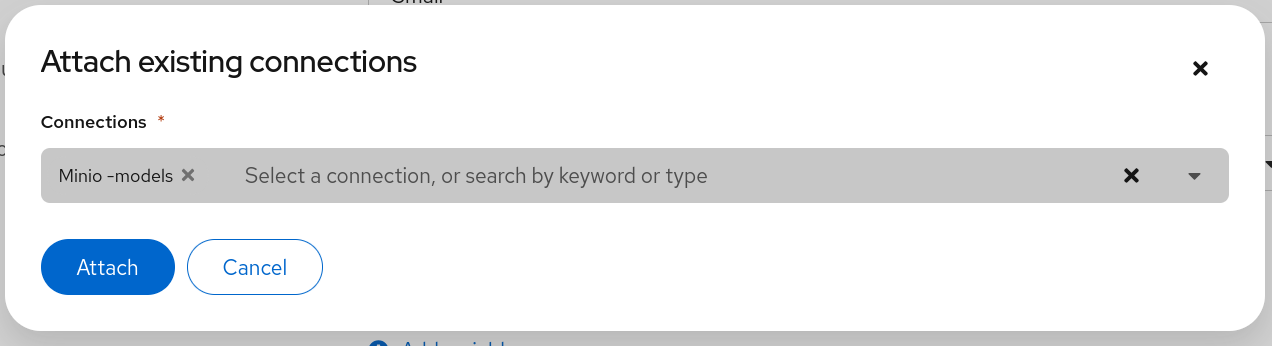
Add the created Data Connection by clicking on the Connections section and selecting Attach existing connections. Then, click Attach for the created Minio - models connection. 🔗
-
You should not need to modify any other Workbench settings (such as Storage).
-
Then, click on Create Workbench and wait for your workbench to be fully started. ⏳
-
Once it is, click the Open link to connect to it! 🔗
-
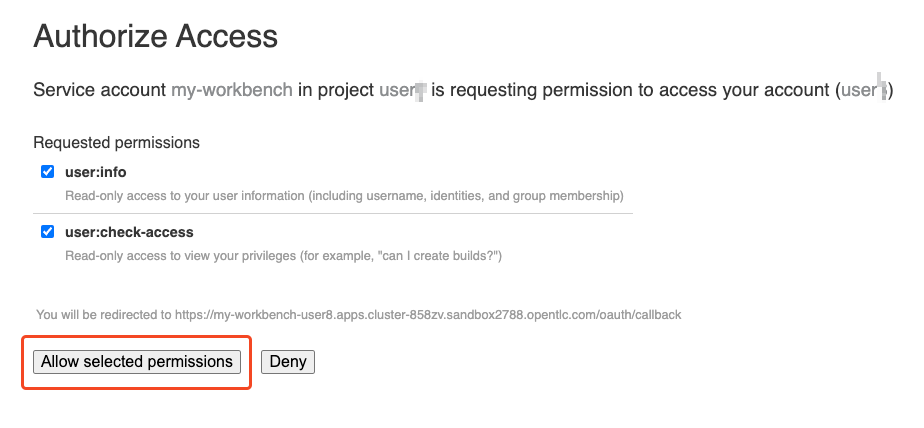
Authenticate with the same credentials as earlier. 🔑
-
You will be asked to accept the following settings:
-
Go ahead and do so! 👍
-
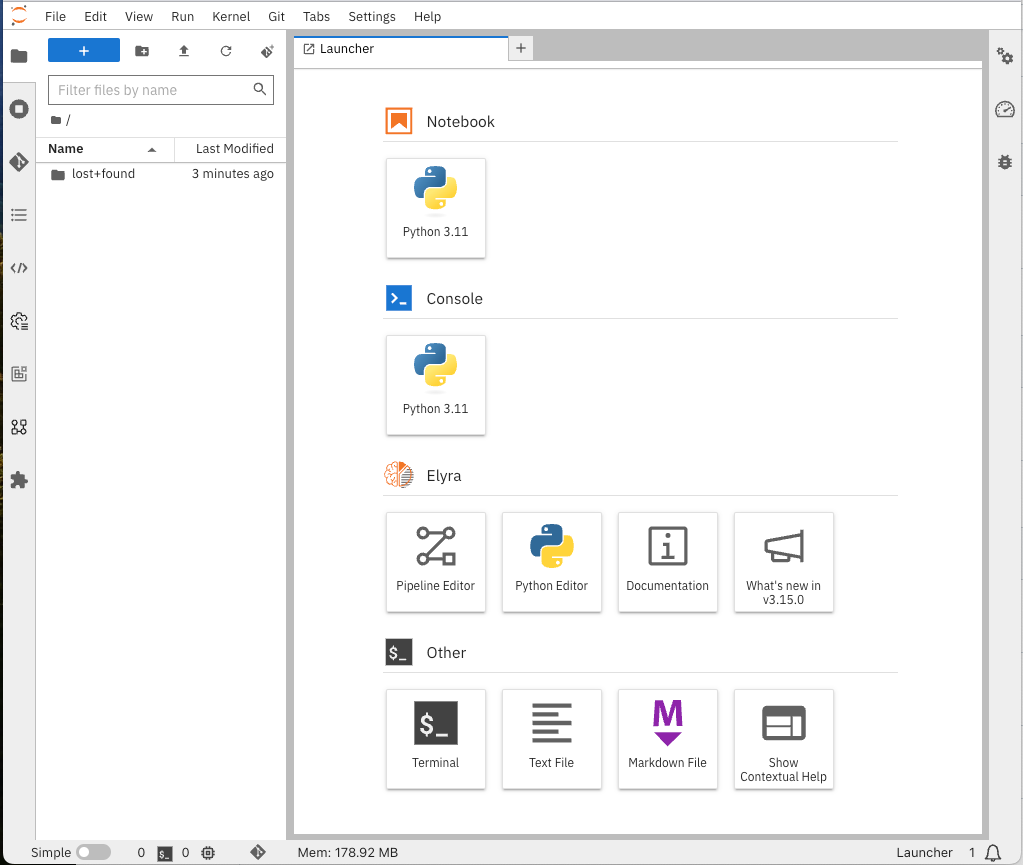
You should now see this:
JupyterLab and Jupyter Notebooks
|
Workbenches utilize JupyterLab, an interactive development environment you’ll access directly through your web browser. Think of JupyterLab as a workbench that’s excellent for hands-on experimentation, which is especially useful in AI development. Within JupyterLab, we’ll be using Jupyter Notebooks. A Notebook is like an interactive document where you can:
Quick interactive introduction to using and customizing your Workbench (recommended)
(This Interactive demo was recorded using a Virtual Machine Based Jupyter Lab but behaves in exactly the same way.) |